Abstract
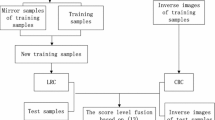
Linear regression classification (LRC) has attracted a great amount of attention owning to its promising performance in face recognition. However, its performance will dramatically decline in the scenario of limited training samples per class, particularly when only single training sample is available for a specific person. In this paper, a novel LRC based method is proposed to solve this problem. Specifically, we first perform LRC on the training set to obtain a kind of residual for each class. Next, a reverse representation residual is derived for each training sample of a class by exploiting the linear combination of the training samples of its nearest classes and the test sample. Then, we combine the reverse representation residuals of the class by an adaptive weighted-average approach to produce the other kind of residual. Finally, two kinds of residuals are fused to classify the test sample. Experimental results on the ORL, FERET, Libor94 and CMU-PIE face databases demonstrate that the proposed method obtains a higher recognition rate than some state-of-the-art face recognition methods.











Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Lai Z, Wong W, Xu Y, Sun M, Zhao C (2014) Sparse alignment for robust tensor learning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(10):1779–1792
Zhang Z, Shao L, Xu Y, Liu L, Yang J (2017) Marginal representation learning with graph structure self-adaptation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2772264
Peng Y, Zhang L, Liu S, Wang X, Guo M (2017) Kernel negative ε dragging linear regression for pattern classification. Complex 2691474:1–14
Chen G, Tao D, Maybank S, Wei L, Kang G, Jie Y (2016) Multi-modal curriculum learning for semi-supervised image classification. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(7):3249–3260
Du B, Xiong W, Wu J, Zhang L, Zhang L, Tao D (2016) Stacked convolutional denoising auto-encoders for feature representation. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(4):1017–1027
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Li X, Zhang D (2015) A survey of sparse representation: algorithms and applications. IEEE Access 3:490–530
Wright J, Yang A, Ganesh A, Sastry S, Yi M (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31:210–227
Lai Z, Wong W, Xu Y, Yang J, Tang J, Zhang D (2016) Approximate orthogonal sparse embedding for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(4):723–735
Zhang L, Yang M, Feng X (2011) Sparse representation or collaborative representation: which helps face recognition. In: International conference on computer vision, pp. 471–478
Zhang Z, Lai Z, Xu Y, Shao L, Wu J, Xie G (2017) Discriminative elastic-net regularized linear regression. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(3):1466–1481
Naseem R, Togneri M, Bennamoun (2010) Linear regression for face recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(11):2106–2112
Xu Y, Zhang D, Yang J, Yang J (2011) A two-phase test sample sparse representation method for use with face recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 21(9):1255–1262
Wen X, Wen J (2016) Improved the minimum squared error algorithm for face recognition by integrating original face images and the mirror images[J]. Opt-Int J Light Electron Opt 127(2):883–889
Zhang Z, Wang L, Zhu Q, Liu Z, Chen Y (2015) Noise modeling and representation based classification methods for face recognition. Neurocomputing 148:420–429
Liu S, Li L, Peng Y, Qiu G, Lei T (2017) An improved sparse representation method for image classification. IET Comput Vis 11(4):319–330
Xu Y, Li X, Yang J, Lai Z, Zhang D (2014) Integrating conventional and inverse representation for face recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(10):1738–1747
Wen J, Xu Y, Li Z et al (2018) Inter-class sparsely based discriminative least square regression[J]. Neural Netw 102:36–47
Candemir S, Borovikov E, Santosh KC, Antani S, Thoma G (2015) Rsilc: rotation-and scale-invariant, line-based color-aware descriptor. Image Vis Comput 42:1–12
Srinivasa Perumal R, Chandra Mouli PVSSR (2016) Dimensionality reduced local directional pattern (DR-LDP) for face recognition. Expert Syst Appl 63:66–73
Zhu L, Shen J, Xie L, Cheng Z (2017) Unsupervised visual hashing with semantic assistance for efficient content-based web image retrieval. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 29(2):472–486
Peng Y, Li L, Liu S, Lei T (2018) Space-frequency domain based joint dictionary learning and collaborative representation for face recognition. Signal Process 147:101–109
Liu S, Peng Y, Ben X, Yang W, Qiu G (2016) A novel label learning algorithm for face recognition. Signal Process 124:141–146
Zhu L, Huang Z, Liu X, Xie L (2017) Discrete multi-modal hashing with canonical views for robust mobile landmark search. IEEE Trans Multimedia 19(9):2066–2079
Lai Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Shen L, Zhang D (2017) Rotational invariant dimensionality reduction algorithms. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(11):3733–3746
Nandakumar K, Chen Y, Dass SC, Jain AK (2008) Likelihood ratio-based biometric score fusion. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30(2):342–347
