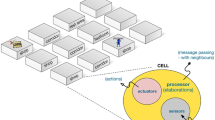
Abstract
Nowadays, large shopping malls provide tools to help and boost customers to buy products. Some of these tools melt down digital operations with physical ones executed by customers into blended commerce experiences. On the other hand, Ambient Intelligence (AmI) represents a paradigm focused on equipping physical environments to define ergonomic spaces for people interacting with computer-based localized services which are ubiquitously accessible. In this context, we propose a Context-Aware Recommender System to assist indoor shopping by localizing shoppers and provide them with suggestions on where to find suitable offerings related to products that meet their wishlists. Recommendations are generated by means of an Indoor Navigation System. The system lies on two well-known formal models: the Computational Ontologies and the Cellular Automata. Ontologies are based on Description Logic and defined by means of languages, methodologies and tools of the Semantic Web Stack provided by W3C. Cellular Automata is a very well known formal computational model, suitable to abstract services deployed into an AmI-based environment along with the paradigm of Pervasive Computing. The integration of the capabilities provided by such two models offers a set of desirable features like adaptivity, scalability, low-costs, and robustness.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Adomavicius G, Tuzhilin A (2011) Context-aware recommender systems. In: Recommender systems handbook, Springer, pp 217–253
Atzori L, Iera A, Morabito G (2010) The internet of things: a survey. Comput Netw 54(15):2787–2805
Bandini S (2002) Cellular automata. Future Gener Comp Syst. doi:10.1016/S0167-739X(02)00067-5
Bellavista P, Kupper A, Helal S (2008) Location-based services: back to the future. Pervasive Comput IEEE 7(2):85–89
Bellavista P, Corradi A, Fanelli M, Foschini L (2012) A survey of context data distribution for mobile ubiquitous systems. ACM Comput Surv CSUR 44(4):24
Colombo-Mendoza LO, Alor-Hernández G, Rodríguez-González A, Valencia-García R (2014) Mobicloup!: a paas for cloud services-based mobile applications. Autom Softw Eng 21(3):391–437
Compton M, Barnaghi P, Bermudez L, GarcíA-Castro R, Corcho O, Cox S, Graybeal J, Hauswirth M, Henson C, Herzog A et al (2012) The SSN ontology of the w3c semantic sensor network incubator group. Web Semant Sci Serv Agents World Wide Web 17:25–32
Conti M, Das SK, Bisdikian C, Kumar M, Ni LM, Passarella A, Roussos G, Tröster G, Tsudik G, Zambonelli F (2012) Looking ahead in pervasive computing: challenges and opportunities in the era of cyber-physical convergence. Pervasive Mob Comput 8(1):2–21
Cui B, Jin H, Liu Z, Deng J (2015) Improved collaborative filtering with intensity-based contraction. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 6(5):661–674. doi:10.1007/s12652-015-0284-9
D’Aniello G, Gaeta M, Loia V, Orciuoli F (2015) An ami-based software architecture enabling evolutionary computation in blended commerce: the shopping plan application. Mob Inf Syst 2015:1–19, Article ID 936125. doi:10.1155/2015/936125
D’Aniello G, Gaeta A, Gaeta M, Lepore M, Orciuoli F, Troisi O (2016) A new DSS based on situation awareness for smart commerce environments. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 7(1):47–61. doi:10.1007/s12652-015-0300-0
De Maio C, Fenza G, Furno D, Loia V (2012a) Swarm-based semantic fuzzy reasoning for situation awareness computing. In: Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), 2012 IEEE International Conference IEEE, pp 1–7
De Maio C, Fenza G, Furno D, Loia V, Senatore S (2012b) OWL-FC: an upper ontology for semantic modeling of fuzzy control. Soft Comput 16(7):1153–1164
Decuir J (2014) Introducing bluetooth smart: Part ii: applications and updates. Consum Electron Mag IEEE 3(2):25–29. doi:10.1109/MCE.2013.2297617
Endsley MR (1995) Toward a theory of situation awareness in dynamic systems. Human Factors J Human Factors Ergon Soc 37(1):32–64
Fallah N, Apostolopoulos I, Bekris K, Folmer E (2013) Indoor human navigation systems: a survey. Interact Comput 25(1):21–33
Fenza G, Furno D, Loia V, Veniero M (2010) Agent-based cognitive approach to airport security situation awareness. In: Complex, Intelligent and Software Intensive Systems (CISIS), 2010 International Conference IEEE, pp 1057–1062
Fenza G, Fischetti E, Fumo D, Loia V (2011) A hybrid context aware system for tourist guidance based on collaborative filtering. In: Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ), 2011 IEEE International Conference IEEE, pp 131–138
Fenza G, Furno D, Loia V (2012) Hybrid approach for context-aware service discovery in healthcare domain. J Comput Syst Sci 78(4):1232–1247
Fuchs B, Ritz T, Halbach B, Hartl F (2011) Blended shopping: Interactivity and individualization. In: e-Business (ICE-B), 2011 Proceedings of the International Conference, pp 1–6
