Abstract
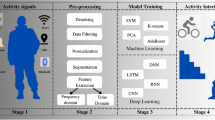
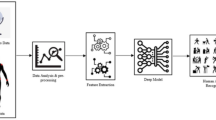
With recent evolvement in smart sensing systems, sensor-based activity recognition has endured numerous research studies that mainly emphasize classifying pre-segmented data chunks having a fixed duration. Each data chunk generally involves a single human activity for classification into one of the predefined activity classes. Such activity recognition models, trained with pre-segmented and fixed-size data chunks, cannot adapt well to natural human activities in real-time settings, where the duration of activities varies. Also, the real-time data available from smart devices is in a continuous form and not discrete chunks. As a result, the real-time implementation of activity-aware applications based on the existing models becomes impractical. Therefore, in this paper, a novel framework, i.e., “S-THAD”, is proposed for sensor-based temporal human activity detection from the continuous and untrimmed 3D motion sensor data. The proposed method is capable of detecting when and which activity of interest appears in a continuous data stream. The publicly available PAMAP2 dataset is used to test the proposed scheme, which entails long and untrimmed data streams from the wearable inertial sensors placed at three different body positions, including hand, chest, and ankle. The experimental results indicate that the proposed scheme achieves significant detection performance on this dataset.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
A public domain dataset, i.e., “PAMAP2”, is used for evaluating the proposed scheme, which is adequately cited in the paper.
Code availability
Code for data processing and analysis will be shared/uploaded to the journal repository once the paper has been conditionally accepted.
References
Ahad MAR, Antar A Das, Ahmed M (2021) Deep learning for sensor-based activity recognition: recent trends. In: IoT Sensor-Based Activity Recognition: Human Activity Recognition, vol 173. Springer, pp 149–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51379-5_9
Akbari A, Wu J, Grimsley R, Jafari R (2018) Hierarchical signal segmentation and classification for accurate activity recognition. In: UbiComp/ISWC 2018 Adjunct Proceedings of the 2018 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and Proceedings of the 2018 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, pp 1596–1605
Alemdar H, Ersoy C (2017) Multi-resident activity tracking and recognition in smart environments. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 8:513–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-016-0440-x
Antos SA, Albert MV, Kording KP (2014) Hand, belt, pocket or bag: practical activity tracking with mobile phones. J Neurosci Methods 231:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.09.015
Asghari P, Soleimani E, Nazerfard E (2020) Online human activity recognition employing hierarchical hidden Markov models. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 11:1141–1152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-019-01380-5
Bharti P, De D, Chellappan S, Das SK (2019) HuMAn: complex activity recognition with multi-modal multi-positional body sensing. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 18:857–870. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2018.2841905
Breiman L (2001) Random Forrest. Mach Learn. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Catal C, Tufekci S, Pirmit E, Kocabag G (2015) On the use of ensemble of classifiers for accelerometer-based activity recognition. Appl Soft Comput J 37:1018–1022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.01.025
Chambers RD, Yoder NC (2020) Filternet: a many-to-many deep learning architecture for time series classification. Sensors (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092498
Chen K, Yao L, Zhang D, et al (2019) Multi-agent attentional activity recognition. In: IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 1344–1350
Chen K, Zhang D, Yao L, et al (2020) Deep learning for sensor-based human activity recognition: overview, challenges and opportunities. https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.07416
Dawar N, Kehtarnavaz N (2018) Action detection and recognition in continuous action streams by deep learning-based sensing fusion. IEEE Sens J 18:9660–9668. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2018.2872862
Diete A, Stuckenschmidt H (2019) Fusing object information and inertial data for activity recognition. Sensors (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19194119