Peng Y, Li L, Liu S, Lei T, Wu J (2018) A new virtual samples-based CRC method for face recognition. Neural Process Lett 48:313–327
Zhang D, Song FX, Xu Y, Liang ZZ (2009) Advanced pattern recognitiontechnol-ogies with applications to biometrics. Medical Information Science Reference, New York
Brunelli R, Falavigna D (1995) Person identification using multiple cues. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 17(10):955–966
Ma Y, Cukic B, Singh H (2005) A classification approach to multibiometric score fusion. In: Proceedings of the fifth international conference on audiovideo-based biometric person authentication, pp 484–493
Xu Y, Zhang D (2010) Represent and fuse bimodal biometric images at the feature level: complex-matrix-based fusion scheme. Opt Eng 49(3):037002
Bengio S, Marcel C, Marcel S, Mariethoz J (2002) Confidence measures for multi-modal identity verification. Inf Fusion 3(4):267–276
Moin MS, Parviz M, Exploring AUC (2009) Boosting approach in multimodal biometrics score level fusion IIH-MSP. IEEE Computer Society, Kyoto pp 616–619
Jain AK, Rosss AA (2002) Learning user-specific parameters in a multibiometric system. In: Proceedings of the international conference on image processing (ICIP), Rochester, September, pp 22–25
Gao G, Zhang L, Yang J, Zhang L, Zhang D (2013) Reconstruction based finger-knuckle-print verification with score level adaptive binary fusion. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(12):5050–5062
Moumene ME, Nourine R, Ziou D (2014) Generalized exposure fusion weights estimation. Canadian Conference on Computer and Robot Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 6–9 May 2014, pp 71–76
Xu Y, Zhang B, Zhong Z (2015) Multiple representations and sparse representation for image classification. Pattern Recogn Lett 68:9–14
Samaria FS, Harter AC (1994) Parameterisation of a stochastic model for human face identication. In: Proceedings of 2nd IEEE workshop applications computer vision, vol 557, pp 138–142 (4)
Georghiades AS, Belhumeur PN, Kriegman D (2001) From few to many: illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 23(6):643–660
Yang M, Zhang L, Zhang D, Wang S (2012) Relaxed collaborative representation for pattern classification. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2224–2231
Xu Y, Zhu Q, Chen Y, Pan J (2013) An improvement to the nearest neighbor classifier and face recognition experiments. Int J Innov Comput Inf Control 9(2):543–554
Yang Z, Zhou A, Balasubramanian S, Sastry Y, Ma (2017) Fast l1-minimization algorithms for robust face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(8):3234–3246
Xu Y, Zhu Q, Fan Z, Qiu M, Chen Y, Liu H (2013) Coarse to fine K nearest neighbor classifier. Pattern Recogn Lett 34:980–986
Osborne MR, Presnell B, Turlach BA (2000) A new approach to variable selection in least squares problems. IMA J Numer Anal 20(3):389–403
Xu Y, Zhong Z, Yang J, You J, Zhang D (2017) A new discriminative sparse representation method for robust face recognition via L2 regularization. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(10):2233–2242
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Shao L, Yang J (2017) Discriminative block-diagonal representational learning for image recognition. In: IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, pp 2712801. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS
Tong S, Koller D (2001) Support vector machine active learning with applications to text classification. J Mach Learn Res 2(11):45–66
Phillips PJ, Moon H, Rizvi SA, Rauss PJ (2000) The FERET evaluation methodology for face-recognition algorithms. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(10):1090–1104
http://cswww.essex.ac.uk/mv/allfaces/index.html. Accessed 12 Aug 2018
Sim T, Baker S, Bsat M (2002) The CMU, Pose Illumination, and expression (PIE) database. In: Proceedings of the fifth IEEE international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition, vol 435, pp 46–51 (19)
Cover TM, Hart PE (1967) Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 13(1):21–27
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61672333, 61402274, 61461025, 61703096), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Special project (No. 2014T70937), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2017M611655), the Program of Key Science and Technology Innovation Team in Shaanxi Province (No. 2014KTC-18), the Key Science and Technology Program of Shaanxi Province, China (No. 2016GY-081), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20170691), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. GK201803059, GK201803088), Interdisciplinary Incubation Project of Learning Science of Shaanxi Normal University, and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2018JM6050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Y., Ke, J., Liu, S. et al. An improvement to linear regression classification for face recognition. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 10, 2229–2243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0862-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0862-1