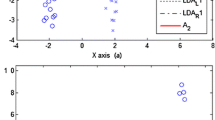
Abstract
Conventional linear discriminant analysis methods commonly ignore the information loss and locality preserving, which greatly limits their performance. To address these issues, we propose a novel discriminant analysis method for feature extraction in this paper. Specially, the proposed method simultaneously exploits the local information and label information to guide the projection learning by constraining the margins of samples from the same class with an adaptively learned weighted matrix, which enables the method to obtain a more compact and discriminative projection. To catch as much discriminant information as possible, a variant of principle component analysis (PCA) term is further introduced to constrain the projection. Besides, to reduce the negative influence of noise and redundant features, a spares error term and a sparse projection constraint are simultaneously introduced to the framework, which enables the method to adaptively select those important features during feature extraction. Compared with the other methods, the proposed method simultaneously holds many good properties including discriminability, locality, data reconstruction, and feature selection in a framework, and is robust to noise. These good properties encourage the method to perform better than the other methods. Extensive experimental results conducted on face, object, scene, and noisy databases verify the effectiveness of the proposed in feature extraction.






Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Notes
Available at http://www2.ece.ohio-state.edu/~aleix/ARdatabase.html.
Available at http://www.ri.cmu.edu/projects/project_418.html.
References
Lai Z, Wan M, Jin Z, Yang J (2011) Sparse two-dimensional local discriminant projections for feature extraction. Neurocomputing 74(4):629–637
Lai Z, Mo D, Wong WK, Xu Y, Miao D, Zhang D (2017) Robust discriminant regression for feature extraction. IEEE Trans Cybern 48:2472–2484
Liu Q, Lu X, He Z, Zhang C, Chen W-S (2017) Deep convolutional neural networks for thermal infrared object tracking. Knowl Based Syst 134:189–198
Sun F, Yao Y, Li X (2018) The heat and mass transfer characteristics of superheated steam coupled with non-condensing gases in horizontal wells with multi-point injection technique. Energy 143:995–1005
Luo G, Dong S, Wang K, Zuo W, Cao S, Zhang H (2017) Multi-views fusion cnn for left ventricular volumes estimation on cardiac mr images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 9:1924–1934
Fei L, Lu G, Jia W, Teng S, Zhang D (2018) Feature extraction methods for palmprint recognition: a survey and evaluation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2018.2795609
Fang X, Yong X, Li X, Lai Z, Teng S, Fei L (2017) Orthogonal self-guided similarity preserving projection for classification and clustering. Neural Netw 88:1–8
Lai Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Shen L, Zhang D (2016) Rotational invariant dimensionality reduction algorithms. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(11):3733–3746
Sun F, Yao Y, Chen M, Li X, Zhao L, Meng Y, Sun Z, Zhang T, Feng D (2017) Performance analysis of superheated steam injection for heavy oil recovery and modeling of wellbore heat efficiency. Energy 125:795–804
Lu Y, Yuan C, Lai Z, Li X, Wong WK, Zhang D (2017) Nuclear norm-based 2DLPP for image classification. IEEE Trans Multimed 19(11):2391–2403
Dong S, Luo G, Wang K, Cao S, Li Q, Zhang H (2018) A combined fully convolutional networks and deformable model for automatic left ventricle segmentation based on 3D echocardiography. BioMed Res Int 2018:5682365
Li J, Zhang B, Lu G, Ren H, Zhang D (2018) Visual classification with multikernel shared Gaussian process latent variable model. IEEE Trans Cybern (99): 1–14
Lu Y, Lai Z, Li X, Wong WK, Yuan C, Zhang D (2018) Low-rank 2-D neighborhood preserving projection for enhanced robust image representation. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2018.2815559
Wen J, Lai Z, Zhan Y, Cui J (2016) The L2, 1-norm-based unsupervised optimal feature selection with applications to action recognition. Pattern Recogn 60:515–530
Lu Y, Yuan C, Li X, Lai Z, Zhang D, Shen L (2018) Structurally incoherent low-rank 2DLPP for image classification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2018.2849757
