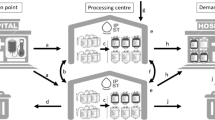
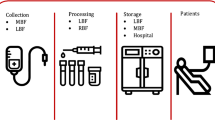
Abstract
Blood supply chain (BSC) management represents a vital and challenging task; blood is essentially needed, and in cases it is not available, patients may face death or other serious consequences. The BSC involves numerous complicated factors such as uncertainties in blood supply/demand, blood type distribution, limitations associated with blood shelf life, and production and collection methods. Given these issues, researchers have focused on developing efficient methodologies that could strike a balance between blood supply and demand, while minimizing blood shortage/waste. Review studies could help to highlight the findings and trends in this research area. The purpose of this study was to provide a systematic literature review of research on the BSC, using a bibliometric method. Such an approach was not previously used in the literature. Identifying and analyzing the impacts of the existing publications, the study could help researchers and institutions interested in this field to recognize hot topics and research trends. In doing so, the study investigated the articles published in journals indexed on Web of Science (WoS) between 1990 and August 2021, by considering three keyword echelons. As such, 485 articles were found and systematically analyzed. The study used content analysis software to compute author influence and affiliation statistics, while conducting citation analysis, co-citation analysis, keyword analysis, and co-word analysis. Furthermore, through co-word analysis and keyword co-occurrence analysis, the hot topics in research on the BSC were identified. The study also specifically investigated the supply chain of red blood cells, although it did not separately explore other blood by-products.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Abbasi B, Vakili G, Chesneau S (2017) Impacts of reducing the shelf life of red blood cells: a view from down under. Interfaces 47(4):336–351
Abbaspour A, Jahan A, Rezaiee M (2020) A simple empirical model for blood platelet production and inventory management under uncertainty. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput 1–17
An XY, Wu QQ (2011) Co-word analysis of the trends in stem cells field based on subject heading weighting. Scientometrics 88(1):133–144
Arani M, Chan Y, Liu X, Momenitabar M (2021) A lateral resupply blood supply chain network design under uncertainties. Appl Math Model 93:165–187
Archetti C, Bertazzi L, Laporte G, Speranza MG (2007) A branch-and-cut algorithm for a vendor-managed inventory-routing problem. Transport. Sci. 41(3):382–391
Basran S, Frumento RJ, Cohen A, Lee S, Du Y, Nishanian E, Bennett-Guerrero E (2006) The association between duration of storage of transfused red blood cells and morbidity and mortality after reoperative cardiac surgery: retracted. Anesth Anal 103(1):15–20
Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M (2009) Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Third international AAAI conference on weblogs and social media. Stanford, CA: AAAI.
Beliën J, Forcé H (2012) Supply chain management of blood products: a literature review. Eur J Oper Res 217(1):1–16
Bianchi L, Dorigo M, Gambardella LM, Gutjahr WJ (2009) A survey on metaheuristics for stochastic combinatorial optimization. Nat Comput 8(2):239–287
Blake JT (2010) An Introduction to Platelet Inventory and Ordering Problems. Wiley Encyclopedia of Operations Research and Management Science
Brodheim E, Derman C, Prastacos G (1975) On the evaluation of a class of inventory policies for perishable products such as blood. Manage Sci 21(11):1320–1325
Callon M, Courtial JP, Turner WA, Bauin S (1983) From translations to problematic networks: An introduction to co-word analysis. Information (International Social Science Council) 22(2):191–235
Chapman JF, Cook R (2002) The Blood Stocks Management Scheme, a partnership venture between the National Blood Service of England and North Wales and participating hospitals for maximizing blood supply chain management. Vox Sang 83(3):239–246
