Abstract
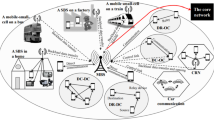
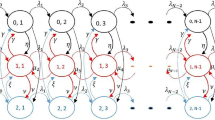
The service discipline of weighted fair queueing (WFQ) has been practically used in many telecommunication systems. The development of analytically tractable models with WFQ discipline to determine their performances is vitally important. Motivated by a practical project on routers’ optimization from the Huawei Company, this paper deals with a two-class single server MAP/PH/1 queue with a finite capacity under the WFQ discipline, which is little investigated in the literature. To capture the most generality of stochastic factors in traffic traces, we assume that the arrive process is a Markovian arrival process (MAP) and the service time obeys a phase-type (PH) distribution. This paper focuses on the performance analysis of our proposed queueing system and its application to traffic flow performances. We model this system as a five-dimensional Markov chain and use the matrix-geometric method to derive its stationary probabilities and performance measures, such as the average queue length and sojourn time of each class of customers. In order to validate our analysis results, we further develop a simulator to evaluate the system performance with a real data of Internet packet traces. Experiment comparison demonstrates the effectiveness and applicability of our theoretical model.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Huawei Company but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under licence for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of the Huawei Company.
References
Al-Sawaai A, Awan I, Fretwell R (2009a) Analysis of the weighted fair queuing system with two classes of customers with finite buffer. In: 2009 international conference on advanced information networking and applications workshops. IEEE, pp 218–223
Al-Sawaai A, Awan I, Fretwell R (2009b) Performance evaluation of weighted fair queuing system using matrix geometric method. In: 2009 international conference on research in networking. Springer, pp 66–78
Balogh T, Medveckỳ M (2011) Performance evaluation of WFQ, WF\(^{ 2}\)Q+ and WRR queue scheduling algorithms. In: 2011 international conference on telecommunications and signal processing (TSP). IEEE, pp 136–140
Boussada MEH, Garcia JM, Frikha M (2018) New fluid approaches for studying the performance of elastic traffic under class based weighed fair queuing system. Int J Netw Manage 28(6):e2037
Chen Y, Turner JS (1998) Design of a weighted fair queueing cell scheduler for ATM networks. In: 1998 IEEE global communications conference, pp 405–410
D’Arienzo M, Dudin AN, Dudin SA, Manzo R (2020) Analysis of a retrial queue with group service of impatient customers. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 11(6):2591–2599
Dudin SA (2009) The MAP+MAP/PH/1/N queuing system with single and batch arrivals of customers. Autom Remote Control 70(5):872–884
Gaver D, Jacobs P, Latouche G (1984) Finite birth-and-death models in randomly changing environments. Adv Appl Probab 16(4):715–731
Guillemin F, Pinchon D (2004) Analysis of the weighted fair queuing system with two classes of customers with exponential service times. J Appl Probab 41(3):832–858
He QM (2014) Fundamentals of matrix-analytic methods. Springer, New York
Heyman DP, Lucantoni D (2003) Modeling multiple IP traffic streams with rate limits. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 11(6):948–958
Horváth G, Telek M (2017) Butools 2: a rich toolbox for Markovian performance evaluation. In: ValueTools 2016 EAI international conference on performance evaluation methodologies and tools, association for computing machinery, pp 137–142
Hussain S, Marshall A (2003) An agent-based control mechanism for WFQ in IP networks. Control Eng Pract 11(10):1143–1151
Kim C, Dudin S, Klimenok V (2009) The MAP/PH/1/N queue with flows of customers as a model for traffic control in telecommunication networks. Perform Eval 66(9–10):564–579
Klemm A, Lindemann C, Lohmann M (2003) Modeling IP traffic using the batch Markovian arrival process. Perform Eval 54(2):149–173
Latouche G, Ramaswami V (1999) Introduction to matrix analytic methods in stochastic modeling. ASA-SIAM series on statisticsand applied probability. SIAM, Philadelphia
Li CC, Tsao SL, Chen MC, Sun Y, Huang YM (2000) Proportional delay differentiation service based on weighted fair queuing. In: 2000 international conference on computer communications and networks. IEEE, pp 418–423
Li QL, Lian Z, Liu L (2005) An RG-factorization approach for a BMAP/M/1 generalized processor-sharing queue. Stoch Model 21(2–3):507–530
Mahmood DA, Horváth G (2017) A simple approximation for the response times in the two-class weighted fair queueing system. In: 2017 international conference on analytical and stochastic modeling techniques and applications. Springer, pp 125–137
Masuyama H, Takine T (2003) Sojourn time distribution in a MAP/M/1 processor-sharing queue. Oper Res Lett 31(5):406–412
Neuts MF (1979) A versatile Markovian point process. J Appl Probab 16(4):764–779
Okamura H, Dohi T (2016) Fitting phase-type distributions and Markovian arrival processes: algorithms and tools. In: 2016 performance and reliability modeling and evaluation. Springer, pp 49–75
Parini A, Pattavina A (2005) Modelling voice call interarrival and holding time distributions in mobile networks. In: 2005 international teletraffic congress, pp 729–738
Parveen AS (2014) A survey of an integrated scheduling scheme with long-range and short-range dependent traffic. Int J Eng Sci Res Technol 3(1):430–439
Riska A, Diev V, Smirni E (2002) Efficient fitting of long-tailed data sets into hyper exponential distributions. In: 2002 IEEE global telecommunications conference, pp 2513–2517
Samanta SK, Das K (2022) Computing stationary distributions of the D-MAP/D-MSP\(^{(a, b)}\)/1 queueing system. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 13(1):571–590
Shortle JF, Fischer MJ (2010) Approximation for a two-class weighted fair queueing discipline. Perform Eval 67(10):946–958
Tsimba H, Maharaj BT, Alfa A (2020) Optimal spectrum utilisation in cognitive radio networks based on processor sharing techniques. Int J Commun Syst 33(4):e4242
Vishnevskii VM, Dudin AN (2017) Queueing systems with correlated arrival flows and their applications to modeling telecommunication networks. Autom Remote Control 78(8):1361–1403
Wang L, Min G, Kouvatsos DD, Jin X (2010) Analytical modeling of an integrated priority and WFQ scheduling scheme in multi-service networks. Comput Commun 33:S93–S101
Zhao JA, Li B, Cao XR, Ahmad I (2006) A matrix-analytic solution for the DBMAP/PH/1 priority queue. Queueing Syst 53(3):127–145
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2021A1515011984, 2020A1515110824), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62073346, 11671404, 61573206), the Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Computational Science at the Sun Yat-Sen University (2020B1212060032), and a collaborated project between the Sun Yat-Sen University and the Huawei Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Xia, L., Jiang, Z. et al. A two-class MAP/PH/1 weighted fair queueing system and its application to telecommunications. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 16361–16372 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-03857-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-03857-2