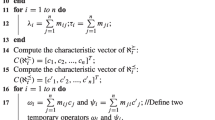Abstract
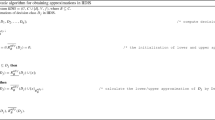
With the development of information technology and the rapid updating of data sets, the object sets in an information system may evolve in time when new information arrives and redundancy information leaves in real life. Interval-valued decision information systems are important type of data decision tables and generalized models of single-valued information systems. Fast updating the lower and upper approximations is the core technology of knowledge discovery that is based rough set theory in dynamic data environment. Consequently, in this paper we focus on incremental approaches updating approximations with dynamic data sets in interval-valued decision system. Firstly, we define an interval similarity degree by which a binary relation can be constructed, followed a rough set model be established. Then, incremental approaches for updating approximations are proposed and the incremental algorithms are shown. At last, comparative experiments on several UCI data sets show the proposed incremental updating methods are efficient and effective for dynamic data sets, namely, these approaches significantly outperform the classical methods with a dramatic reduction in the computational time.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bang WC, Bien Z (1999) New incremental learning algorithm in the framework of rough set theory. Int J Fuzzy Syst 1:25–36
Chan CC (1998) A rough set approach to attribute generalization in data mining. Inf Sci 107(1–4):169–176
Chen HM, Li TR, Qiao SJ, Ruan D (2010) A rough set based dynamic maintenance approach for approximations in coarsening and refining attribute values. Int J Intell Syst 25(10):1005–1026
Chen HM, Li TR, Ruan D (2012) Maintenance of approximations in incomplete ordered decision systems while attribute values coarsening or refining. Knowl Based Syst 31:140–161
Chen HM, Li TR, Ruan D, Lin JH, Hu CX (2013) A rough-set based incremental approach for updating approximations under dynamic maintenance environments. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25:274–284
Dai JH, Wang WT, Xu Q, Tian HW (2012) Uncertainty measurement for interval-valued decision systems based on extended conditional entropy. Knowl Based Syst 27:443–450
Gong ZT, Sun BZ, Chen DG (2008) Rough set theory for the interval-valued fuzzy information systems. Inf Sci 178:1968–1985
Leung Y, Fischer MM, Wu WZ, Mi JS (2008) A rough set approach for the discovery of classification rules in interval-valued information systems. Int J Approx Reason 47:233–246
Li HX, Wang MH, Zhou XZ, Zhao JB (2012) An interval set model for learning rules from incomplete information table. Int J Approx Reason 53:24–37
Li TR, Ruan D, Geert W (2007) A rough sets based characteristic relation approach for dynamic attribute generalization in data mining. Knowl Based Syst 20:485–494
Li TR, Ruan D, Song J (2007) Dynamic maintenance of decision rules with rough set under characteristic relation. In: Wireless communications, networking and mobile computing, pp 3713–3716
Liu D, Li TR, Ruan D, Zou WL (2009) An incremental approach for inducing knowledge from dynamic information systems. Fundam Inf 94:245–260
Liu D, Li TR, Ruan D, Zhang JB (2011) Incremental learning optimization on knowledge discovery in dynamic business intelligent systems. J Global Optim 51:325–344
Liu D, Li TR, Zhang JB (2014) A rough set-based incremental approach for learning knowledge in dynamic incomplete information systems. Int J Approx Reason 55:1764–1786
Liu D, Li TR, Zhang JB (2015) Incremental updating approximations in probabilistic rough sets under the variation of attributes. Int J Knowl Based Syst 73:81–96
Li SY, Li TR, Liu D (2013) Dynamic maintenance of approximations in dominance-based rough set approach under the variation of the object set. Int J Intell Syst 28:729–751
Luo C, Li TR, Chen HM, Liu D (2013) Incremental approaches for updating approximations in set-valued ordered information systems. Int J Knowl Based Syst 50:218–233
Li JH, Mei CL, Lv YJ (2011) Knowledge reduction in decision formal contexts. Knowl Based Syst 24:709–715
Li JH, Mei CL, Lv YJ (2012) Knowledge reduction in real decision formal contexts. Inf Sci 189:191–207