Cheraghi S, Hoseini Motlagh S, Ghatreh Samani M (2019) A robust bi-objective model for integrated blood supply chain network design considering transshipment between facilities under uncertainty. Quart J Transport Eng 10(4):737–770 ((In Persian))
Clauset A, Newman ME, Moore C (2004) Finding community structure in very large networks. Phys Rev E 70(6):066111
Cobo MJ, López-Herrera AG, Herrera‐Viedma E, Herrera F (2011) Science mapping software tools: Review, analysis, and cooperative study among tools. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 62(7):1382–1402
Coelho LC, Laporte G (2013) A branch-and-cut algorithm for the multi-product multi-vehicle inventory-routing problem. Int J Prod Res 51(23-24):7156–7169
Coelho LC, Cordeau JF, Laporte G (2014) Thirty years of inventory routing. Transport Sci 48(1):1–19
Cohen MA, Pierskalla WP (1979) Target inventory levels for a hospital blood bank or a decentralized regional blood banking system. Transfusion 19(4):444–454
Dehghani Ashkezari H, Yaghoubi S (2020) Designing an integrated blood plasma supply chain under uncertainty demand of both therapy and medicine. J Ind Syst Eng
Dehghani M, Abbasi B (2018) An age-based lateral-transshipment policy for perishable items. Int J Prod Econ 198:93–103
Dehghani M, Abbasi B, Oliveira F (2021) Proactive transshipment in the blood supply chain: A stochastic programming approach. Omega 98:102112
Dillon M, Oliveira F, Abbasi B (2017) A two-stage stochastic programming model for inventory management in the blood supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 187:27–41
Doodman M, Bozorgi Amiri A (2020) Integrate Blood Supply Chain Network Design with Considering Lateral Transshipment under Uncertainty. J Ind Manag Perspect 9(4), 9-40. (In Persian)
Duan Q, Liao TW (2014) Optimization of blood supply chain with shortened shelf lives and ABO compatibility. Int J Prod Econ 153:113–129
Eghtesadifard M, Khalifeh M, Khorram M (2020) A systematic review of research themes and hot topics in assembly line balancing through the web of science within 1990–2017. Comput Ind Eng 139:106182
FABER JC (2003) Hemovigilance: Definition and overview of current hemovigilance systems. Transfus Altern Transfus Med 5(1):237–245
Fahimnia B, Jabbarzadeh A, Ghavamifar A, Bell M (2017) Supply chain design for efficient and effective blood supply in disasters. Int J Prod Econ 183:700–709
Fahimnia B, Sarkis J, Davarzani H (2015) Green supply chain management: A review and bibliometric analysis. Int J Prod Econ 162:101–114
Feng Y, Zhu Q, Lai KH (2017) Corporate social responsibility for supply chain management: A literature review and bibliometric analysis. J Clean Prod 158:296–307
Fergusson DA, Hébert P, Hogan DL, LeBel L, Rouvinez-Bouali N, Smyth JA, … Lachance C (2012) Effect of fresh red blood cell transfusions on clinical outcomes in premature, very low-birth-weight infants: the ARIPI randomized trial. Jama 308(14):1443–1451
Fontaine MJ, Chung YT, Erhun F, Goodnough LT (2010) Age of blood as a limitation for transfusion: potential impact on blood inventory and availability. Transfusion 50(10):2233–2239
Fries BE (1975) Optimal ordering policy for a perishable commodity with fixed lifetime. Oper Res 23(1):46–61
Ghandforoush P, Sen TK (2010) A DSS to manage platelet production supply chain for regional blood centers. Decis Support Syst 50(1):32–42
Glynn SA (2010) The red blood cell storage lesion: a method to the madness. Transfusion 50(6):1164–1169
Goyal SK, Giri BC (2001) Recent trends in modeling of deteriorating inventory. European Journal of operational research 134(1):1–16
Grandjean M (2015) GEPHI: Introduction to Network Analysis and Visualisation
Gunpinar S, Centeno G (2015) Stochastic integer programming models for reducing wastages and shortages of blood products at hospitals. Comput Oper Res 54:129–141
Habibi-Kouchaksaraei M, Paydar MM, Asadi-Gangraj E (2018) Designing a bi-objective multi-echelon robust blood supply chain in a disaster. Appl Math Model 55:583–599
