Abstract
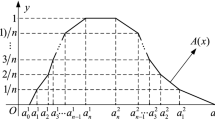
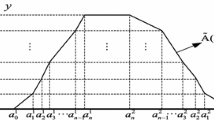
As a generalization of ladder fuzzy numbers, the polygonal fuzzy numbers can be approximately represented by a group of ordered real numbers, it not only keeps the closeness of arithmetic operations, and also inherits some excellent properties of ladder fuzzy numbers. To modify defects of the definition of the original polygonal fuzzy numbers, the method of an equidistant subdivision is firstly introduced, and the specific algorithm of general fuzzy numbers into the polygonal fuzzy numbers by two examples is explained in detail. Secondly, using the extension operations of polygonal fuzzy numbers, a polygonal fuzzy neural network is constructed by mathematical methods, and the coefficients transform formulas of the new network are obtained. In addition, it is also proved that the new network still possesses approximation with respect to a continuous polygonal fuzzy valued function. Finally, the approximation algorithm and realization process of the polygonal fuzzy neural networks to a two-polygonal fuzzy valued function are given by means of an example.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buckley JJ, Hayashi Y (1994) Can fuzzy neural nets approximate continuous fuzzy functions. Fuzzy Sets Syst 61(1):43–51
Feuring T, Lippe WM (1999) The fuzzy neural network approximation lemma. Fuzzy Sets Syst 102(2):227–237
Chung FL, Duan JC (2000) On multistage fuzzy neural network modeling. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8:125–142
Liu PY, Wang H (1999) Approximation capability of regular fuzzy neural networks to continuous fuzzy functions. Sci China Ser E 29(1):54–60
Liu PY (2000) Analyses of regular fuzzy neural networks for approximation capability. Fuzzy Sets Syst 114(3):329–338
Liu PY (2001) Universal approximation of continuous analyses fuzzy valued functions by multi-layer regular fuzzy neural networks. Fuzzy Sets Syst 119(2):313–320
Zhao FX, Li HX (2004) Approximation of regular fuzzy neural networks in sense integral norm. Prog Nat Sci 14(9):1025–1031
Wang GJ, Li D (2013) Capability of universal approximation of feed forward regular fuzzy neural networks in K-int egral norm. Acta Math Appl Sin 36(1):141–152
Liu PY (2002) A new Fuzzy neural network and its approximation capability. Sci China Ser F 32(1):76–86
Liu PY, Li HX (2007) Symmetric polygonal fuzzy number space. J Fuzzy Math 15(1):27–42
He CM, Ye YP (2011) Evolution Computation based learning algorithms of polygonal fuzzy neural networks. Int J Intell Syst 26(4):340–352
Wang GJ, Li XP (2011) Universal approximation of polygonal fuzzy neural networks in sense of K-integral norms. Science China. Inf Sci 54(11):2307–2323
Báez-Sánchez AD, Morettib AC, Rojas-Medar MA (2012) On polygonal fuzzy sets and numbers. Fuzzy Sets Syst 209:54–65
Wang GJ, Li XP (2014) Construction of the polygonal fuzzy neural network and its approximation based on K-integral norm. Neural Netw World 24(4):357–376
Wang GJ, He Y, Li XP (2015) Optimization algorithms for MISO polygonal fuzzy neural networks science China. Inf Sci 45(5):650–667
He Y, Wang GJ (2012) Conjugate gradient algorithm of the polygonal fuzzy neural networks. Acta Electron Sin 40(10):2079–2084
Sui XL, Wang GJ (2012) Influence of perturbations of training pattern pairs on stability of polygonal fuzzy neural network. Pattern Recog Artif Intell 25(6):928–936
Mahdavi I, Mahdavi-Amiri N, Nejati S (2011) Algorithms for biobjective shortest path problems in fuzzy networks. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 8(4):9–37
Llanas B, Sainz FJ (2006) Constructive approximate interpolation by neural networks. J Comput Appl Math 182(2):283–308
Lin D, Liu HJ, Song H, Zhang FC (2014) Fuzzy neural control of uncertain chaotic systems with backlash nonlinearity. Int J Mach Learn Cybernet 5(5):721–728
Castro JR, Castillo O, Melin P et al (2009) A hybrid learning algorithm for a class of interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks. Inf Sci 179(13):2175–2193
Diamond P, Kloeden P (1994) Metric spaces of fuzzy sets. World Scientific Press, Singapore
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work has been supported by National Natural Science Foundation China (Grant No. 61374009).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Li, D. The structure and realization of a polygonal fuzzy neural network. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 7, 375–389 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-015-0391-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-015-0391-0