Abstract
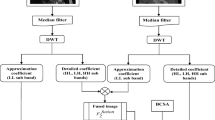
Multimodal medical image fusion aims to reduce insignificant information and improve clinical diagnosis accuracy. The purpose of image fusion is to retain salient image features and detail information of multiple source images to yield a more informative fused image. A hybrid algorithm based on both pixel and feature levels of multimodal medical image fusion is presented in this paper. For the pixel-level fusion, the source images are decomposed into low- and high-frequency components using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), and then the low-frequency coefficients are fused using maximum fusion rule. Thereafter, the curvelet transform is applied on the high-frequency coefficients. The obtained high-frequency subbands (fine scale) are fused using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) fusion rule. On the other hand, the feature-level fusion is accomplished by extracting various features form the coarse and detail subbands and using them for the fusion process. These features involve mean, variance, entropy, visibility, and standard deviation. Thereafter, the inverse curvelet transform is implemented on the fused high-frequency coefficients, and finally the resultant fused image is acquired by applying the inverse DWT on the fused low- and high-frequency components. The proposed method is evaluated and implemented on different pairs of medical image modalities. The results demonstrate that the proposed method improves the quality of the final fused image in terms of Mutual Information (MI), Correlation Coefficient (CC), entropy, Structural Similarity index (SSIM), Edge Strength Similarity for Image quality (ESSIM), Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), and edge-based similarity measure (QAB/F).










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computerized Tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- SPECT:
-
Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography
- MRA:
-
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
- PET:
-
Positron Emission Tomography
- DWT:
-
Discrete Wavelet Transform
- PCA:
-
Principal Component Analysis
- HSV:
-
Hue–Saturation-Value domain
- SWT:
-
Stationary Wavelet Transform
- NSCT:
-
Non-Subsampled Contourlet Transform
- NSST:
-
Non-Subsampled Shearlet Transform
- PCNN:
-
Pulse Coupled Neural Network
- IHS:
-
Intensity Hue Saturation
- FTR:
-
Fuzzy Transform
- GMSF:
-
Gradient Minimization Smoothing Filter
- K-SVD:
-
K-means generalized Singular Value Decomposition
- HCS-GWO:
-
Hybrid Cuckoo search-Grey Wolf Optimization
- ODL:
-
Online Dictionary Learning
- LARS:
-
Least Angle Regression
- SR:
-
Sparse Representation
- SSF:
-
Sum of Salient Features
- MSF:
-
Modified Spatial Frequency
- OMP:
-
Orthogonal Matching Pursuit
- ICMs:
-
Intersecting Cortical Models
- OFG:
-
Oscillation Frequency Graph
- HM:
-
Histogram Matching
- USFFT:
-
Unequally Spaced Fast Fourier Transform
- FDCT-wrapping:
-
Fast Discrete Curvelet Transform via wrapping method
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier Transform
- MI:
-
Mutual Information
- CC:
-
Correlation Coefficient
- ESSIM:
-
Edge Strength Similarity for Image quality
- PSNR:
-
Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio
- QAB/F :
-
Edge-based similarity measure
- SSIM:
-
Structural Similarity index
References
Aishwarya N, Bennila Thangammal C (2018) A novel multimodal medical image fusion using sparse representation and modified spatial frequency. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 28:175–185. https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22268
Anandan P, Sabeenian RS (2016) Medical image compression using wrapping based fast discrete Curvelet transform and arithmetic coding. Circuits Syst 07:2059–2069. https://doi.org/10.4236/cs.2016.78179
Arif M, Wang G (2020) Fast Curvelet transform through genetic algorithm for multimodal medical image fusion. Soft Comput 24:1815–1836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04011-5
Ashiba HI, Mansour HM, Ahmed HM et al (2018) Enhancement of infrared images based on efficient histogram processing. Wirel Pers Commun 99:619–636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4958-9
Bhateja V, Patel H, Krishn A et al (2015) Multimodal medical image sensor fusion framework using cascade of Wavelet and Contourlet transform domains. IEEE Sens J 15:6783–6790. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2015.2465935
Bhatnagar G, Wu QMJ, Liu Z (2015) A new contrast based multimodal medical image fusion framework. Neurocomputing 157:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.01.025
Bhavana V, Krishnappa HK (2015) Multi-modality medical image fusion using discrete Wavelet transform. Proc Comput Sci 70:625–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.10.057
Candès E, Demanet L, Donoho D, Ying L (2005) Fast discrete Curvelet transforms. Multiscale Model Simul 5:861–899. https://doi.org/10.1137/05064182X
Chen G-H, Yang C-L, Po L-M, Xie S-L (2006) Edge-based structural similarity for image quality assessment. In: Acoust Speech Signal Process 2006 ICASSP 2006 Proceedings 2006 IEEE Int Conf 2: II. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2006.1660497
Daniel E (2018) Optimum Wavelet-based homomorphic medical image fusion using hybrid genetic-Grey Wolf optimization algorithm. IEEE Sens J 18:6804–6811. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2018.2822712
Daniel E, Anitha J, Gnanaraj J (2017a) Optimum laplacian wavelet mask based medical image using hybrid cuckoo search—grey wolf optimization algorithm. Knowl-Based Syst 131:58–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.05.017
Daniel E, Anitha J, Kamaleshwaran KK, Rani I (2017b) Optimum spectrum mask based medical image fusion using Gray Wolf Optimization. Biomed Signal Process Control 34:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.01.003
El-Gamal FE-ZA, Elmogy M, Atwan A (2016) Current trends in medical image registration and fusion. Egypt Inf J 17:99–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eij.2015.09.002
Haribabu M, Hima Bindu C (2017) Feature level based multimodal medical image fusion with hadamard transform. Int J Control Theory Appl 9(42):453–460
James AP, Dasarathy BV (2014) Medical image fusion: a survey of the state of the art. Inf Fusion 19:4–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2013.12.002