Haeri A, Hosseini-Motlagh SM, Samani G, M. R., and Rezaei M (2020) A mixed resilient‐efficient approach toward blood supply chain network design. International Transactions in Operational Research 27(4):1962–2001
Haijema R (2014) Optimal ordering, issuance and disposal policies for inventory management of perishable products. Int J Prod Econ 157:158–169
Haijema R, van der Wal J, van Dijk NM (2007) Blood platelet production: Optimization by dynamic programming and simulation. Comput Oper Res 34(3):760–779
Haijema R, van Dijk N, van der Wal J, Sibinga CS (2009) Blood platelet production with breaks: optimization by SDP and simulation. Int J Prod Econ 121(2):464–473
Heddle NM, Arnold DM, Acker JP, Liu Y, Barty RL, Eikelboom JW, … Cook RJ (2016) Red blood cell processing methods and in-hospital mortality: a transfusion registry cohort study. The Lancet Haematology 3(5):246–254
Hemmelmayr V, Doerner KF, Hartl RF, Savelsbergh MW (2010) Vendor managed inventory for environments with stochastic product usage. Eur J Oper Res 202(3):686–695
Hjorland B (2013) Citation analysis: A social and dynamic approach to knowledge organization. Information Processing Management 49(6):1313–1325
Hoff A, Andersson H, Christiansen M, Hasle G, Løkketangen A (2010) Industrial aspects and literature survey: Fleet composition and routing. Comput Oper Res 37(12):2041–2061
Hosseini-Motlagh SM, Larimi G, Oveysi Nejad M (2020a) A qualitative, patient-centered perspective toward plasma products supply chain network design with risk controlling. Operational Research, 1–46
Hosseini-Motlagh SM, Samani MRG, Cheraghi S (2020) Robust and stable flexible blood supply chain network design under motivational initiatives. Socio-Econ Plan Sci 70:100725
Hosseini-Motlagh SM, Samani MRG, Homaei S (2020) Toward a coordination of inventory and distribution schedules for blood in disasters. Socio-Econ Plan Sci 72:100897
Hosseini-Motlagh SM, Samani MRG, Homaei S (2020c) Blood supply chain management: robust optimization, disruption risk, and blood group compatibility (a real-life case). J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 11(3):1085–1104
Huang F, Zhou Q, Leng BJ, Mao QL, Zheng LM, Zuo MZ (2018) A bibliometric and social network analysis of pelvic organ prolapse during 2007–2016. J Chin Med Assoc 81(5):450–457
Jabbarzadeh A, Fahimnia B, Seuring S (2014) Dynamic supply chain network design for the supply of blood in disasters: A robust model with real world application. Transp Res E 70:225–244
Jennings JB (1973) Blood bank inventory control. Manage Sci 19(6):637–645
Karaesmen IZ, Scheller–Wolf A, Deniz B (2011) Managing perishable and aging inventories: review and future research directions. In: Planning production and inventories in the extended enterprise. Springer, New York, pp 393–436
Katsaliaki K (2008) Cost-effective practices in the blood service sector. Health policy 86(2-3):276–287
Katsaliaki K, Brailsford SC (2007) Using simulation to improve the blood supply chain. J Oper Res Soc 58(2):219–227
Katsaliaki K, Mustafee N, Kumar S (2014) A game-based approach towards facilitating decision making for perishable products: An example of blood supply chain. Expert Syst Appl 41(9):4043–4059
Kim J, Choi KY, Youn KW, Kim Y, Min HK, Kim HO (2018) Requirement of establishment of frozen blood storage system for management of rare blood supply and strategic national stockpile. Korean J Blood Transfus 29(1):3–17
Koch CG, Li L, Sessler DI, Figueroa P, Hoeltge GA, Mihaljevic T, Blackstone EH (2008) Duration of red-cell storage and complications after cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med 358(12):1229–1239
Kopach R, Balcıoğlu B, Carter M (2008) Tutorial on constructing a red blood cell inventory management system with two demand rates. Eur J Oper Res 185(3):1051–1059
Kudrol KR, Samartha V, Anand A (2019) Mapping Blood Supply Chain: Systematic Literature review using Bibliometric Visualization techniques. Global Health & Medical Tourism (GloHMT)
Lacroix J, Hébert PC, Fergusson DA, Tinmouth A, Cook DJ, Marshall JC, … Blajchman MA (2015) Age of transfused blood in critically ill adults. N Engl J Med 372(15):1410–1418
