Abstract
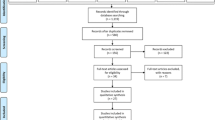
In a world with an increasing population, an alternative for aiding healthcare systems is the use of sensors and wearable devices for monitoring patient physiological data. The analysis of collected data can help guide health services or the self-care of patients. This paper explores literature related to the collection and analysis of physiological data in smart environments by means of a systematic mapping study, organized in three steps: (1) identification of research questions; (2) elaboration of the search process; (3) definition of the criteria for filtering results. Papers were added using the snowball sampling method. This work encompassed 5870 papers published in the past 11 years, up to April 2019. The final selection resulted in 32 papers. Among these, 25 works collected cardiac data, 23 used Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GSM, or ZigBee technologies, and 14 used techniques for the analysis of physiological data. Mapping verified the more prevalent trends and technologies in the collected and analyzed physiological data from smart environments. The filtering process allowed for a focus on communication technologies and vital sign data types. Three general questions (GQ), two specific questions (SQ), and two statistical questions (STQ) were answered. Similar reviews have already been conducted focusing on sensors, rather than collecting techniques and physiological data analysis. This denotes an opportunity for further studies in the vital sign analysis area.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Achouri M, Alti A, Roose P (2017) A new two-Layered architecture for efficient situations management in smart environments. In: Proceedings of the 9th international conference on management of digital EcoSystems, pp 6–13
Adib F, Mao H, Kabelac Z, Katabi D, Miller RC (2015) Smart homes that monitor breathing and heart rate. In: Proceedings of the 33rd annual ACM conference on human factors in computing systems—CHI ’15, pp 837–846. https://doi.org/10.1145/2702123.2702200. URL http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=2702123.2702200
Apiletti D, Baralis E, Bruno G, Cerquitelli T (2009) Real-time analysis of physiological data to support medical applications. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 13(3):313–321. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2008.2010702 ISSN 10897771
Barreto C, da Silva A, Xavier-Júnior J, Soares de Aquino G (2018) A cardiac arrhythmia monitoring platform based on feature selection and classification methods. \(10^{\circ }\) Simpósio Brasileiro de Computação Ubíqua e Pervasiva (SBCUP 2018) 08
Budgen D, Turner M, Brereton P, Kitchenham B (2008) Using mapping studies in software engineering. Proc PPIG 2(01):2008
Chen M, Gonzalez S, Vasilakos A, Cao H, Leung VC (2010) Body area networks: a survey. Mobile Netw Appl 16(2):171–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-010-0260-8 ISSN 1383469X
Chen M-F (2012) Integrated circuits and systems toward smart ubiquitous patient-centered medical environment. In: Solid state circuits conference (A-SSCC), 2012 IEEE Asian, pp 121–124. https://doi.org/10.1109/IPEC.2012.6522620. URL http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?tp=&arnumber=6522620
Chen YL, Chiang HH, Lee, TT (2013) Design and realization of a knowledge-based framework for personalized home healthcare systems. In: 2013 CACS international automatic control conference, CACS 2013—conference digest, pp 180–185. https://doi.org/10.1109/CACS.2013.6734129
Choi A, Shin H (2018) Longitudinal healthcare data management platform of healthcare iot devices for personalized services. J Univers Comput Sci 24:1153–1169 01
Cook D, Das S (2007) How smart are our environments? an updated look at the state of the art. Pervasive Mobile Comput 3:53–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmcj.2006.12.001 03
Cooper ID (2016) What is a mapping study ? J Med Library Assoc 104(January):76–78. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.104.1.013
Copetti A, Loques O, Leite JCB, Barbosa TPC, da Nobrega ACL (2009) Intelligent context-aware monitoring of hypertensive patients. In: Proceedings of the 3d international ICST conference on pervasive computing technologies for healthcare. https://doi.org/10.4108/ICST.PERVASIVEHEALTH2009.6058. URL http://eudl.eu/doi/10.4108/ICST.PERVASIVEHEALTH2009.6058
Curmi F, Ferrario MA, Whittle J (2017) Biometric data sharing in the wild: Investigating the effects on online sports spectators. Int J Hum-Comput Stud 105:56 – 67. ISSN 1071-5819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2017.03.008. URL http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1071581917300484
Dalmina L, Barbosa JLV, Vianna HD (2019) A systematic mapping study of gamification models oriented to motivational characteristics. Behav Inf Technol 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2019.1576768
