Abstract
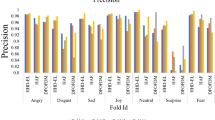
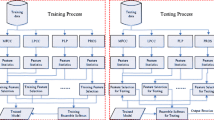
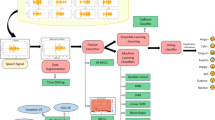
To make the best use of speech recognition, it is imperative that it can recognize not just speech or speaker, but also the domain of communication. This paper proposes an approach for recognition of the acoustic domain using ensemble-based 3-level architecture instead of a single classifier for training and testing. It is estimated the predictions of various classifiers and then selects a set of three classifiers such that, any of the three classifiers must contain the target predictions and finally, these predictions are used to train another random forest classifier. It yields the final classification results of test data set. Experimental results indicate that the proposed method has consistent performance even if data size is increased with acceptable accuracy i.e. 76.36%.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Casale S, Russo a, Scebba G, Serrano S (2008) Speech emotion classification using machine learning algorithms. 2008 IEEE Int Conf Semantic Comput 118(13):167–174
Chuang Z, Wu C-h (2004) Multi-modal emotion recognition from speech and text. J Comput Linguist Chin 9(2):45–62
Dahl G, Yu D, Deng L, Acero A (2012) Context-dependent pre-trained deep neural networks for large-vocabulary speech recognition. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 20(1):30–42
Davletcharova A, Sugathan S, Abraham B, James A (2015) Detection and analysis of emotion from speech signals. Proc Comput Sci 58:91–96
Deng L, Li X (2013) Machine learning paradigms for speech recognition: an overview. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 21(5):1060–1089
Garofolo JS (1993) TIMIT acoustic phonetic continuous speech corpus. Linguistic Data Consortium 1993
Giannoulis D, Benetos E, Stowell D, Rossignol M, Lagrange M, Plumbley MD (2015) Detection and classification of acoustic scenes and events. An IEEE AASP challenge. In: 2013 IEEE workshop on applications of signal processing to audio and acoustics (WASPAA). IEEE, pp 1–4
Huang CW, Narayanan S (2017) Characterizing types of convolution in deep convolutional recurrent neural networks for robust speech emotion recognition 1–19. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.02901
Imoto K, Ono N (2017) Spatial cepstrum as a spatial feature using a distributed microphone array for acoustic scene analysis. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 25(6):1335–1343
Ming J, Crookes D (2017) Speech enhancement based on full-sentence correlation and clean speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 25(3):531–543
Ming J, Srinivasan R, Crookes D (2011) A corpus-based approach to speech enhancement from nonstationary noise. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 19(4):822–836
Mun S, Park S, Han DK, Ko H (2017) Generative adversarial network based acoustic scene training set augmentation and selection using SVM hyper-plane. Proc. DCASE, pp 93–97
Panayotov V, Chen G, Povey D, Khudanpur S (2015) Librispeech: an ASR corpus based on public domain audio books. In: Acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), 2015 IEEE international conference on, pp 5206–5210)
Sarikaya R, Hinton G, Deoras A (2014) Application of deep belief networks for natural language understanding. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 22(4):778–784
Valenti M, Diment A, Parascandolo G, Squartini S, Virtanen T (2016) Acoustic scene classification using convolutional neural networks. Proceedings of the detection and classification of acoustic scenes and events 2016 workshop (DCASE2016) (September), pp 95–99
Wu C-H, Chuang Z-J, Lin Y-C (2006) Emotion recognition from text using semantic labels and separable mixture models. ACM Trans Asian Lang Inf Process 5(2):165–183
Yadollahi A, Shahraki A, Zaiane O (2017) Current state of text sentiment analysis from opinion to emotion mining. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 50(2):25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rathor, S., Jadon, R.S. Acoustic domain classification and recognition through ensemble based multilevel classification. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 10, 3617–3627 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1087-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1087-6