Larimi NG, Yaghoubi S (2019) A robust mathematical model for platelet supply chain considering social announcements and blood extraction technologies. Comput Ind Eng 137:106014
Larimi NG, Yaghoubi S, Hosseini-Motlagh SM (2019) Itemized platelet supply chain with lateral transshipment under uncertainty evaluating inappropriate output in laboratories. Socio-Econ Plan Sci 68:100697
Le T, Diabat A, Richard JP, Yih Y (2013) A column generation-based heuristic algorithm for an inventory routing problem with perishable goods. Optim Lett 7(7):1481–1502
Lowalekar H, Ravichandran N (2014) Blood bank inventory management in India. Opsearch 51(3):376–399
Moral-Munoz JA, López-Herrera AG, Herrera-Viedma E, Cobo MJ (2019) Science Mapping Analysis Software Tools: A Review. In: Springer Handbook of Science and Technology Indicators. Springer, Cham, pp 159–185
Nagurney A, Masoumi AH, Yu M (2012) Supply chain network operations management of a blood banking system with cost and risk minimization. Computational management science 9(2):205–231
Nahmias S (1975) Optimal ordering policies for perishable inventory—II. Oper Res 23(4):735–749
Nahmias S (1982) Perishable inventory theory: A review. Oper Res 30(4):680–708
Nahmias S (2011) Perishable inventory systems, vol 160. Springer Science & Business Media
Nguyen T, Li ZHOU, Spiegler V, Ieromonachou P, Lin Y (2018) Big data analytics in supply chain management: A state-of-the-art literature review. Comput Oper Res 98:254–264
Osorio AF, Brailsford SC, Smith HK (2015) A structured review of quantitative models in the blood supply chain: a taxonomic framework for decision-making. Int J Prod Res 53(24):7191–7212
Osorio AF, Brailsford SC, Smith HK (2018) Whole blood or apheresis donations? A multi-objective stochastic optimization approach. Eur J Oper Res 266(1):193–204
Osorio AF, Brailsford SC, Smith HK, Forero-Matiz SP, Camacho-Rodríguez BA (2017) Simulation-optimization model for production planning in the blood supply chain. Health Care Manag Sci 20(4):548–564
Page B (1980) A review of computer systems in blood banks and discussion of the applicability of mathematical decision methods. Methods Inf Med 19(02):75–82
Pi D, Shih AW, Sham L, Zamar D, Roland K, Hudoba M (2019) Establishing performance management objectives and measurements of red blood cell inventory planning in a large tertiary care hospital in British Columbia, Canada. ISBT Science Series 14(2):226–238
Pierskalla WP (2005) Supply chain management of blood banks. In: Operations research and health care. Springer, Boston, pp 103–145
Pierskalla WP, Sassetti RJ, Director BC, Chicaqo IL (1980) Regionalization of Blood Banking Services. National Health Care Management Center, University of Pennsylvania
Pirabán A, Guerrero WJ, Labadie N (2019) Survey on blood supply chain management: Models and methods. Comput Oper Res 112:104756
Pouraliakbari-Mamaghani M, Ghodratnama A, Pasandideh SHR, Saif A (2021) A robust possibilistic programming approach for blood supply chain network design in disaster relief considering congestion. Oper Res 2:1–46
Prastacos GP (1984) Blood inventory management: an overview of theory and practice. Management science 30(7):777–800
Prastacos GP, Brodheim E (1980) PBDS: a decision support system for regional blood management. Manage Sci 26(5):451–463
Radicchi F, Castellano C, Cecconi F, Loreto V, Parisi D (2004) Defining and identifying communities in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(9):2658–2663
Ramezanian R, Behboodi Z (2017) Blood supply chain network design under uncertainties in supply and demand considering social aspects. Transp Res E 104:69–82
Rytilä JS, Spens KM (2006) Using simulation to increase efficiency in blood supply chains. Manag Res News 29(12):801–819
Sahinidis NV (2004) Optimization under uncertainty: state-of-the-art and opportunities. Comput Chem Eng 28(6-7):971–983
Samani MRG, Hosseini-Motlagh SM (2019) An enhanced procedure for managing blood supply chain under disruptions and uncertainties. Ann Oper Res 283(1):1413–1462
Samani MRG, Hosseini-Motlagh SM (2021) A robust framework for designing blood network in disaster relief: a real-life case. Oper Res Int J 21(3):1529–1568