Furey E, Curran K, Kevitt PM (2013) Probabilistic indoor human movement modeling to aid first responders. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 4(5):559–569. doi:10.1007/s12652-012-0112-4
Gangemi A (2009) DOLCE+ DnS ultralite. RDF + OWL ontology. http://www.ontologydesignpatterns.org/ont/dul/DUL.owl
Gruber TR (1995) Toward principles for the design of ontologies used for knowledge sharing? Int J Human Comput Stud 43(5):907–928
Gruska J, La Torre S, Parente M (2004) Optimal time and communication solutions of firing squad synchronization problems on square arrays, toruses and rings. In: Developments in language theory, (DLT), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3340, Springer, pp 200–211
Gruska J, La Torre S, Parente M (2007) The firing squad synchronization problem on squares, toruses and rings. Int J Found Comput Sci 18(3):637–654
Gu Y, Lo A, Niemegeers I (2009) A survey of indoor positioning systems for wireless personal networks. Commun Surv Tutor IEEE 11(1):13–32
Henricksen K, Indulska J (2006) Developing context-aware pervasive computing applications: models and approach. Pervasive Mob Comput 2(1):37–64
Hepp M (2008) Goodrelations: an ontology for describing products and services offers on the web. In: Knowledge engineering: practice and patterns, Springer, pp 329–346
Horridge M, Drummond N, Goodwin J, Rector AL, Stevens R, Wang H (2006) The manchester owl syntax. In: OWL ed, vol 216
Krötzsch M, Simancik F, Horrocks I (2014) Description logics. IEEE Intell Syst 29(1):12–19
La Torre S, Napoli M, Parente D (1998) Synchronization of a line of identical processors at a given time. Fundam Inf 34(1–2):103–128. doi:10.3233/FI-1998-341204
La Torre S, Napoli M, Parente M (2000) A compositional approach to synchronize two dimensional networks of processors. ITA 34(6):549–564. doi:10.1051/ita:2000130
Lin Z (2013) Indoor location-based recommender system. PhD thesis, University of Toronto
Moore EF (1962) The firing squad synchronization problem. Sequ Mach, pp 213–214
Olugbara OO, Ojo SO, Mphahlele M (2010) Exploiting image content in location-based shopping recommender systems for mobile users. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 9(05):759–778
Orciuoli F, Parente M, Vitiello A (2015) Solving the shopping plan problem through bio-inspired approaches. Soft Comput, pp 1–13
Purohit A, Sun Z, Pan S, Zhang P (2013) Sugartrail: indoor navigation in retail environments without surveys and maps. In: Sensor, mesh and ad hoc communications and networks (SECON), 2013 10th Annual IEEE Communications Society Conference IEEE, pp 300–308
Resnick P, Varian HR (1997) Recommender systems. Commun ACM 40(3):56–58
Rosenberg AL (2008) Cellular antomata: food-finding and maze-threading. In: Parallel Process. ICPP’08. 37th International Conference IEEE, pp 528–535
Rosenberg AL (2012) Cellular antomata. Adv Complex Syst 15(06):28
Sadri F (2011) Ambient intelligence: a survey. ACM Comput Surv CSUR 43(4):36
Schafer JB, Konstan J, Riedl J (1999) Recommender systems in e-commerce. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM conference on electronic commerce, ACM, pp 158–166
Shearer R, Motik B, Horrocks I (2008) Hermit: a highly-efficient owl reasoner. In: OWLED, vol 432, p 91
TalebiFard P, Leung VCM (2014) Context-aware dissemination of information and services in heterogeneous network environments. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 5(6):775–787. doi:10.1007/s12652-013-0210-y
Tapia DI, Abraham A, Corchado JM, Alonso RS (2010) Agents and ambient intelligence: case studies. Journal of Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 1(2):85–93. doi:10.1007/s12652-009-0006-2
Umeo H, Kubo K (2010) A seven-state time-optimum square synchronizer. In: Bandini S, Manzoni S, Umeo H, Vizzari G (eds) Cellular automata. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 6350. Springer, Berlin, pp 219–230
Winkler C, Broscheit M, Rukzio E (2011) Navibeam: indoor assistance and navigation for shop-ping malls through projector phones. In: CHI 2011 Workshop on Mobile and Personal Projection
Yang WS, Cheng HC, Dia JB (2008) A location-aware recommender system for mobile shopping environments. Expert Syst Appl 34(1):437–445
Acknowledgments
The authors thanks students and research assistants of GandALF Lab (Università di Salerno) for supporting early experimentation activities of the system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orciuoli, F., Parente, M. An ontology-driven context-aware recommender system for indoor shopping based on cellular automata. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 8, 937–955 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-016-0411-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-016-0411-2