Ehatisham-ul-Haq M, Azam MA (2020) Opportunistic sensing for inferring in-the-wild human contexts based on activity pattern recognition using smart computing. Futur Gener Comput Syst 106:374–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.01.003
Ehatisham-ul-Haq M, Azam MA, Loo J et al (2017) Authentication of smartphone users based on activity recognition and mobile sensing. Sensors (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17092043
Ehatisham-ul-haq M, Awais M, Naeem U et al (2018) Continuous authentication of smartphone users based on activity pattern recognition using passive mobile sensing. J Netw Comput Appl 109:24–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2018.02.020
Ehatisham-Ul-Haq M, Azam MA, Amin Y, Naeem U (2020) C2FHAR: coarse-to-fine human activity recognition with behavioral context modeling using smart inertial sensors. IEEE Access 8:7731–7747. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2964237
Esfahani P, Malazi HT (2018) PAMS: a new position-aware multi-sensor dataset for human activity recognition using smartphones. In: 2017 19th International Symposium on Computer Architecture and Digital Systems, CADS 2017, pp 1–7
Fatima I, Fahim M, Lee YK, Lee S (2013) A genetic algorithm-based classifier ensemble optimization for activity recognition in smart homes. KSII Trans Internet Inf Syst 7:2853–2873. https://doi.org/10.3837/tiis.2013.11.018
Garcia-Ceja E, Galván-Tejada CE, Brena R (2018) Multi-view stacking for activity recognition with sound and accelerometer data. Inf Fusion 40:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2017.06.004
Guiry JJ, van de Ven P, Nelson J (2014) Multi-sensor fusion for enhanced contextual awareness of everyday activities with ubiquitous devices. Sensors (Switzerland) 14:5687–5701. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140305687
Hancock JM, Zvelebil MJ, Hancock JM (2004) Jaccard Distance (Jaccard Index, Jaccard Similarity Coefficient). Dictionary of bioinformatics and computational biology. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, New Jersey
Hassan MM, Uddin MZ, Mohamed A, Almogren A (2017) A robust human activity recognition system using smartphone sensors and deep learning. Futur Gener Comput Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2017.11.029
Hassan MM, Huda S, Uddin MZ et al (2018) Human activity recognition from body sensor data using deep learning. J Med Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-0948-z
Heilbron FC, Niebles JC, Ghanem B (2016) Fast temporal activity proposals for efficient detection of human actions in untrimmed videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1914–1923
Holmes G, Donkin A, Witten IH (2002) WEKA: a machine learning workbench. Springer, Berlin, pp 357–361
Ignatov A (2018) Real-time human activity recognition from accelerometer data using Convolutional Neural Networks. Appl Soft Comput J 62:915–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.09.027
Igwe OM, Wang Y, Giakos GC, Fu J (2020) Human activity recognition in smart environments employing margin setting algorithm. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02229-y
Kim S, Yoon YI (2018) Ambient intelligence middleware architecture based on awareness-cognition framework. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 9:1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-017-0647-5
Kozina S, Lustrek M, Gams M (2011) Dynamic signal segmentation for activity recognition. Proc Int Jt Conf Artif Intell 5:1–12
Lara OD, Labrador M (2013) A survey on human activity recognition using wearable sensors. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 15:1192–1209. https://doi.org/10.1109/SURV.2012.110112.00192
Li W, Chen C, Su H, Du Q (2015) Local binary patterns and extreme learning machine for hyperspectral imagery classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53:3681–3693. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2014.2381602
Li X, Malebary S, Qu X, et al (2018) ICare: Automatic and user-friendly child identification on smartphones. In: HotMobile 2018 Proceedings of the 19th International Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, pp 43–48
Li JH, Tian L, Wang H et al (2019) Segmentation and recognition of basic and transitional activities for continuous physical human activity. IEEE Access 7:42565–42576. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2905575
Liono J, Qin AK, Salim FD (2016) Optimal time window for temporal segmentation of sensor streams in multi-activity recognition. In: ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, pp 10–19
Ma C, Dai X, Zhu J et al (2017) DrivingSense: dangerous driving behavior identification based on smartphone autocalibration. Mob Inf Syst. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9075653
