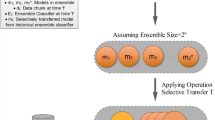
Abstract
We present an ensemble system, recurring dynamic weighted majority (RDWM) that maintains two ensembles of experts, so as to accurately handle drifting concepts mainly recurrent drifts. The primary online ensemble represents the present concepts and the secondary ensemble represents the old concepts since the beginning of learning. An effective pruning methodology helps to remove redundant and old classifiers, which may have otherwise caused interference in learning the new concepts. Experimental evaluation using datasets proves that RDWM achieves very high generalization accuracy, irrespective of the speed or severity of drift; or presence of noise in the dataset.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Baena-Garcia M, Campo-Avila JD, Fidalgo R, Bifet A (2006) Early drift detection method. In: Proc. 4th ECML PKDD Int’l Workshop Knowled. Discovery from Data Streams, pp 77–86
Bifet A, Holmes G, Kirkby R, Pfahringer B (2010) MOA: massive online analysis, a framework for stream classification and clustering, JMLR: workshop and conference proceedings, vol 11, p 44
Gama J, Žliobaitė I, Bifet A, Pechenizkiy M, Bouchachia A (2014) A survey on concept drift adaptation. ACM Comput Surv 46(4):1–37
Dawid A, Vovk V (1999) Prequential probability: principles and proper ties. Bernoulli 5(1):125–162
Dietterich TG (1997) Machine learning research: four current directions. Artif Intell 18(4):97–136
Gama J, Medas P, Castillo G, Rodrigues P (2004) Learning with drift detection, SBIA’04, pp 286–295
Patrick PK, Yeung DS, Ng WWY et al (2012) Dynamic fusion method using localized generalization error model. Inf Sci 217:1–20
Harries M (1999) Splice-2 comparative evaluation: electricity pricing, Technical report. University of New South Wales, Australia, July 1999
Hulten G, Spencer L, Domingos P (2001) Mining time-changing data streams. KDD, San Francisco, pp 97–106
Garcı´a S, Ferna´ndez A, Luengo J et al (2010) Advanced nonparametric tests for multiple comparisons in the design of experiments in computational intelligence and data mining: experimental analysis of power. Inf Sci 180(10):2044–2064
Ramamurthy S, Bhatnagar R (2007) Tracking recurrent concept drift in streaming data Using ensemble classifiers. ICMLA’07, pp 404–409
Kolter JZ, Maloof MA (2007) Dynamic weighted majority: an ensemble method for drifting concepts. JMLR 8:2755–2790
Littlestone N, Warmuth M (1994) The weighted majority algorithm. Inform Comput 108:212–261
Oza N, Russell S (2001) Online bagging and boosting. In: Artificial intelligence and statistics 2001”. Morgan Kaufmann, pp 105–112
Gomes J, Menasalvas E, Sousa P (2011) Learning recurring concepts from data streams with a context-aware ensemble. In: ACM Symp. on Applied Computing, pp 994–999
Minku LL, Yao X (2012) DDD: a new ensemble approach for dealing with concept drift. ITKDE 24(4):619
Demsar J (2006) Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J Mach Learn Res 7:1–30
Nishida K, Yamauchi K (2007) Adaptive classifiers-ensemble system for tracking concept drift. In: ICMLC’07, pp 3607–3612
Kumar Y, Sahoo G (2015) Hybridization of magnetic charge system search and particle swarm optimization for efficient data clustering using neighborhood search strategy. Soft Comput 19(12):3621–3645
Nishida K, Yamauchi K, Omori T (2005) ACE: Adaptive classifiers-ensemble system for concept-drifting environments. In: 6th Int’l Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems, ser. LNCS, vol 3541, pp 176–185
Oza NC, Russell S (2001) Experimental comparisons of online and batch versions of bagging and boosting. In: Proc. of Seventh ACM SIGKDD’01. ACM, NY, pp 359–364
Bach SH, Maloof MA (2008). Paired learners for concept drift. ICDM’08, Los Alamitos, pp 23–32
Bifet A, Gavaldà R (2007) Learning from time-changing data with adaptive windowing. In: SDM’07. SIAM, Florida, pp 443–448
Kumar Y, Sahoo G (2015) A two-step artificial bee colony algorithm for clustering. NCAA, pp 1–15
Zhu X (2010) Stream data mining repository. http://www.cse.fau.edu/~xqzhu/stream.html. Accessed 13 Mar 2016
Schlimmer JC, Granger RH (1986) Incremental learning from noisy data. Mach Learn 1(3):317–354
Alippi C, Boracchi G, Roveri M (2013) Just-in-time classifiers for recurrent concepts. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 24(4):620–634
Hosseini M, Ahmadi Z, Beigy H (2013) Using a classifier pool in accuracy based tracking of recurring concepts in data stream classification. ES 4:43–60
Gama J, Sebastiao R, Rodrigues PP (2009) Issues in evaluation of stream learning algorithms. In: ACM SIGKDD’09, pp 329–338
Sidhu P, Bhatia MPS (2015) A novel online ensemble approach to handle concept drifting data streams: diversified dynamic weighted majority, IJMLC. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Asuncion A, Newman DJ (2007) UCI machine learning repository. University of California, Irvine
Gama J, Sebastião R, Rodrigues PP (2009) Issues in evaluation of stream learning algorithms. In: KDD’09, pp 329–338
Daniel, Wayne W (1990). Friedman two-way analysis of variance by ranks. Applied nonparametric statistics, 2nd edn. PWS-Kent, Boston, pp 262–274. ISBN 0-534-91976-6
The UCI KDD (1999) Archive. http://mlr.cs.umass.edu/ml/databases /kddcup99/kddcup99.html. Accessed 10 May 2016
Wang X-z, Xing H-J, Li Y et al (2015) A study on relationship between generalization abilities and fuzziness of base classifiers in ensemble learning. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 23(5):1638–1654
Wang X, Rana A, Ai-Min F (2015) Fuzziness based sample categorization for classifier performance improvement. JIFS 29:1185–1196
Ashfaq RAR, Wang XZ, Huang JZ, Abbas H, He YL (2017) Fuzziness based semi-supervised learning approach for intrusion detection system., Inf Sci 378:484–497
Khan I, Huang JZ, Ivanov K (2016) Incremental density-based ensemble clustering over evolving data streams. Neurocomputing 191:34–43. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.01.009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sidhu, P., Bhatia, M.P.S. A two ensemble system to handle concept drifting data streams: recurring dynamic weighted majority. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 10, 563–578 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0738-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0738-9