Abstract
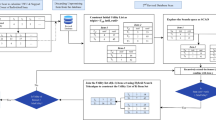
In the big data era, data are usually described by multiple information sources in many practical application fields, and it is infeasible way to mine interesting knowledge from a centralized huge source directly after aggregating all information sources, due to the problems of massive data, privacy concerns, and potential transmission cost. To mine decision rules from multiple information sources, therefore, we can mine local decision rules at different local information sources, and then put these rules to form a set of global decision rules. In this paper, we first present a formal representation of decision rule, which depends on the neighborhood granulation of each sample from the viewpoint of granular computing. Then, we obtain the weight of each local information source based on the consensus measure principle between local information sources. Finally, a weighting model for mining global decision rules via synthesizing all local decision rules is proposed. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed decision rules synthesization model is effective and scalable.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Stouhi S, Reddy C (2016) Transfer learning for class imbalance problems with inadequate data. Knowl Inf Syst 48(1):201–228
Cai M, Li Q, Ma J (2017) Knowledge reduction of dynamic covering decision information systems caused by variations of attribute values. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 8(4):1131–1144
Chen CL, Zhang CY (2014) Data-intensive applications, challenges, techniques and technologies: a survey on big data. Inf Sci 275:314–347
Chen D, Wang C, Hu Q (2007) A new approach to attribute reduction of consistent and inconsistent covering decision systems with covering rough sets. Inf Sci 177:3500–3518
Chen J, Lin Y, Lin G, Li J, Zhang Y (2017) Attribute reduction of covering decision systems by hypergraph model. Knowl-Based Syst 118:93–104
Dai J, Tian H, Wang W, Liu L (2013) Decision rule mining using classification consistency rate. Knowl Based Syst 43:95–102
Du Y, Hu Q, Zhu P, Ma P (2011) Rule learning for classification based on neighborhood covering reduction. Inf Sci 181:5457–5467
Feng Q, Miao D, Cheng Y (2010) Hierarchical decision rules mining. Expert Syst Appl 37(3):2081–2091
Gao J, Fan W, Sun Y et al. (2009) Heterogeneous source consensus learning via decision propagation and negotiation. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, Paris, France, pp 339–347
Hong R, Zhang L, Tao D (2016) Unified photo enhancement by discovering aesthetic communities from flickr. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(3):1124–1135
Hong R, Yang Y, Wang M, Hua X (2015) Learning visual semantic relationships for efficient visual retrieval. IEEE Trans Big Data 1(4):152–161
Hu Q, Yu D, Xie Z (2008) Neighborhood classifiers. Expert Syst Appl 34:866–876
Hu Q, Yu D, Liu J, Wu C (2008) Neighborhood rough set based heterogeneous feature selection. Inf Sci 78:3577–3594
Hu J, Wang G (2009) Knowledge reduction of covering approximation space. Transactions on computational science, special issue on cognitive knowledge representation, pp 69–80
Li F, Qian Y, Wang J, Liang J (2017) Multigranulation information fusion: a Dempster–Shafer evidence theory-based clustering ensemble method. Inf Sci 378:389–409
Li Z, Liu Y, Li Q, Qin B (2016) Relationships between knowledge bases and related results. Knowl Inf Syst 49(1):171–195
Li S, Li T, Zhang Z, Chen H, Zhang J (2015) Parallel computing of approximations in dominance-based rough sets approach. Knowl Based Syst 87:102–111
Lin Y, Hu X, Li X, Wu X (2013) Mining stable patterns in multiple correlated databases. Decis Support Syst 56:202–210
Lin Y, Hu X, Wu X (2014) Ensemble learning from multiple information sources via label propagation and consensus. Appl Intell 41(1):30–41
Lin Y, Hu X, Wu X (2014) Quality of information-based source assessment and selection. Neurocomputing 133:95–102
Lin Y, Li J, Lin P, Lin G, Chen J (2014) Feature selection via neighborhood multi-granulation fusion. Knowl Based Syst 67:162–168
Lin G, Liang J, Qian Y (2015) An information fusion approach by combining multigranulation rough sets and evidence theory. Inf Sci 314:184–199
Lin G, Liang J, Qian Y, Li J (2016) A fuzzy multigranulation decision-theoretic approach to multi-source fuzzy information systems. Knowl Based Syst 91:102–113
Liu H, Lu H, Yao H (2001) Toward multi-database mining: identifying relevant databases. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 13(4):541–553
Luo C, Li T, Yi Z, Fujita H (2016) Matrix approach to decision-theoretic rough sets for evolving data. Knowl Based Syst 99:123–134
Pedrycz W (2013) Granular computing: analysis and design of intelligent systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Qian Y, Liang J, Yao Y, Dang C (2010) MGRS: a multi-granulation rough set. Inf Sci 180:949–970
Qian J, Xia M, Yue X (2017) Parallel knowledge acquisition algorithms for big data using MapReduce. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-016-0624-x
Qian Y, Zhang H, Sang Y, Liang J (2014) Multigranulation decision-theoretic rough sets. Int J Approx Reason 55:225–237
Shakiba A, Hooshmandasl M (2016) Neighborhood system S-approximation spaces and applications. Knowl Inf Syst 49(2):749–794