Samani MRG, Hosseini-Motlagh SM, Homaei S (2020) A reactive phase against disruptions for designing a proactive platelet supply network. Transp Res E 140:102008
Samani MRG, Hosseini-Motlagh SM, Sheshkol MI, Shetab-Boushehri SN (2019) A bi-objective integrated model for the uncertain blood network design with raising products quality. Eur J Ind Eng 13(5):553–588
Sarhangian V, Abouee-Mehrizi H, Baron O, Berman O (2018) Threshold-based allocation policies for inventory management of red blood cells. Manuf Serv Oper Manag 20(2):347–362
Sarhangian V, Abouee-Mehrizi H, Baron O, Berman O, Heddle NM, Barty R (2016) Reducing the age of transfused red blood cells in hospitals: Ordering and allocation policies. Vox Sang 110(4):385–392
Siddaway AP, Wood AM, Hedges LV (2019) How to do a systematic review: a best practice guide for conducting and reporting narrative reviews, meta-analyses, and meta-syntheses. Ann Rev Psychol 70:747–770
Stanger SH, Yates N, Wilding R, Cotton S (2012) Blood inventory management: hospital best practice. Transfus Med Rev 26(2):153–163
Torabi SA, Moghaddam M (2012) Multi-site integrated production-distribution planning with trans-shipment: a fuzzy goal programming approach. Int J Prod Res 50(6):1726–1748
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J manag 14(3):207–222
Vamvakas EC, Carven JH (2000) Length of storage of transfused red cells and postoperative morbidity in patients undergoing coronary artery bypassgraft surgery. Transfusion 40(1):101–109
Van Dijk N, Haijema R, Van Der Wal J, Sibinga CS (2009) Blood platelet production: a novel approach for practical optimization. Transfusion 49(3):411–420
Walter C, Ribière V (2013) A citation and co-citation analysis of 10 years of KM theory and practices. Knowledge Management Research Practice 11(3):221–229
Wang C, Chen S (2020) A distributionally robust optimization for blood supply network considering disasters. Transp Res E 134:101840
Wang KM, Ma ZJ (2015) Age-based policy for blood transshipment during blood shortage. Transp Res E 80:166–183
Whitaker BI, Hinkins S (2014) The 2011 national blood collection and utilization survey report. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2013
Whitaker BI, Green J, King MR, Leibeg LL, Mathew SM, Schlumpf KS, Schreiber GB (2011) National blood collection and utilization survey. American Association of Blood Banks
World Health Organization (2011) Global database on blood safety. Summary Report, 2011, 3-4
Yaghoubi S, Hosseini-Motlagh SM, Cheraghi S, Larimi NG (2020) Designing a robust demand-differentiated platelet supply chain network under disruption and uncertainty. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 11(8):3231–3258
Yalçındağ S, Güre SB, Carello G, Lanzarone E (2020) A stochastic risk-averse framework for blood donation appointment scheduling under uncertain donor arrivals. Health Care Manag Sci 23(4):535–555
Yazer M, Eder AF, Land KJ (2013) How we manage AB plasma inventory in the blood center and transfusion service. Transfusion 53(8):1627–1633
Zahiri B, Pishvaee MS (2017) Blood supply chain network design considering blood group compatibility under uncertainty. Int J Prod Res 55(7):2013–2033
Zahiri B, Torabi SA, Mousazadeh M, Mansouri SA (2015) Blood collection management: Methodology and application. Appl Math Model 39(23-24):7680–7696
Zhou D, Leung LC, Pierskalla WP (2011) Inventory management of platelets in hospitals: Optimal inventory policy for perishable products with regular and optional expedited replenishments. Manuf Serv Oper Manag 13(4):420–438
Zupic I, Čater T (2015) Bibliometric methods in management and organization. Organ Res Methods 18(3):429–472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eghtesadifard, M., Jozan, F. A systematic literature review on the blood supply chain: exploring the trend and future research directions. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 13, 1173–1200 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03563-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03563-5