Dey AK, Abowd GD (2001) A conceptual framework and a toolkit for supporting the rapid prototyping of context-aware applications. J Hum-Comput Interact 16:97–166
Dias LPS, Barbosa JLV, Vianna HD (2018) Gamification and serious games in depression care: a systematic mapping study. Telemat Inform 35(November 2017):213–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2017.11.002
Fernandes CO, Lucena CJPD (2017) A software framework for remote patient monitoring by using multi-agent systems support. JMIR Med Inform 5(1):e9. ISSN 2291-9694. https://doi.org/10.2196/medinform.6693. URL http://medinform.jmir.org/2017/1/e9/
Furberg RD, Taniguchi T, Aagaard B, Ortiz AM, Hegarty-Craver M, Gilchrist KH, Ridenour TA (2017) Biometrics and policing: a protocol for multichannel sensor data collection and exploratory analysis of contextualized psychophysiological response during law enforcement operations. JMIR Res Protoc 6(3):e44. ISSN 1929-0748. https://doi.org/10.2196/resprot.7499. URL http://www.researchprotocols.org/2017/3/e44/
Goncales L, Farias K, Scholl M, Veronez M, Oliveira T (2014) Model comparison: a systematic mapping study. PIPCA, University of Vale do Rio dos Sinos, p 6. https://doi.org/10.18293/seke2015-116
Hassan MK, Desouky AIE, Elghamrawy SM, Sarhan AM (2019) A hybrid real-time remote monitoring framework with nb-woa algorithm for patients with chronic diseases. Future Gener Comput Syst 93:77 – 95. ISSN 0167-739X. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.10.021. URL http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167739X17326596
Hossain MS, Muhammad G (2016) Cloud-assisted industrial internet of things (iiot) - enabled framework for health monitoring. Comput Netw 101:192 – 202. ISSN 1389-1286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2016.01.009. URL http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1389128616300019. Industrial Technologies and Applications for the Internet of Things
Hu F, Celentano L, Xiao Y (2009) Error-resistant rfid-assisted wireless sensor networks for cardiac telehealthcare. Wirel Commun Mobile Comput 9:85–101. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcm.607 01
Hu S, Wei H, Chen Y, Tan J (2012) A real-time cardiac arrhythmia classification system with wearable sensor networks. Sensors (Switzerland) 12(9):12844–12869. https://doi.org/10.3390/s120912844 ISSN 14248220
Hung K, Lee CC, Chan WM, Choy SO, Kwok P (2012) Development of a wearable system integrated with novel biomedical sensors for ubiquitous healthcare. In: Proceedings of the annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, EMBS, p 5802–5805. ISSN 1557170X. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2012.6347313
Jovanov E, Milenkovic A (2011) Body area networks for ubiquitous healthcare applications: opportunities and challenges. J Med Syst 35(5):1245–1254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9661-x ISSN 01485598
Kang K, Kim Y, Lee J, Choi H (2008) Ubiquitous health-assistant system based on accessory-type physiological signal sensing device. In: Digest of technical papers—IEEE international conference on consumer electronics, pp 2–3. ISSN 0747668X. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCE.2008.4587923
Kemp J, Gaura EI, Brusey J, Thake CD (2008) Using body sensor networks for increased safety in bomb disposal missions. In: Proceedings—IEEE international conference on sensor networks, ubiquitous, and trustworthy computing, pp 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1109/SUTC.2008.25
Keshav SS (2016) How to read a paper. ACM SIGCOMM Comput Commun Rev 37(3):83. https://doi.org/10.1145/1273445.1273458 (ISSN 01464833)
Kwon HC, Na D, Ko BG, Lee S (2008) An energy-efficient communication method based on the relationships between biological signals for ubiquitous health monitoring. In: Conference proceedings : ... annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Annual Conference, 2008:1541–1544. ISSN 1557-170X (Print). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2008.4649463
Madias JE (2016) A proposal for monitoring patients with heart failure via smart phone technology-based electrocardiograms. J Electrocardiol 49(5):699–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2016.06.001 ISSN 15328430
Nikolidakis SA, Georgakakis E, Giotsas V, Vergados DD, Douligeris C (2010) A secure ubiquitous healthcare system based on IMS and the HL7 standards. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments - PETRA ’10, pp 1. https://doi.org/10.1145/1839294.1839345. URL http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=1839294.1839345
Petersen K, Feldt R, Mujtaba S, Mattsson M (2008) Systematic mapping studies in software engineering. In: 12th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering 17:10. ISSN 02181940. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218194007003112
