Abstract
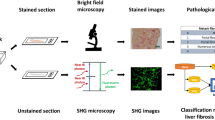
Liver cirrhosis is an advanced, diffuse stage of liver injury which usually entails pathologists to check a large number of microscopic images. Obvious differences between liver cirrhosis microscopic images and normal microscopic images, such as the arrangement of hepatocytes, the degree of hepatic fibrosis and the appearance of pseudo lobule, can be efficiently used in medical images classification systems. In this paper, deep learning and standard machine learning methods were applied for helping pathologists making disease diagnosis easier. Firstly, convolutional neural networks and support vector machine were employed to complete the pre-classification of mice liver cirrhosis microscopic images and normal images. We trained the existed convolutional neural networks by our microscopic image datasets after image preprocessing, and we extracted some texture features from all the microscopic images to train the support vector machines; secondly, convolutional neural networks deployed the 98% optimal accuracy that is obviously outperforms support vector machine of 86% final performance. Data augmentation is an efficient approach for solving the problem of insufficient image number. Finally, in experiments, the classification results after data augmentation are more accurate and the trained models are more stable. Moreover, more samples need to be obtained to train the used convolutional neural networks and more features also need to be extracted that are critical to diagnose for pathologists in future works.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Al-Tubaikh JA (2010) Liver cirrhosis. In: Okita K (ed) Internal medicine. Springer, Berlin
Chatfield K, Simonyan K, Vedaldi A, Zisserman A (2014) Return of the devil in the details: delving deep into convolutional nets. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. BMVA Press, Nottingham
Chen YW, Kaibori M, Shindo T, Miyawaki K, Foruzan AH, Tateyama T (2013) Computer-aided liver surgical planning system using CT volumes. In: 35th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE Press, Osaka, pp 2360–2363
Chen Q, Zhang G, Yang X, Li S, Li Y, Wang HH (2017) Single image shadow detection and removal based on feature fusion and multiple dictionary learning. Multimed Tools Appl 6:1–24
Christiyana CC, Rajamani VP (2013) Second order statistical texture features from a new CSLBPGLCM for ultrasound kidney images retrieval. Appl Med Inform 33(4):32–39
Cour T, Huang T (2011) Large-scale image classification: fast feature extraction and SVM training. In: Proceedings of 2011 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, IEEE computer society, pp 1689–1696
Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J, Swetter SM, Blau HM (2017) Corrigendum: dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542(7639):115–118
Fan RE, Chen PH, Lin CJ (2015) Working set selection using second order information for training support vector machines. J Mach Learn Res 6(4):1889–1918
Fawcett T (2016) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit Lett 27(8):861–874
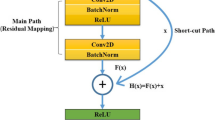
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), IEEE Press, USA, pp 770–778
He J, Shang L, Ji H, Zhang XL (2017) Deep learning features for lung adenocarcinoma classification with tissue pathology images. In: International conference on neural information processing, Springer, Cham, pp 742–751
Kawahara J, Hamarneh G (2016) Multi-resolution-tract CNN with hybrid pretrained and skin-lesion trained layers, vol 10019. Springer, Berlin, pp 164–171
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of NIPS, advances in neural information processing systems 25 (NIPS 2012), pp 1097–1105
Li Z, Dey N, Ashour AS, Cao L, Wang Y, Wang D (2017) Convolutional neural network based clustering and manifold learning method for diabetic plantar pressure imaging dataset. J Med Imaging Health Inform 7(3):639–652
Liang RZ, Shi L, Wang H, Meng J, Wang JY, Sun Q (2017) Optimizing top precision performance measure of content-based image retrieval by learning similarity function. In: International conference on pattern recognition, IEEE, pp 2954–2958
Minarno AE, Munarko Y, Kurniawardhani A, Bimantoro F, Suciati N (2014) Texture feature extraction using co-occurrence matrices of sub-band image for batik image classification. In: International conference on information and communication technology, IEEE, pp 249–254
Pirbhulal S, Zhang HY, Mukhopadhyay SC, Li CY, Wang YM, Li GL, Wu WQ (2015) An efficient biometric-based algorithm using heart rate variability for securing body sensor networks. Sensors 15(7):15067–15089
Pirbhulal S, Zhang HY, Alahi MEE, Ghayvat H, Mukhopadhyay SC, Zhang YT, Wu WQ (2016) A novel secure IoT-based smart home automation system using a wireless sensor network. Sensors 17(1):69–88
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, Springer, Cham, pp 234–241
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, Berg AC, Li FF (2015) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. IJCV 11:211–252
Suzuki K (2017) Overview of deep learning in medical imaging. Radiol Phys Technol 10:257–273
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D (2014) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). IEEE Press, Boston, MA, pp 1–9
Vos BDD, Wolterink JM, Jong PAD, Viergever MA, Isgum I (2016) 2D image classification for 3D anatomy localization: employing deep convolutional neural networks. In: Medical imaging 2016: image processing, international society for optics and photonics, pp 97841Y
Wang Y, Cao L, Dey N, Ashour AS, Shi F (2017) Mice liver cirrhosis microscopic image analysis using gray level co-occurrence matrix and support vector machines. Frontiers in artificial intelligence and applications, vol 296. In: Proceedings of ITITS 2017, Xian, China, pp 509–515
Wang D, He T, Li Z, Cao L, Dey N, Ashour AS, Balas EV, Pamela M, Lin Y, Xu J, Shi F (2018) Image feature-based affective retrieval employing improved parameter and structure identification of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Neural Comput Appl 29(4):1087–1102
Wu WQ, Zhang HY, Pirbhulal S, Mukhopadhyay SC, Zhang YT (2015) Assessment of biofeedback training for emotion management through wearable textile physiological monitoring system. IEEE Sens J 15(12):7087–7095
Xiao X, Pirbhulal S, Dong K, Wu WQ, Xi M (2017) Performance evaluation of plain weave and honeycomb weave electrodes for human ECG monitoring. J Sens 7(5):1–13
Xu J, Luo XF, Wang GH, Glimore H, Madabhushi A (2015) A deeping convolutional neural network for segmenting and classifying epithelial and stromal regions in histopathological images. Neurocomputing 191:214–223
Zhang S, Wang H, Huang W, Huang W, You Z (2017) Plant diseased leaf segmentation and recognition by fusion of superpixel, K-means and PHOG. Optik Int J Light Electron Opt 157:866–872
Zulpe NS, Pawar VP (2012) GLCM textural features for brain tumor classification. Int J Comput Sci Issues 9(3):354–359
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant no. LY17F030014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Wang, Y., Hemanth, D.J. et al. Data augmentation on mice liver cirrhosis microscopic images employing convolutional neural networks and support vector machine. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 10, 4023–4032 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0951-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0951-8