Lu SX, Wang XZ, Zhang GQ, Zhoua X (2015) Effective algorithms of the Moore–Penrose inverse matrices for extreme learning machine. Intell Data Anal 19(4):743–760
Miao DQ, Zhang N, Yue XD (2009) Knowledge reduction in interval-valued information systems. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE international conference on cognitive informatics, pp 320–327
Moore RE (1966) Interval analysis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11:341–356
Pawlak Z (1991) Rough sets: theoretical aspects of reasoning about data. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Pawlak Z (1998) Rough set theory and its applications to data analysis. Cybern Syst 29:661–688
Qian YH, Liang JY, Dang CY (2008) Interval ordered information systems. Comput Math Appl 56:1994–2009
Shan N, Ziarko W (1995) Data-based acquisition and incremental modification of classification rules. Comput Intell 11(2):357–370
Sun BZ, Gong ZT, Chen DG (2008) Fuzzy rough set theory for the interval-valued fuzzy information systems. Inf Sci 178:2794–2815
Wang XZ, Aamir R, Fu AM (2015) Fuzziness based sample categorization for classifier performance improvement. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 29:1185–1196
Wang R, Kwon S, Wang XZ, Jiang QS (2015) Segment based decision tree induction with continuous valued attributes. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(7):1262–1275
Wang XZ, Xing HJ, Li Y et al (2015) A study on relationship between generalization abilities and fuzziness of base classifiers in ensemble learning. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 23(5):1638–1654
Wang XZ (2015) Uncertainty in learning from big data-editorial. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 28(5):2329–2330
Yang XB, Yu DJ, Yang JY, Wei LH (2009) Dominance-based rough set approach to incomplete interval-valued information system. Data Knowl Eng 68:1331–1347
Yang XB, Qi Y, Yu DJ, Yu HL, Yang JY (2015) \(\alpha\)-Dominance relation and rough sets in interval-valued information systems. Inf Sci 294:334–347
Yao YY (1993) Interval-set algebra for qualitative knowledge representation. In: Proceedings of the 5th international conference on computing and information, pp 370–375
Yao YY, Li XN (1996) Comparison of rough-set and interval-set models for uncertain reasoning. Fundam Inf 27:289–298
Yao YY (2009) Interval sets and interval-set algebras. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE international conference on cognitive informatics, pp 307–314
Yang HZ, Yee L, Shao MW (2011) Rule acquisition and attribute reduction in real decision formal contexts. Soft Comput 15:1115–1128
Zhang HY, Su YJ (2007) A ranking approach with inclusion measure in multiple-attribute interval-valued decision making. In: RSFDGrC, LNAI, vol 4482, pp 411–418
Zhang JB, Li TR, Ruan D, Liu D (2012) Neighborhood rough sets for dynamic data mining. Int J Intell Syst 27(4):317–342
Zhang WX, Wu WZ, Liang JY, Li DY (2001) Theory and method of rough sets. Science Press, Beijing
Zhang X, Mei CL, Chen DG, Li JH (2014) Multi-confidence rule acquisition and confidence-preserved attribute reduction in interval-valued decision systems. Int J Approx Reason 55:1787–1804
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank the valuable suggestions from the anonymous referees and the editor in chief for improving the quality of the paper. This work is supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61105041, No. 61472463, No. 61402064), National Natural Science Foundation of CQ CSTC (No. cstc 2013jcyjA40051, cstc2015jcyjA40053), Key Laboratory of Intelligent Perception and Systems for High-Dimensional Information (Nanjing University of Science and Technology), Ministry of Education (No. 30920140122006), Key Laboratory of Oceanographic Big Data Mining and Application of Zhejiang Province (No.OBDMA201503), and Graduate Innovation Foundation of Chongqing University of Technology (No.YCX2015227, YCX2014236), and Graduate Innovation Foundation of CQ (No.CYS15223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Xu, W. Incremental knowledge discovering in interval-valued decision information system with the dynamic data. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 8, 849–864 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-015-0473-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-015-0473-z