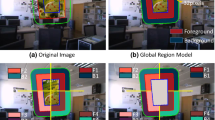
Abstract
Building a robust and fully automatic framework for human motion tracking in 2D images and videos remains a challenging task in computer vision due to cluttered backgrounds, self-occlusions, variations of body shape and complexities of human postures. In this paper we propose a robust framework for human motion tracking without motion priors. The proposed framework builds an accurate/uncontaminated specific appearance model and then tracks the target’s postures with this specific appearance model. The main contribution of this work is a novel process to build an accurate appearance model by identifying non-target pixels and removing them. In addition, for the goal of tracking in multiple scales, a novel strategy for scale evaluation and adjustment is proposed to adaptively change the scale values during the tracking process. Experiments show that the accurate specific appearance model outperforms existing work, and the proposed tracking system is able to successfully track challenging sequences with different appearances, motions, scales and angles of view.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Poppe R (2007) Vision-based human motion analysis: an overview. Comput Vis Image Underst 108(1C2), 4–18
Zhou H, Hu H (2008) Human motion tracking for rehabilitationła survey. Biomed Signal Process Control 3(1):1–18
Ramanan D, Forsyth DA, Zisserman A (2007) Tracking people by learning their appearance. Pattern analysis and machine intelligence. IEEE Trans 29(1):65–81
Okuma K, Taleghani A, De Freitas N, Little JJ, Lowe DG (2004) A boosted particle filter: multitarget detection and tracking in ECCV. Springer, Berlin, pp 28–39
Lu Y, Li L, Peursum P (2012) Human pose tracking based on both generic and specific appearance models. ICARCV
Lu Y, Li L, Peursum P (2012) Background suppression for building accurate appearance models in human motion tracking. DICTA
Tian J, Li L, Liu W (2014) Multi-scale human pose tracking in 2D monocular images. J Comput Commun 2:78
Sigal L, Balan AO, Black MJ (2010) Humaneva: synchronized video and motion capture dataset and baseline algorithm for evaluation of articulated human motion. Int J Comput Vis 87(1):4–27
Sidenbladh H, Black M, Sigal L (2002) Implicit probabilistic models of human motion for synthesis and tracking. ECCV, pp 784–800
Sidenbladh H, Black M, Fleet D (2000) Stochastic tracking of 3D human figures using 2d image motion. ECCV, pp 702–718
Fablet R, Black MJ (2002) Automatic detection and tracking of human motion with a view-based representation in ECCV. Springer, Berlin, pp 476–491
Deutscher J, Blake A, Reid I (2000) Articulated body motion capture by annealed particle filtering in CVPR, vol 2. IEEE, pp 126–133
Kaliamoorthi P, Kakarala R (2013) Parametric annealing: a stochastic search method for human pose tracking. Pattern Recognit 46(5), 1501–1510 [Online]. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031320312004669
Bai T, Li Y (2012) Robust visual tracking with structured sparse representation appearance model. Pattern Recognit 45(6):2390–2404
Sullivan J, Carlsson S (2002) Recognizing and tracking human action in ECCV. Springer, Berlin, pp 629–644
Song Y, Feng X, Perona P (2000) Towards detection of human motion in CVPR, vol 1. IEEE, pp 810–817
Viola P, Jones MJ, Snow D (2005) Detecting pedestrians using patterns of motion and appearance. Int J Comput Vis 63(2):153–161
Ponce J, Forsyth D, Willow E-P, Antipolis-Méditerranée S (2011) R. d’activité RAweb, L. Inria, and I. Alumni. Comput vision: a modern approach. Computer 16:11
Fischler MA, Elschlager RA (1973) The representation and matching of pictorial structures. Comput IEEE Trans 100(1):67–92
Felzenszwalb PF, Huttenlocher DP (2005) Pictorial structures for object recognition. Int J Comput Vis 61(1):55–79
Andriluka M, Roth S, Schiele B (2009) Pictorial structures revisited: people detection and articulated pose estimation in CVPR. IEEE, pp 1014–1021
Andriluka M, Roth S, Schiele B (2012) Discriminative appearance models for pictorial structures. Int J Comput Vis 1–22
Mori G, Ren X, Efros AA, Malik J (2004) Recovering human body configurations: combining segmentation and recognition in CVPR, vol 2. IEEE, pp II-326
Ramanan D (2007) Learning to parse images of articulated bodies. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 19:1129
Ferrari V, Marín-Jiménez M, Zisserman A (2009) 2D human pose estimation in tv shows. Stat Geometr Approach Vis Motion Anal 128–147
Artner NM, Ion A, Kropatsch WG (2011) Reprint of: multi-scale 2d tracking of articulated objects using hierarchical spring systems. Pattern Recognit 44(9):1969–1979
Comaniciu D, Meer P (2002) Mean shift: a robust approach toward feature space analysis. Pattern Anal Mach Intell IEEE Trans 24(5):603–619
Ferrari V, Marin-Jimenez M, Zisserman A (2008) Progressive search space reduction for human pose estimation in CVPR 2008. IEEE Conference on. IEEE, pp 1–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, J., Lu, Y., Li, L. et al. Tracking human poses in various scales with accurate appearance. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 8, 1667–1680 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0537-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0537-8