Ma C, Li W, Cao J et al (2020) Adaptive sliding window based activity recognition for assisted livings. Inf Fusion 53:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2019.06.013
Malhotra A, Schizas ID, Metsis V (2018) Correlation analysis-based classification of human activity time series. IEEE Sens J 18:8085–8095. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2018.2864207
Mekruksavanich S, Jitpattanakul A (2020) Exercise activity recognition with surface electromyography sensor using machine learning approach. In: 2020 Joint International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology with ECTI Northern Section Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Computer and Telecommunications Engineering, ECTI DAMT and NCON 2020, pp 75–78
Mettes P, Van Gemert JC, Cappallo S, et al (2015) Bag-of-fragments: Selecting and encoding video fragments for event detection and recounting. In: ICMR 2015 Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, pp 427–434
Minh Dang L, Min K, Wang H et al (2020) Sensor-based and vision-based human activity recognition: A comprehensive survey. Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107561
Minnen D, Westeyn TL, Starner T et al (2006) Performance metrics and evaluation issues for continuous activity recognition. Proc Int Work Perform Metrics Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1145/1889681.1889687
Mohammed Hashim BA, Amutha R (2020) Human activity recognition based on smartphone using fast feature dimensionality reduction technique. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02351-x
Morales J, Akopian D (2017) Physical activity recognition by smartphones, a survey. Biocybern Biomed Eng 37:388–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2017.04.004
Murtaza F, Yousaf MH, Velastin SA, Qian Y (2020) Vectors of temporally correlated snippets for temporal action detection. Comput Electr Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2020.106654
Noor MHM, Salcic Z, Wang KIK (2017) Adaptive sliding window segmentation for physical activity recognition using a single tri-axial accelerometer. Pervasive Mob Comput 38:41–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmcj.2016.09.009
Norgaard S, Saeedi R, Gebremedhin AH (2020) Multi-sensor time-series classification for activity tracking under variable length. IEEE Sens J 20:2701–2709. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2019.2953938
Nweke HF, Teh YW, Al-garadi MA, Alo UR (2018) Deep learning algorithms for human activity recognition using mobile and wearable sensor networks: state of the art and research challenges. Expert Syst Appl 105:233–261
Rault T, Bouabdallah A, Challal Y, Marin F (2017) A survey of energy-efficient context recognition systems using wearable sensors for healthcare applications. Pervasive Mob Comput 37:23–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmcj.2016.08.003
Ravi D, Wong C, Lo B, Yang GZ (2017) A deep learning approach to on-node sensor data analytics for mobile or wearable devices. IEEE J Biomed Heal Inform 21:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2016.2633287
Reiss A, Stricker D (2012) Introducing a new benchmarked dataset for activity monitoring. In: Proceedings International Symposium on Wearable Computers, ISWC, pp 108–109
Rivera P, Valarezo E, Choi M-T, Kim T-S (2017) Recognition of human hand activities based on a single wrist IMU using recurrent neural networks. Int J Pharma Med Biol Sci 6:114–118. https://doi.org/10.18178/ijpmbs.6.4.114-118
San-Segundo R, Montero JM, Barra-Chicote R et al (2016) Feature extraction from smartphone inertial signals for human activity segmentation. Signal Process 120:359–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.09.029
Shoaib M, Bosch S, Durmaz Incel O et al (2014) Fusion of smartphone motion sensors for physical activity recognition. Sensors (Switzerland) 14:10146–10176. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140610146
Subasi A, Khateeb K, Brahimi T, Sarirete A (2020) Human activity recognition using machine learning methods in a smart healthcare environment. Innovation in health informatics. Springer, Berlin, pp 123–144
Sucerquia A, López JD, Vargas-Bonilla JF (2017) SisFall: a fall and movement dataset. Sensors (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010198
Thornton C, Hutter F, Hoos HH, Leyton-Brown K (2013) Auto-WEKA: combined selection and hyperparameter optimization of classification algorithms. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp 847–855
