Abstract
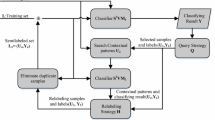
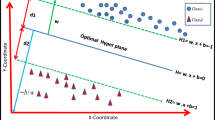
This article introduces a semisupervised support vector machine classification technique that exploits both labeled and unlabeled points for addressing the problem of pixel classification of remote sensing images. The proposed technique is based on applying the margin maximization principle to both labeled and unlabeled patterns. Semisupervised SVM progressively searches a reliable discriminant hyperplane in the high dimensional space through iterative method exploiting both labeled and unlabeled samples. In particular, the dynamic thresholding and successive filtering of the unlabeled set are exploited to find a reliable separating hyperplane. The proposed technique is first demonstrated for six labeled datasets described in terms of feature vectors and then identifying different land cover regions in remote sensing imagery and compared with the standard SVM. Experimental results confirm that employing this learning scheme removes unnecessary points to a great extent from the unlabeled set and increases the accuracy level on the other hand. Comparison is made in terms of accuracy, ROC, AUC and F-measure for the labeled data and quantitative cluster validity indices as well as classified image quality for the image data.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Plaza A, Benediktsson JA, Boardman JW, Brazile J, Bruzzone L, Cams-Valls G, Chanussort J, Fauvel M, Gamba P, Gualtieri A, Marconcini M, Tilton JC, Trianni G (2009) Recent advances in techniques for hyperspectral image processing. Remote Sens Environ 113:5110–5122
Bandyopadhyay S, Pal SK (2001) Pixel classification using variable string genetic algorithms with chromosome differentiation. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39(2):303–308
Bandyopadhyay S, Maulik U, Mukhopadhyay A (2007) Multiobjective genetic clustering for pixel classification in remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 45(5):1506–1511
Bandyopadhyay S, Maulik U (2002) Genetic clustering for automatic evolution of clusters and application to image classification. Pattern Recognit 35(2):1197–1208
Baraldi A, Bruzzone L, Blonda P (2005) Quality assessment and cluster maps without ground truth knowledge. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 43(4):857–873
Belkin M, Niyogi P, Sindhwani V (2004) Manifold regularization: a geometric framework for learning from examples. Technical Report TR 2004–06, University of Chicago
Bennett KP, Demiriz A (1998) Semi-supervised support vector machines. In: Proc. Adv. Neural Inform. Process Syst., vol 10, pp 368–374
Bezdek JC (1981) Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms. Plenum, New York
Bruzzone L, Chi M, Marconcini M (2006) A novel transductive SVM for semisupervised classification of remote-sensing images. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 44(11):3363–3373
Burges CJC (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Knowl Discov Data Min 2:121–167
Camps-Valls G, Bandos T, Zhou D (2007) Semi-supervised graph-based hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 45(10):3044–3054
Chen Y, Wang G, Dong S (2003) Learning with progressive transductive support vector machine. Pattern Recognit Lett 34(12):1845–1855
Chi M, Bruzzone L (2005) A semilabeled-sample driven bagging technique for ill-posed classification problem. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens Lett 2(1):69–73
Chi M, Bruzzone L (2007) Semi-supervised classification hyperspectral images by SVMs optimized in the primal. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens Lett 45(6):1870–1880
Cingolani AM, Renison D, Cabido MR (2004) Mapping vegetation in a heterogeneous mountain range land using landsat data: an alternative method to define and classify land-cover units. Remote Sens Environ 92:84–97
Collobert R, Sinz F, Weston J, Bottou L (2006) Large scale transductive SVMs. J Mach Learn Res 7:1687–1712
Dempster A, Laird N, Rubin D (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc B 39:1–38
Hughes GF (1968) On the mean accuracy of statistical pattern recognition. IEEE Trans Inf Theory IT-14(1):55–63
Joachims T (1999) Transductive inference for text classification using support vector machines. In: Proc. ICML, pp 200–209
Liu Z, Wu Q, Zhang U, Philip Chen CL (2011) Adaptive least square support vector machines filter for hand tremor canceling in microsurgery. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 2:37–47
Maulik U, Bandyopadhyay S (2002) Performance evaluation of some clustering algorithms and validity indices. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 24(12):1650–1654
Merz CJ, Murphy PM, Aha DW (1997) UCI repository of machine learning databases. Department of Information and Computer Science, University of California, Irvine, CA. http://www.ics.uci.edu/mlearn/∼MLRepository.html
Nigam K, McCallum A, Thrun S, Mitchell TM (1998) Learning to classify text from labeled and unlabeled documents. In: AAAI/IAAI, 792
Pontil M, Verri A (1998) Support vector machines for 3-D object recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 20:637–646
van Rijsbergen CJ (1979) Information retireval. Butterworths, London
Scholkopf B, Kah-Kay C, Burges CJC, Girosi F, Niyogi P, Poggio T, Vapnik V (1997) Comparing support vector machines with gaussian kernels to radial basis fuction classifiers. IEEE Trans Signal Process 45:2758–2765
Shahshahani BM, Landgrebe DA (1994) The effect of unlabeled samples in reducing the small sample size problem and mitigating the Hughes phenemenon. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 32(5):1087–1095
Small K, Roth D (2010) Margin based active learning for structure predictions. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 1:3–25
Tadjudin S, Landgrebe DA (2000) Robust parameter estimation for mixture model. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 38(1):439–445
Vapnik V (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Vapnik V (1999) The nature of statistical learning theory. 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Wan V, Campbell WM (2000) Support vector machines for speaker verification and Identification. In: Proceedings IEEE Workshop Neural Networks for signal procesings, Sydney, Australia, pp 775–784
Xie XL, Beni G (1991) A validity measure for fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intel 13:841–847
Zhang S, McCullagh P, Nugent C, Zheng H, Baumgarten M (2011) Optimal model for posture recognition in home-based healthcare. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 2:1–14
Zhu X, Ghahramani Z, Lafferty J (2003) Semisupervised learning using Gaussian fields and harmonic functions. In: ICML-05, 20th International Conference on Machine Learning
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maulik, U., Chakraborty, D. A novel semisupervised SVM for pixel classification of remote sensing imagery. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 3, 247–258 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-011-0059-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-011-0059-3