Abstract
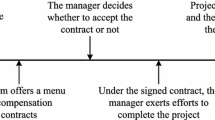
This paper discusses an optimal contracting problem between a principal and an agent by establishing an uncertain agency model. Compared with the existing work, this research focuses on the risk cost caused by the wrong investment in a task based on an inaccurate assessment about the potential output. To avoid it, the principal authorizes the professional agent to make a more accurate assessment about the output in the light of his professional knowledge and experience, and then to show the principal the optimal amount invested in the task. Meanwhile, as an incentive for the agent to pay great forecasting effort to make the more accurate assessment about the output, the principal provides the agent with a revenue-sharing contract including a sharing ratio for him. On this view, this paper proposes the optimal revenue-sharing contract that provides guidance for the two participators to make their respective optimal decisions. Furthermore, the proposed work is supported with the numerical results by analyzing the evolutions of the optimal contract under various influencing factors.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Ali MS (2014) Robust stability of stochastic uncertain recurrent neural networks with Markovian jumping parameters and time-varying delays. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 5(1): 13–22
Berle AA, Means CC (1932) The modern corporation and private property. Macmillan, New York
Cachon GP, Lariviere MA (2005) Supply chain coordination with revenue-sharing contracts: strengths and limitations. Manag Sci 51(1):30–44
Cui LX, Zhao RQ, Tang WS (2007) Principal-agent problem in a fuzzy environment. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15(6):1230–1237
De Kok AG, Graves SC (2003) Supply chain management: design, coordination and operation. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Dubois D, Prade H (1988) Possibility theory: an approach to computerized processing of uncertainty. Plenum, New York
Giannoccaro I, Pontrandolfo P (2004) Supply chain coordination by revenue sharing contracts. Int J Prod Econ 89(2):131–139
Gilbert SM, Weng ZK (1998) Incentive effects favor non consolidating queues in a service system: the principal-agent perspective. Manag Sci 44(12):1662–1669
Groves T (1973) Incentives in teams. Econometrica 41(4):617–631
Guesnerie R, Laffont JJ (1984) A complete solution to a classical of principal-agent problems with an application to the control on a self-managed firm. J Public Econ 25:329–369
Holmstrom B (1979) Moral hazard and observability. Bell J Econ 10(1):74–91
Jensen MC, Meckling WH (1976) Theory of the firm: managerial behavior, agency costs and ownership structure. J Fin Econ 3(4):305–360
Kunter M (2012) Coordination via cost and revenue sharing in manufacturerCretailer channels. Eur J Oper Res 216(2):477–486
Laffont J, Martimort D (2002) The theory of incentives: the principal-agent model. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Lan YF, Du HB (2013) A warranty contract model with uncertain demands. Inform Int Interdisc J 16(2): 1037–1045
Lan YF, Liu YK, Sun GJ (2010) An approximation-based approach for fuzzy multi-period production planning problem with credibility objective. Appl Math Model 34(11):3203–3215
Lan YF, Zhao RQ, Tang WS (2011) A bilevel fuzzy principal-agent model for optimal nonlinear taxation probelms. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 10(3):211–232
Lan YF, Zhao RQ, Tang WS (2011) Minimum risk criterion for uncertain production planning problems. Comput Ind Eng 61(3):591–599
Lan YF, Zhao RQ, Tang WS (2013) A yardstick competition approach to a multi-firm regulation problem under asymmetric information. J Comput Appl Math 249: 24–36
Liu B (2010) Uncertainty theory: a branch of mathematics for modeling human uncertainty. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Liu B (2013) Uncertainty theory, 4th ed.. http://orsc.edu.cn/liu/ut.pdf, Beijing
Liu B, Liu YK (2002) Expected value of fuzzy variable and fuzzy expected value models. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 10(4):445–450
Liu YH, Ha MH (2010) Expected value of function of uncertain variables. J Uncertain Syst 4(3):181–186
Mirrlees J (1974) Notes on welfare economics, information and uncertainty. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Mirrlees J (1976) The optimal structure of authority and incentives within an organization. Bell J Econ 7(1):105–131
Nahmias S (1978) Fuzzy variables. Fuzzy Sets Syst 1(2):97–110
Palsule-Desai OD (2013) Supply chain coordination using revenue-dependent revenue sharing contracts. Omega 41(4):780–796
Patrick B, Mathias D (2005) Contract theory. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, London
Ross S (1973) The economic theory of agency: the principal’s problem. Am Econ Rev 63(2):134–139
Mu R, Lan YF, Tang WS (2013) An uncertain contract model for rural migrant worker’s employment problems. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 12(1):29–39
She YH, He XL (2013) Uncertainty measures in rough algebra with applications to rough logic. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. doi: 10.1007/s13042-013-0206-0
Spence M, Zechhauser R (1971) Insurance, information and individual action. Am Econ Rev 61(2):380–387
Sun GJ, Liu YK, Lan YF (2010) Optimizing material procurement planning problem by two-stage fuzzy programming. Comput Ind Eng 58(1):97–107
Wang GL, Tang WS, Zhao RQ (2013) An uncertain price discrimination model in labor market. Soft Comput 17(4):579–585
Wang XS, Gao ZC, Guo HY (2012) Delphi method for estimating uncertainty distributions. Inform Int Interdisc J 15(2):449–459
Wang XZ, Dong LC, Yan JH (2012) Maximum ambiguity based sample selection in fuzzy decision tree induction. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(8): 1491–1505
Wang XZ, He YL, Wang DD (2014) Non-naive bayesian classifiers for classification problems with continuous attributes. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(1): 21–39
Wilson R (1969) The structure of incentive for decentralization under uncertainty. La Decision, Paris
Yao Z, Leungb S, Lai KK (2008) Manufacturer’s revenue-sharing contract and retail competition. Eur J Oper Res 186(2):637–651
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inform Control 8:338–353
Acknowledgment
This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 71271151 and No. 71301114, and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education under Grant No. 20130032110015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Lan, Y. & Liu, H. Optimal revenue-sharing contract based on forecasting effort for uncertain agency problem. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 5, 971–979 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-014-0243-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-014-0243-3