Zhang L, Han J, Deng S (2018) Unsupervised temporal feature learning based on sparse coding embedded BoAW. In: Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH, 3284–3288
Turk M, Pentland A (1991) Eigenfaces for recognition. J Cognit Neurosci 3(1):71–86
Li L, Liu S, Peng Y, Sun Z (2016) Overview of principal component analysis algorithm. Opt Int J Light Electron Opt 127(9):3935–3944
He X, Niyogi P (2004) Locality preserving projections. In: Proceedings of the advances in neural information processing systems, 153–160
He X, Cai D, Yan S, Zhang H-J (2005) Neighborhood preserving embedding [C]. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 1208–1213
Wong WK, Lai Z, Wen J, Fang X, Lu Y (2017) Low-rank embedding for robust image feature extraction [J]. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(6):2905–2917
Camps-Valls G, Marsheva TVB, Zhou D (2007) Semi-supervised graph-based hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 45(10):3044–3054
Fang X, Yong X, Li X, Lai Z (2016) Robust semi-supervised subspace clustering via non-negative low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(8):1828–1838
Sun F, Yao Y, Li X, Yu P, Zhao L, Zhang Y (2017) A numerical approach for obtaining type curves of superheated multi-component thermal fluid flow in concentric dual-tubing wells. Int J Heat Mass Transf 111:41–53
Fei L, Xu Y, Fang X, Yang J (2017) Low rank representation with adaptive distance penalty for semi-supervised subspace classification. Pattern Recogn 67:252–262
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Shao L, Yang J (2017) Discriminative block-diagonal representation learning for image recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 1:1–16
Fei L, Lu G, Jia W, Wen J, Zhang D (2018) Complete binary representation for 3-D palmprint recognition. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 67(12):2761–2771
Li J, Zhang B, Lu G, Zhang D (2019) Generative multi-view and multi-feature learning for classification. Inf Fus 45:215–226
Zhang Z, Shao L, Xu Y, Liu L, Yang J (2018) Marginal representation learning with graph structure self-adaptation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 29(10):4645–4659
Li L, Peng Y, Qiu G, Sun Z, Liu S (2018) A survey of virtual sample generation technology for face recognition. Artif Intell Rev 50(1):1–20
Li J, Zhang B, Zhang D (2017) Shared autoencoder Gaussian process latent variable model for visual classification. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst
Peng Y, Li L, Liu S, Li J, Wang X, Extended sparse representation-based classification method for face recognition [J]. Machine Vision and Applications 2018: 1–17
Izenman J (2013) Linear discriminant analysis, Springer, Berlin
Ma Z, Wen J, Liu Q, Tuo G (2015) Near-infrared and visible light image fusion algorithm for face recognition. J Mod Opt 62(9):745–753
Lai Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Tang J, Zhang D (2013) Sparse tensor discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(10):3904–3915
Yang J, Zhang D, Yong X, Yang J-y (2005) Two-dimensional discriminant transform for face recognition. Pattern Recogn 38(7):1125–1129
Lu Y, Yuan C, Lai Z, Li X, Zhang D, Wong WK (2018) Horizontal and vertical nuclear norm-based 2DLDA for image representation. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2018.2822761
Ye J, Janardan R, Li Q, Park H (2006) Feature reduction via generalized uncorrelated linear discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 18(10):1312–1322
Shi X, Yang Y, Guo Z, Lai Z (2014) Face recognition by sparse discriminant analysis via joint L 2,1 -norm minimization. Pattern Recogn 47(7):2447–2453
Li X, Hu W, Wang H, Zhang Z (2010) Linear discriminant analysis using rotational invariant L1 norm. Neurocomputing 73(13–15):2571–2579
Zheng W, Lin Z, Wang H (2014) L1-norm kernel discriminant analysis via Bayes error bound optimization for robust feature extraction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(4):793–805
Wang H, Lu X, Hu Z, Zheng W (2014) Fisher discriminant analysis with L1-norm. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(6):828–842
Clemmensen L, Hastie T, Witten D, Ersbøll B (2011) Sparse discriminant analysis. Technometrics 53(4):406–413
Zhang X, Chu D, Tan RCE (2016) Sparse uncorrelated linear discriminant analysis for undersampled problems. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(7):1469–1485
