Abstract
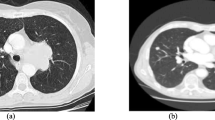
In order to improve the contrast of image fusion and highlight the unique characteristics of medical images, a multi-modal medical image fusion algorithm in the framework of non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT) is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the computed tomography images and magnetic resonance image are decomposed into low- and high-frequency sub-bands through the NSCT of multi-scale geometric transformation; secondly, for the low-frequency sub-band, the local area standard deviation method is selected or the fusion, while for the high-frequency sub-band, an adaptive pulse coupling neural network model is constructed and the fusion rules are set by the cumulative ignition times of iterative operation in the network; finally, the fusion image is obtained through image reconstruction. Experimental results show that the fusion results of the algorithm in this paper can improve the image fusion quality significantly and it has certain advantages in both visual effects and objective evaluation indexes, which provides a more reliable basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment of diseases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aishwarya N, Thangammal CB (2018) A novel multimodal medical image fusion using sparse representation and modified spatial frequency. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 28(3):175–185
Benjamin JR, Jayasree T (2018) Improved medical image fusion based on cascaded PCA and shift invariant wavelet transforms. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 13(2):229–240
Chen T, Ma X, Ying X (2019) Multi-modal fusion learning for cervical dysplasia diagnosis. In: Proceedings of international symposium on biomedical imaging, pp 1505–1509
Da Cunha AL, Zhou J, Do MN (2006) The nonsubsampled contourlet transform: theory, design, and applications. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(10):3089–3101
Do MN, Vetterli M (2002) Contourlets: a directional multiresolution image representation. In: Proceedings of international conference on image processing, vol 1, pp 357–360
Du J, Li W, Lu K (2016) An overview of multi-modal medical image fusion. Neurocomputing 215(26):3–20
Fei Y, Wei G, Zongxi S (2017) Medical image fusion based on feature extraction and sparse representation. Int J Biomed Imaging 2017:1–11
Huang Z, Ding M, Zhang X (2017) Medical image fusion based on non-subsampled shearlet transform and spiking cortical model. J Med Imaging Health Inform 7(1):229–234
Li Y, Zuo Z, Jin G, Ke S (2018) The research progress of the wavelet transform based PET/CT image fusion algorithm. China Med Imaging Technol 34(08):1267–1270
Liang X, Hu P, Zhang L, Sun J, Yin G (2019) Mcfnet: multi-layer concatenation fusion network for medical images fusion. IEEE Sens J 19(16):7107–7119
Lin Z, Yan J, Yuan Y (2013) The sparse representation and PCNN based multi-modal image fusion. J Shandong Univ (Eng Sci Ed) 43(4):13–17
Liu Y, Chen X, Cheng J, Peng H (2017) A medical image fusion method based on convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of 20th international conference on information fusion, pp 1–7
Luo G, Dong S, Wang K, Zuo W, Cao S, Zhang H (2018) Multi-views fusion CNN for left ventricular volumes estimation on cardiac MR images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 65(9):1924–1934
Qiu H, Li H, Yu Z (2017) The sparse representation based medical image fusion. Sens Microsyst 10(1):330–341
Shen Y, Dang J, Wang Y (2013) A new multi-scale geometric analysis based image fusion method. Optoelectron Laser 12:2446–2451
Singh S, Anand RS (2020) Multimodal medical image fusion using hybrid layer decomposition with CNN-based feature mapping and structural clustering. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 69(6):3855–3865
Tan Z (2018) A study on the pulse coupled neural network based image segmentation and fusion method. Shenzhen University, Shenzhen
Zhou T, Lu H, Wei X (2017) A Piella framework and DT-CWT based lung cancer PET/CT adaptive fusion algorithm. J Univ Sci Technol China 01:13–20
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Project of the Shandong Medicine and Health Science Technology Development Plan under Grant 2017WSB04071, Shandong Province Science and Technology Development Plan Project under Grant 2014GSF118086.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhao, J. A novel multi-modal medical image fusion algorithm. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 12, 1995–2002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02293-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02293-4