Abstract
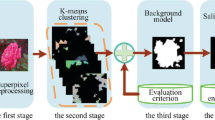
The extraction of salient objects from a cluttered background without any prior knowledge is a challenging task in salient object detection and segmentation. A salient object can be detected from the uniqueness, rarity, or unproductivity of the salient regions in an image. However, an object with a similar color appearance may have a marginal visual divergence that is even difficult for the human eyes to recognize. In this paper, we propose a technique which compose and fuse the fast fuzzy c-mean (FFCM) clustering saliency maps to separate the salient object from the background in the image. To be specific, we first generate the maps using FFCM clustering, that contain specific parts of the salient region, which are composed later by using the Porter–Duff composition method. Outliers in the extracted salient regions are removed using a morphological technique in the post-processing step. To extract the final map from the initially constructed blended maps, we use a fused mask, which is the composite form of color prior, location prior, and frequency prior. Experiment results on six public data sets (MSRA, THUR-15000, MSRA-10K, HKU-IS, DUT-OMRON, and SED) clearly show the efficiency of the proposed method for images with a noisy background.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, Susstrunk S (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: Ieee International Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (cvpr 2009), pp 1597–1604
Azaza A, van de Weijer J, Douik A, Masana M (2018) Context proposals for saliency detection. Comput Vis Image Underst 174:111
Badoual A, Unser M, Depeursinge A (2019) Texture-driven parametric snakes for semiautomatic image segmentation. Comput Vis Image Underst 188:102793
Barranco F, Diaz J, Pino B, Ros E (2014) Realtime visual saliency architecture for fpga with top-down attention modulation. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 10(3):1726–1735
Chen L-Q, Xie X, Fan X, Ma W-Y, Zhang H-J, Zhou H-Q (2003) A visual attention model for adapting images on small displays. Multimed Syst 9(4):353–364
Chen S, Wang B, Tan X, Hu X (2020) Embedding attention and residual network for accurate salient object detection. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(5):2050–2062
Ding M, Tong R-F (2010) Content-aware copying and pasting in images. Vis Comput 26(6–8):721–729
Duff P (2015) Retrieved from https://www.w3.org/TR/compositing-1
Gao Y, Shi M, Tao D, Xu C (2015) Database saliency for fast image retrieval. IEEE Trans Multimed 17(3):359–369
Goferman S, Zelnik-Manor L, Tal A (2011a) Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(10):1915–1926
Goyal P, Mahajan D, Gupta A, Misra I (2019) Scaling and benchmarking self-supervised visual representation learning. In: Proceedings of the ieee/cvf International Conference on computer vision, pp 6391–6400
Harel J, Koch C, Perona P (2007) Graph-based visual saliency. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 545–552
Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E (1998) A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(11):1254–1259
Jian M, Lam K-M, Dong J, Shen L (2014) Visual- patch-attention-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(8):1575–1586
Jiang B, Zhang L, Lu H, Yang C, Yang M-H (2013) Saliency detection via absorbing Markov chain. In: Proceedings of the ieee International Conference on computer vision, pp 1665–1672
Kim G, Yang S, Sim J-Y (2017) Saliency-based initialisation of gaussian mixture models for fully-automatic object segmentation. Electron Lett 53(25):1648–1649
Li X, Li Y, Shen C, Dick A, Van Den Hengel A (2013a) Contextual hypergraph modeling for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the ieee International Conference on computer vision, pp 3328–3335
Li X, Lu H, Zhang L, Ruan X, Yang M-H (2013b) Saliency detection via dense and sparse reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the ieee International Conference on computer vision, pp 2976–2983
Liu T, Yuan Z, Sun J, Wang J, Zheng N, Tang X, Shum H-Y (2010) Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(2):353–367
Liu Z, Zou W, Le Meur O (2014) Saliency tree: a novel saliency detection framework. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(5):1937–1952
Murabito F, Spampinato C, Palazzo S, Giordano D, Pogorelov K, Riegler M (2018) Top-down saliency detection driven by visual classification. Comput Vis Image Underst 172:67–76
Nawaz M, Yan H (2020) Saliency detection using deep features and affinity-based robust background subtraction. IEEE Trans Multimed
Nawaz M, Khan S, Cao J, Qureshi R, Yan H (2019a) Saliency detection by using blended membership maps of fast fuzzy-c-mean clustering. In: Eleventh International Conference on machine vision (icmv 2018), Vol. 11041, p. 1104123
Nawaz M, Khan S, Qureshi R, Yan H (2019b) Clustering based one-to-one hypergraph matching with a large number of feature points. Signal Process Image Commun 74:289–298
Perazzi F, Krahenbuhl P, Pritch Y, Hornung A (2012) Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: 2012 ieee Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 733740
Rahtu E, Kannala J, Salo M, Heikkila J (2010) Segmenting salient objects from images and videos. In: European Conference on computer vision, pp 366–379
Seo HJ, Milanfar P (2009) Static and space-time visual saliency detection by self-resemblance. J Vis 9(12):15
Shahid AR, Khan S, Yan H (2020a) Contour and region harmonic features for sub-local facial expression recognition. J Vis Commun Image Represent 73:102949
Shahid AR, Khan S, Yan H (2020b) Human expression recognition using facial shape based fourier descriptors fusion. In: Twelfth International Conference on machine vision (ICMV 2019), 11433, 114330P
Sokhandan A, Monadjemi A (2018) Visual tracking in video sequences based on biologically inspired mechanisms. Comput Vis Image Underst
Tavakoli HR, Rahtu E, Heikkila J(2011) Fast and efficient saliency detection using sparse sampling and kernel density estimation. In: Scandinavian Conference on image analysis, pp 666–675
THUR-15000 (2013) Retrieved from https://mmcheng.net/gsal/
Wang W, Lai Q, Fu H, Shen J, Ling H (2019) Salient object detection in the deep learning era: an in-depth survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.09146
Wang Z, Xiang D, Hou S, Wu F (2016) Background-driven salient object detection. IEEE Trans Multimed 19(4):750–762
Xi X, Luo Y, Wang P, Qiao H (2019) Salient object detection based on an efficient end-to-end saliency regression network. Neurocomputing 323:265–276
Xue Y, Shi R, Liu Z (2011) Saliency detection using multiple region-based features. Opt Eng 50(5):057008
Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H (2013a) Graph-regularized saliency detection with convex-hull-based center prior. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20(7):637640
Yang C, Zhang L, Lu H, Ruan X, Yang M-H (2013b) Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: Proceedings of the ieee Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 31663173
Yuan Y, Li C, Kim J, Cai W, Feng DD (2017) Reversion correction and regularized random walk ranking for saliency detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(3):1311–1322
Zhang L, Gu Z, Li H (2013) Sdsp: a novel saliency detection method by combining simple priors. In: 2013 ieee International Conference on image processing, pp 171–175
Zhu W, Liang S, Wei Y, Sun J (2014) Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: Proceedings of the ieee Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2814–2821
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nawaz, M., Qureshi, R., Teevno, M.A. et al. Object detection and segmentation by composition of fast fuzzy C-mean clustering based maps. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 7173–7188 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03570-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03570-6