Triboan D, Chen L, Chen F, Wang Z (2017) Semantic segmentation of real-time sensor data stream for complex activity recognition. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 21:411–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-017-1005-5
Triboan D, Chen L, Chen F, Wang Z (2019) A semantics-based approach to sensor data segmentation in real-time ACTIVITY RECOGNition. Future Gener Comput Syst 93:224–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.09.055
Uddin MZ, Hassan MM, Alsanad A, Savaglio C (2020) A body sensor data fusion and deep recurrent neural network-based behavior recognition approach for robust healthcare. Inf Fusion 55:105–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2019.08.004
Vaizman Y, Ellis K, Lanckriet G, Weibel N (2018) ExtraSensory app: data collection in-the-wild with rich user interface to self-report behavior. Proc CHI. https://doi.org/10.1145/3173574.3174128
Varamin AA, Abbasnejad E, Shi Q, et al (2018) Deep auto-set: a deep auto-encoder-set network for activity recognition using wearables. In: Proceedings of the 15th EAI International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services, pp 246–253
Vavoulas G, Chatzaki C, Malliotakis T, et al (2016) The MobiAct dataset: recognition of activities of daily living using smartphones. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health, pp 143–151
Wan S, Qi L, Xu X et al (2020) Deep Learning Models for Real-time Human Activity Recognition with Smartphones. Mob Netw Appl 25:743–755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-019-01445-x
Wang Y, Cang S, Yu H, Member S (2018) A data fusion-based hybrid sensory system for older people ’ s daily activity and daily routine recognition. IEEE Sens J 18:6874–6888. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2018.2833745
Wang J, Chen Y, Hao S et al (2019) Deep learning for sensor-based activity recognition: a survey. Pattern Recognit Lett 119:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.02.010
Wang H, Zhao J, Li J et al (2020) Wearable sensor-based human activity recognition using hybrid deep learning techniques. Secur Commun Netw. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2132138
Ward JA, Lukowicz P, Tröster G (2006) Evaluating performance in continuous context recognition using event-driven error characterisation. Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Springer, Berlin, pp 239–255
Ward JA, Lukowicz P, Gellersen HW (2011) Performance metrics for activity recognition. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol. https://doi.org/10.1145/1889681.1889687
Wu D, Zhang H, Niu C et al (2019) Inertial sensor based human activity recognition via reduced kernel PCA. Internet of things. Springer, Cham, pp 447–456
Xing R, Tong H, Ji P (2014) Activity recognition with smartphone sensors. Tsinghua Sci Technol 19:235–249. https://doi.org/10.1109/TST.2014.6838194
Yao R, Lin G, Shi Q, Ranasinghe DC (2018) Efficient dense labelling of human activity sequences from wearables using fully convolutional networks. Pattern Recognit 78:252–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2017.12.024
Ye J, Dobson S, Zambonelli F (2019) Lifelong learning in sensor-based human activity recognition. IEEE Pervasive Comput 18:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1109/MPRV.2019.2913933
Zebin T, Sperrin M, Peek N, Casson AJ (2018) Human activity recognition from inertial sensor time-series using batch normalized deep LSTM recurrent networks. Conf Proc Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc Annu Conf 2018:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2018.8513115
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Z et al (2018) Human activity recognition based on time series analysis using U-Net. J Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4752191
Zhao Y, Yang R, Chevalier G et al (2018) Deep residual Bidir-LSTM for human activity recognition using wearable sensors. Math Probl Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7316954
Zhuang Z, Xue Y (2019) Sport-related human activity detection and recognition using a smartwatch. Sensors (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19225001
Funding
This research work is sponsored by the Directorate of Advanced Studies, Research, and Technological Development (ASR&TD), University of Engineering and Technology (UET), Taxila, Punjab, Pakistan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehatisham-ul-Haq, M., Azam, M.A., Murtaza, F. et al. S-THAD: a framework for sensor-based temporal human activity detection from continuous data streams. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 13, 1037–1051 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-02931-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-02931-5