Abstract
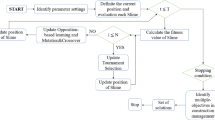
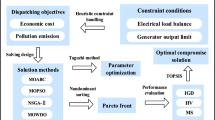
A service evaluation model and a solution strategy for agricultural machinery maintenance services based on big data areproposed considering the characteristics of a large business volume, a diversity of service types, a wide geographical distribution and on-site service for agricultural machinery maintenance services in China. First, a maintenance order priority evaluation model is developed based onanevaluation model of quality of service (QoS), and order confirmation is followed by developing a staffing evaluation model. A fuzzy analytical hierarchy process is used to determine the weights of the evaluation indicators. The evaluation models are solved by an improved genetic-bee colony algorithm (GAABC). In the selection operation stage of the genetic algorithm, a combination of an elite retention strategy and a roulette strategy is adopted, which not only guarantees the convergence speed of the algorithm and the diversity of individuals, but also prevents the loss of good genes of individual parents after the crossover and mutation operations. The attractor is introduced at the onlooker bee stage, where the onlooker bees shrink in proportion to the attractor at the center, thereby increasing the convergence speed and algorithm development for subsequent stages, as well as developing the area at the current stage. The mutation operation is added to the artificial bee colony algorithm (ABC) according to the degree of honey source aggregation to improve the local search ability. In addition, the best fusion point assessment strategy is used to determine the switching time between the genetic algorithm (GA) and the artificial bee colony algorithm to increase the convergence speed and accuracy of the solution. Finally, the feasibility and effectiveness of the agricultural machinery maintenance service model and the solution algorithm are verified by simulation experiments. This research provides theoretical support for the decision analysis of agricultural machinery maintenance enterprises in China.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Aslan S (2020) A comparative study between artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm and its variants on big data optimization. Memetic Comput 12(2):129–150
Garg S, Modi K, Chaudhary S (2016) A QoS-aware approach for runtime discovery, selection and composition of semantic web services. Int J Semant Web Inf 12(2):177–200
He W, Xu L (2015) A state-of-the-art survey of cloud manufacturing. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 28(3):239–250
Hu YG, Liu Y, Wang Z et al (2020) A two-stage dynamic capacity planning approach for agricultural machinery maintenance service with demand uncertainty. Biosys Eng 190:201–217
Li Y, Yao X, Liu M (2020) Multiobjective optimization of cloud manufacturing service composition with improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Math Probl Eng 2020:1–17
Liu J, Wei X, Ye J et al (2020) Research on preventive group maintenance strategy for in-service agricultural machinery and equipment. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 51(S2):316–322+448
Moghaddam SH, Akbaripour H, Houshmand M (2021) Integrated forward and reverse logistics in cloud manufacturing: an agent-based multi-layer architecture and optimization via genetic algorithm. Prod Eng 15:1–19
Moradi MH, Abedini M (2012) A combination of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for optimal DG location and sizing in distribution systems. Int J Electr Power Energy 34(1):66–74
Stodola P (2020) Hybrid ant colony optimization algorithm applied to the multi-depot vehicle routing problem. Nat Comput 19(2):463–475
Tapale MT, Goudar RH, Birje MN et al (2020) Utility based load balancing using firefly algorithm in cloud. J Data, Inform Manag 2(4):215–224
Velliangiri S, Karthikeyan P, Xavier VMA et al (2021) Hybrid electro search with genetic algorithm for task scheduling in cloud computing. Ain Shams Eng J 12(1):631–639
Wu QW, Ishikawa F, Zhu Q et al (2016) QoS-aware multigranularity service composition: modeling and optimization. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 46(11):1565–1577
Yang Y, Yang B, Wang S et al (2019) A dynamic ant-colony genetic algorithm for cloud service composition optimization. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 102(1–4):355–368
Yi N, Xu J, Yan L et al (2020) Task optimization and scheduling of distributed cyber-physical system based on improved ant colony algorithm. Futur Gener Comput Syst 109:134–148
Zeng L, Benatallah B, Ngu A et al (2004) QoS-aware middleware for web services composition. IEEE Trans Softw Eng 30(5):311–327
Zhang R, Zhang Y, Zheng Z et al (2020) Parametrical optimization of particle dampers based on particle swarm algorithm. Appl Acoust 160:107083
Zheng XQ, Liu M, Kong FR (2013) Research on MRO maintenance service schedule based on cloud-based genetic algorithm. Comput Integr Manuf Syst 19(9):2348–2354
Zheng H, Yu D, Zhang L (2017) Multi-QoS cloud workflow scheduling based on firefly algorithm and dynamic priorities. Comput Integr Manuf Syst 5:6
Zhou J, Yao X (2017a) A hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm for optimal selection of QoS-based cloud manufacturing service composition. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 88(9–12):3371–3387
Zhou J, Yao X (2017b) Multi-objective hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm enhanced with Lévy flight and self-adaption for cloud manufacturing service composition. Appl Intell 47(3):721–742
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out with the support of the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2022QE103), the University Youth lnnovation Science and Technology Support Program of Shandong Province, the Key Research and Development Plan Project of Shandong Province (2021CXG010813, 2022SFGC0203), the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-24-D-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, K., Ni, Z., Yin, Y. et al. Study of the strategy for agricultural machinery maintenance in China based on the improved genetic-bee colony algorithm. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 2275–2289 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-04485-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-022-04485-6