Jin X, Chen G, Hou J et al (2018) Multimodal sensor medical image fusion based on nonsubsampled Shearlet transform and S-PCNNs in HSV space. Signal Process 153:379–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.08.002
Ławicki T, Zhirnova O (2015) Application of curvelet transform for denoising of CT images. In: Photonics applications in astronomy, communications, industry, and high-energy physics experiments, vol 9662, pp 966226. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2205483
Li M, Li G, Cai W, Li XY (2008) A novel pixel-level and feature-level combined multisensor image fusion scheme. Lect Notes Comput Sci (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 5264:658–665. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-87734-9-75
Liu Y, Liu S, Wang Z (2015) A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf Fusion 24:147–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2014.09.004
Liu X, Mei W, Du H (2016) Multimodality medical image fusion algorithm based on gradient minimization smoothing filter and pulse coupled neural network. Biomed Signal Process Control 30:140–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2016.06.013
Liu X, Mei W, Du H (2017a) Structure tensor and nonsubsampled shearlet transform based algorithm for CT and MRI image fusion. Neurocomputing 235:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.01.006
Liu Y, Chen X, Cheng J, Peng H (2017b) A medical image fusion method based on convolutional neural networks. In: 20th international conference on information fusion, Fusion 2017—Proceedings, pp 1–7
Liu X, Mei W, Du H (2018) Multi-modality medical image fusion based on image decomposition framework and nonsubsampled shearlet transform. Biomed Signal Process Control 40:343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.10.001
Malviya P, Saxena A (2014) An improved image fusion technique based on texture feature optimization using Wavelet transform and particle of swarm optimization (POS). Int J Comput Appl 101:19–22. https://doi.org/10.5120/17691-8656
Manchanda M, Sharma R (2016) A novel method of multimodal medical image fusion using fuzzy transform. J Vis Commun Image Represent 40:197–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2016.06.021
Mazaheri S, Sulaiman PS, Wirza R et al (2015) Hybrid pixel-based method for cardiac ultrasound fusion based on integration of PCA and DWT. Comput Math Methods Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/486532
Nava R (2007) Mutual information improves image fusion quality assessments. SPIE Newsroom. https://doi.org/10.1117/2.1200708.0824
Nirmala E, Vaidehi V (2015) Comparison of pixel-level and feature level image fusion methods. In: International conference on computing for sustainable global development, pp 743–748
Patil V, Sale D, Joshi MA (2013) Image fusion methods and quality assessment parameters. Asian J Eng Appl Technol 2:40–46
Prakash O, Park CM, Khare A et al (2019) Multiscale fusion of multimodal medical images using lifting scheme based biorthogonal wavelet transform. Optik (Stuttg) 182:995–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2018.12.028
Qi G, Wang D, Zhu Z et al (2019) A phase congruency and local Laplacian energy based multi-modality medical image fusion method in NSCT domain. IEEE Access 7:1. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2898111
Ramlal SD, Sachdeva J, Kamal C, Niranjan A (2018) Multimodal medical image fusion using non-subsampled shearlet transform and pulse coupled neural network incorporated with morphological gradient. Signal, Image Video Process 12:1479–1487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-018-1303-z
Reena Benjamin J, Jayasree T (2018) Improved medical image fusion based on cascaded PCA and shift invariant wavelet transforms. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 13:229–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1692-4
Sharma A, Saroliya A (2013) A brief review of different image fusion algorithm. Int J Sci Res 4:2319–7064
Singh S, Gupta D, Anand RS, Kumar V (2015) Nonsubsampled shearlet based CT and MR medical image fusion using biologically inspired spiking neural network. Biomed Signal Process Control 18:91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2014.11.009
Srivastava R, Khare A, Prakash O (2016) Local energy-based multimodal medical image fusion in Curvelet domain. IET Comput Vis 10:513–527. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cvi.2015.0251
Tawfik N, Elnemr HA, Fakhr M, Dessouky MI, FEAE-S (2020) Survey study of multimodality medical image fusion methods. Multimed Tools Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08834-5
Tirupal T, Chandra Mohan B, Srinivas Kumar S (2019) Multimodal medical image fusion based on yager’s intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 16:33–48. https://doi.org/10.22111/IJFS.2019.4482
Xia J, Chen Y, Chen A, Chen Y (2018a) Medical image fusion based on sparse representation and PCNN in NSCT domain. Comput Math Methods Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2806047
Xia K, Yin H, Wang J (2018b) A novel improved deep convolutional neural network model for medical image fusion. Cluster Comput 1:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-018-2026-1
Yang Y, Que Y, Huang S, Lin P (2016) Multimodal sensor medical image fusion based on type-2 fuzzy logic in NSCT domain. IEEE Sens J 16:3735–3745. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2016.2533864
Yin M, Liu X, Liu Y, Chen X (2018) Medical image fusion with parameter-adaptive pulse coupled-neural network in nonsubsampled Shearlet transform domain. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2018.2838778
Zhang X, Feng X, Wang W, Xue W (2013) Edge strength similarity for image quality assessment. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20:319–322. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2013.2244081
Zhu Z, Chai Y, Yin H et al (2016) A novel dictionary learning approach for multi-modality medical image fusion. Neurocomputing 214:471–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.06.036
Zong J, Qiu T (2017) Medical image fusion based on sparse representation of classified image patches. Biomed Signal Process Control 34:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2017.02.005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tawfik, N., Elnemr, H.A., Fakhr, M. et al. Hybrid pixel-feature fusion system for multimodal medical images. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 12, 6001–6018 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02154-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02154-0