Song M, Shang W, Wang L, Pedrycz W (2017) Analysis of spatiotemporal data relationship using information granules. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 8(5):1439–1446
Tsang Eric CC, Hu Q, Chen D (2016) Feature and instance reduction for PNN classifiers based on fuzzy rough sets. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 7(1):1–11
Wang C, Wu C, Chen D, Hu Q (2008) Communication between information systems. Inf Sci 178:3228–3239
Wang C, Chen D, Zhu L (2009) Homomorphisms between fuzy information systems. Appl Math Lett 22:1045–1050
Wang C, Chen D, Hu Q (2014) Fuzzy information systems and their homomorphisms. Fuzzy Sets Syst 249:128–138
Wang X, Dong C, Fan T (2007) Training T-S norm neural networks to refine weights for fuzzy if-then rules. Neurocomputing 70(13–15):2581–2587
Wang X, Li C (2005) A new definition of sensitivity for RBFNN and its applications to feature reduction. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 3496: 81–86
Wang X, Hong J (1998) On the handling of fuzziness for continuous-valued attributes in decision tree generation. Fuzzy Sets Syst 99(3):283–290
Wang R, Wang X, Kwong S (2017) Incorporating diversity and informativeness in multiple-instance active learning. IEEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 25(6):1460–1475
Tsang B, Liang J, Qian Y (2015) Determining decision makers’ weights in group ranking: a granular computing method. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 6(3):511–521
Wu X, Zhu X, Wu G, Ding W (2014) Data mining with big data. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 26(1):97–107
Wu X, Zhang S, Zhang C (2005) Database classification for multi-database mining. Inf Syst 30(1):71–88
Wu X, Zhang S (2013) Synthesizing high-frequency rules from different data sources. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 15(2):353–367
Wu W, Qian Y, Li T, Gu S (2017) On rule acquisition in incomplete multi-scale decision tables. Inf Sci 378:282–302
Wu W, Leung Y (2013) Optimal scale selection for multi-scale decision tables. Int J Approx Reason 54(8):1107–1129
Wu W, Leung Y (2013) Theory and applications of granular labelled partitions in multi-scale decision tables. Inf Sci 181:3878–3897
Wu W., Shao M, Wang X (2017) Using single axioms to characterize (S, T)-intuitionistic fuzzy rough approximation operators. In J Mach Learn Cybern 1–16
Xu W, Yu J (2017) A novel approach to information fusion in multi-source datasets: a granular computing viewpoint. Inf Sci 378:410–423
Xu W, Li M, Wang X (2016) Information fusion based on information entropy in fuzzy multi-source incomplete information system. Int J Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-016-0230-9
Xu W, Li W, Zhang X (2013) Generalized multigranulation rough sets and optimal granularity selection. Granul Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-017-0042-9
Yang X, Qian Y, Yang J (2012) Hierarchical structures on multigranulation spaces. J Comput Sci Technol 27(6):1169–1183
Yao J, Vasilakos A, Pedrycz W (2013) Granular computing: perspectives and challenges. IEEE Trans Cybern 43(6):1977–1989
Yao YY (1998) Relational interpretations of neighborhood operators and rough set approximation operators. Inf Sci 101:239–259
Yao YY (2016) Rough set models in multigranulation spaces. Inf Sci 327:40–56
Yu J, Xu W (2017) Incremental knowledge discovering in interval-valued decision information system with the dynamic data. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 8(3):849–864
Zadeh L (1997) Toward a theory of fuzzy information granulation and its centrality in human reasoning and fuzzy logic. Fuzzy Sets Syst 90:111–127
Zhang Y, Hu X, Li P, Li L, Wu X (2015) Cross-domain sentiment classification-feature divergence, polarity divergence or both? Pattern Recogn Lett 65:44–50
Zhao Y, Li J, Liu W, Xu W (2017) Cognitive concept learning from incomplete information. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 8(1):159–170
Zhu X, Jin R (2009) Multiple information sources cooperative learning. In: Proceedings of the 21st international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI-09), California, 1369–1376
Zhu P, Hu Q (2013) Adaptive neighborhood granularity selection and combination based on margin distribution optimization. Inf Sci 249:1–12
Zhu P, Hu Q, Zuo W, Yang M (2014) Multi-granularity distance metric learning via neighborhood granule margin maximization. Inf Sci 282:321–331
Zhu P, Hu Q, Han Y, Zhang C, Du Y (2016) Combining neighborhood separable subspaces for classification via sparsity regularized optimization. Inf Sci 370–371:270–287
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61672272, 61303131, and 61603173), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M581298), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Fujian Province University, and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (Nos. 2016J01315, 2017J01507, and 2016J01314).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y., Chen, H., Lin, G. et al. Synthesizing decision rules from multiple information sources: a neighborhood granulation viewpoint. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 9, 1919–1928 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0791-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0791-z