Zhou Y, Sun S (2016) Manifold partition discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(4):830–840
Yan S, Xu D, Zhang B, Zhang H-J, Yang Q, Lin S (2007) Graph embedding and extensions: a general framework for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29(1):40–51
Zhang T, Tao D, Yang J, (2008) Discriminative locality alignment. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, 725–738
Li X, Chen M, Nie F, Wang Q (2017) Locality adaptive discriminant analysis. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2201–2207
Wen J, Xu Y, Li Z, Ma Z, Xu Y (2018) Inter-class sparsity based discriminative least square regression. Neural Netw 102:36–47
Ma X, Liu Q, Ou W, Zhou Q (2018) Visual object tracking via coefficients constrained exclusive group LASSO. Mach Vis Appl 29: 1–15
Zhong Z, Zhang B, Lu G, Zhao Y, Xu Y (2017) An adaptive background modeling method for foreground segmentation. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 18(5):1109–1121
Zhang Z, Liu L, Shen F, Shen HT, Shao L (2018) Binary multi-view clustering. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell
Wen J, Fang X, Cui J, Fei L, Yan K, Chen Y, Xu Y (2018) Robust sparse linear discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2018.2799214
Zou H, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2006) Sparse principal component analysis. J Comput Graphical Stat 15(2):265–286
Xiang S, Nie F, Meng G, Pan C, Zhang C (2012) Discriminative least squares regression for multiclass classification and feature selection. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 23(11):1738–1754
Fang X, Yong X, Li X, Lai Z, Wong WK, Fang B (2018) Regularized label relaxation linear regression. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(4):1006–1018
Wen J, Zhang B, Xu Y, Yang J, Han N (2018) Adaptive weighted nonnegative low-rank representation. Pattern Recogn 81:326–340
Boyd S, Parikh N, Chu E, Peleato B, Eckstein J (2011) Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers. Found Trends® Mach Learn 3(1):1–122
Wen J, Fang X, Xu Y, Tian C, Fei L (2018) Low-rank representation with adaptive graph regularization. Neural Netw 108:83–96
Wen J, Zhang Z, Xu Y, Zhong Z (2018) Incomplete multi-view clustering via graph regularized matrix factorization. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, Munich, Germany
Cand EJ, s X, Li Y, Ma, Wright J (2009) Robust principal component analysis?. J ACM 58(1):1–73
Wen J, Han N, Fang X, Fei L, Yan K, Zhan S (2018) Low-rank preserving projection via graph regularized reconstruction. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2018.2799862
Qiao Z, Zhou L, Huang JZ (2009) Sparse linear discriminant analysis with applications to high dimensional low sample size data. Iaeng Int J Appl Math 39(1):48–60
Baudat G, Anouar F (2000) Generalized discriminant analysis using a kernel approach. Neural Comput 12(10):2385–2404
Fan Z, Xu Y, Ni M, Fang X, Zhang D (2016) Individualized learning for improving kernel Fisher discriminant analysis. Pattern Recogn 58:100–109
A. SKN, Nene HMSA (1996) Columbia object image library (COIL-20). Technical Report CUCS-005-96 1–6
Georghiades S, Belhumeur PN, Kriegman DJ (2001) From few to many: illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(6):643–660
Martinez M (1998) The AR face database. Cvc Technical Report, 24
Sim T, Baker S, Bsat M (2003) The CMU pose, illumination, and expression database. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(12):1615–1618
Jiang Z, Lin Z, Davis LS (2013) Label consistent K-SVD: learning a discriminative dictionary for recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(11):2651–2664
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 61703112, 61773128), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (nos. 2014A030308009) and Guangdong Science and Technology Planning Project (nos. 2016B030308001, 2013B091300009, 2014B090907010, 2015B010131014 and 2017B010125002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Xie, S. & Han, N. Robust discriminant analysis with adaptive locality preserving. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 10, 2791–2804 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-00903-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-00903-4