Petersen K, Vakkalanka S, Kuzniarz L (2015) Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: an update. Inf Softw Technol 64:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2015.03.007 ISSN 09505849
Petticrew M, Roberts H (2006) Systematic reviews in the social sciences: a practical guide. Oxford: Blackwell. 352 pp. ISBN 1 4051 2110 6., volume 6. Routledge, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1080/14733140600986250
Pham M, Mengistu Y, Do HM, Sheng W (2016) Cloud-Based Smart Home Environment (CoSHE) for home healthcare. In: IEEE international conference on automation science and engineering 2016-Novem:483–488. ISSN 21618089. https://doi.org/10.1109/COASE.2016.7743444
Pittoli F, Damasceno H, Luis J, Barbosa V, Butzen E, Ângela M, Soares J (2018) An intelligent system for prognosis of noncommunicable diseases ’ risk factors. Telemat Inform 35(5):1222–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2018.02.005
Punj R, Kumar R (2018) Technological aspects of WBANs for health monitoring: a comprehensive review. Wirel Netw 3:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1694-3 ISSN 15728196
Rosa H, Barbosa JLV, Ribeiro GD (2015) ORACON: an adaptative model for context prediction. Expert Syst with Appl 25(January):455–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.09.016 ISSN 0957-4174
Rosa JH, Barbosa JLV, Kich M, Brito L (2015) A multi-temporal context-aware system for competences management. Int J Artif Intell Educ 25(4):455–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-015-0047-y ISSN 1560-4306
Salim F, Belbasis A, Prohasky D, Houshyar S, Fuss FK (2014) Design and evaluation of smart wearable undergarment for monitoring physiological extremes in firefighting. In: Proceedings of the 2014 ACM international symposium on wearable computers adjunct program—ISWC ’14 Adjunct, pp 249–254. ISSN 15504816. https://doi.org/10.1145/2641248.2666716. URL http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=2641248.2666716
Siddharth PD, Deshpande S (2016) Embedded system design for real-time interaction with Smart Wheelchair. In: 2016 symposium on colossal data analysis and networking, CDAN 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/CDAN.2016.7570917
Sugimoto C, Kohno R (2011) Wireless sensing system for healthcare monitoring thermal physiological state and recognizing behavior. In: Proceedings—2011 international conference on broadband and wireless computing, communication and applications, BWCCA 2011, pp 285–291. https://doi.org/10.1109/BWCCA.2011.44
Touati F, Tabish R (2013) U-healthcare system: State-of-the-art review and challenges. J Med Syst 37(3). ISSN 01485598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-013-9949-0
Touati F, Ben Mnaouer A, Erdene-Ochir O, Mehmood W, Hassan A, Gaabab B (2015) Feasibility and performance evaluation of a 6lowpan-enabled platform for ubiquitous healthcare monitoring: performance of a 6lowpan platform for ubiquitous healthcare monitoring. Wirel Commun Mobile Comput 16:05. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcm.2601
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (2017) World population prospects the 2017 revision key findings and advance tables
Vianna HD, Luis J, Barbosa V (2017) In search of computer-aided social support in non-communicable diseases care. Telemat Inform 34(8):1419–1432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2017.06.005 ISSN 0736-5853
World Health Organization (2016) Cardiovascular disease. URL https://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/world-heart-day/en/
Young CP, Chang DW, Liang SF, Shaw FZ (2012) A portable multi-channel behavioral state and physiological signal monitoring system. In: 2012 IEEE I2MTC—international instrumentation and measurement technology conference, proceedings, pp 2687–2691. https://doi.org/10.1109/I2MTC.2012.6229401
Zheng YL, Ding XR, Poon CCY, Lo BPL, Zhang H, Zhou XL, Yang GZ, Zhao N, Zhang YT (2014) Unobtrusive sensing and wearable devices for health informatics. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(5):1538–1554. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2014.2309951 ISSN 15582531
Acknowledgements
This work was financed in part by FAPERGS/Brazil (Foundation for the Supporting of Research in the State of Rio Grande do Sul - http://www.fapergs.rs.gov.br), CNPq/Brazil (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development - http://www.cnpq.br) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001. We would also like to thank the University of Vale do Rio dos Sinos - Unisinos (http://www.unisinos.br) and the FEEVALE University (http://www.feevale.br) for embracing this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aranda, J.A.S., Dias, L.P.S., Barbosa, J.L.V. et al. Collection and analysis of physiological data in smart environments: a systematic mapping. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 11, 2883–2897 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01409-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01409-9