Abstract
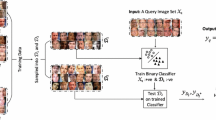
Description and classification of face images is a significant task of computer vision, machine learning and pattern recognition communities. In the past, researchers have made tremendous efforts in this task. Previous researchers always seek high-resolution face images for better image classification. However, with this paper, we present and demonstrate a new opinion that in some cases the use of alternative representations of facial images are very useful for face recognition and properly reducing the image resolution might be beneficial to better classification of face images. This may be attributed to the deformable property of faces and the fact that the proposed alternative representations can in some extent reduce the within-class difference of facial images. Also, the presented idea appear to be useful for helping people to improve face recognition techniques in real worlds.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Kan M, Wu J, Shan S, Chen X (2014) Domain adaptation for face recognition: targetize source domain bridged by common subspace. Int J Comput Vis 109(1–2):94–109
Kim SG, Chang DY (2009) Underdetermined blind source separation based on subspace representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 57(7):2604–2614
Fan Z, Xu Y, Zuo W, Yang J, Tang J, Lai Z, Zhang D (2017) Modified principal component analysis: an integration of multiple similarity subspace models. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(8):1538–1552
Lai Z, Mo D, Wen J, Shen L, Wong WK (2018) Generalized robust regression for jointly sparse subspace learning. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(3):756–772
Li Z, Zhang Z, Qin J, Zhang Z, Shao L (2020) Discriminative fisher embedding dictionary learning algorithm for object recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(3):786–800
Zhang Z, Yan S, Zhao M (2014) Similarity preserving low-rank representation for enhanced data representation and effective subspace learning. Neural Netw 53(5):81–94
Xu Y, Zhong A, Yang J, Zhang D (2010) Lpp solution schemes for use with face recognition. Pattern Recognit 43(12):4165–4176
Mi J, Zhu Q, Lu J (2019) Principal component analysis based on block-norm minimization. Appl Intell 49(6):2169–2177
Mi J, Zhang Y, Lai Z, Li W, Zhou L, Zhong F (2019) Principal component analysis based on nuclear norm minimization. Neural Netw 118:1–16
Mansano A, Matsuoka JA, Afonso LCS, Papa JP, Faria F, Torres RDS (2012) Improving image classification through descriptor combination. In: Sibgrapi conference on graphics
Yong X, Zhu X, Li Z, Liu G, Lu Y, Hong L (2013) Using the original and ’symmetrical face’ training samples to perform representation based two-step face recognition. Pattern Recognit 46(4):1151–1158
Shuai W, Jian C (2014) ‘Symmetrical face’ based improved lpp method for face recognition. Opt Int J Light Electron Opt 125(14):3530–3533
Xu Y, Li X, Yang J, Zhang D (2014) Integrate the original face image and its mirror image for face recognition. Neurocomputing 131(7):191–199
Wen X, Jie W (2016) Improved the minimum squared error algorithm for face recognition by integrating original face images and the mirror images. Opt Int J Light Electron Opt 127(2):883–889
Xu Y, Li X, Yang J, Lai Z, Zhang D (2014) Integrating conventional and inverse representation for face recognition. IEEE Trans Cybernet 44(10):1738–1746
Sanderson C, Paliwal KK (2003) Noise compensation in a person verification system using face and multiple speech features. Pattern Recognit 36(2):293–302
Wang Y, Min W, Yan C, Qi Z (2014) A novel virtual samples-based sparse representation method for face recognition. Opt Int J Light Electron Opt 125(15):3908–3912
Ryu YS, Oh SY (2002) Simple hybrid classifier for face recognition with adaptively generated virtual data. Pattern Recognit Lett 23(7):833–841
Xu Y, Zhang B, Zhong Z (2015) Multiple representations and sparse representation for image classification. Pattern Recognit Lett 68:9–14
Mi J, Fu Q, Li W (2017) Adaptive class preserving representation for image classification, pp 2624–2632
Lai Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Shen L, Zhang D (2016) Rotational invariant dimensionality reduction algorithms. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(11):3733–3746
Gao W, Shan S, Chai X, Fu X (2003) Virtual face image generation for illumination and pose insensitive face recognition. In: Proceedings of 2003 international conference on multimedia and expo, ICME’03 (Cat. No. 03TH8698), IEEE. vol 3, p 149
Thian NPH, Marcel S, Bengio S (2003) Improving face authentication using virtual samples. In: Proceedings of 2003 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, 2003 (ICASSP’03), IEEE. vol 3, p 233
Tang B, Luo S, Hua H (2004) High performance face recognition system by creating virtual sample. In: International conference on neural networks & signal processing
Shi X, Yang Y, Guo Z, Lai Z (2014) Face recognition by sparse discriminant analysis via joint l2,1-norm minimization. Pattern Recognit 47(7):2447–2453
Wright J, Ma Y, Mairal J, Sapiro G, Huang TS, Yan S (2010) Sparse representation for computer vision and pattern recognition. Proc IEEE 98(6):1031–1044
Wright J, Yang AY, Ganesh A, Sastry SS, Ma Y (2009) Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31(2):210–227
Liu T, Mi J, Liu Y, Li C (2016) Robust face recognition via sparse boosting representation. Neurocomputing 214:944–957
Lai Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Tang J, Zhang D (2013) Sparse tensor discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(10):3904–3915
Xu Y, Zhang D, Yang J, Yang JY (2011) A two-phase test sample sparse representation method for use with face recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 21(9):1255–1262
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Li X, Zhang D (2017) A survey of sparse representation: algorithms and applications. IEEE Access 3:490–530
Lei Z, Meng Y, Feng X (2012) Sparse representation or collaborative representation: which helps face recognition? In: International conference on computer vision
Xu Y, Fang X, Li X, Yang J, You J, Liu H, Teng S (2014) Data uncertainty in face recognition. IEEE Trans Cybern 44(10):1950–1961
Shi Q, Eriksson A, Hengel AVD, Shen C (2011) Is face recognition really a compressive sensing problem? In: Computer vision & pattern recognition
Xu Y, Zhu Q, Fan Z, Zhang D, Mi J, Lai Z (2013) Using the idea of the sparse representation to perform coarse-to-fine face recognition. Inf Sci 238(7):138–148
Yu C, Jin Z, Chen H, Zhang Y, Yin X (2016) A fast and robust face recognition approach combining gabor learned dictionaries and collaborative representation. Int J Mach Learn Cybernet 7(1):47–52
Song Z, Cui K, Cheng G (2020) Image set face recognition based on extended low rank recovery and collaborative representation. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:71–80
Cai S, Lei Z, Zuo W, Feng X (2016) A probabilistic collaborative representation based approach for pattern classification. In: IEEE conference on computer vision & pattern recognition
Zhu P, Zhang L, Hu Q, Shiu SCK (2012) Multi-scale patch based collaborative representation for face recognition with margin distribution optimization. In: European conference on computer vision
Yang M, Zhang D, Wang S (2012) Relaxed collaborative representation for pattern classification. In: IEEE conference on computer vision & pattern recognition
Xu Y, Zhu Q, Chen Y, Pan J-S et al (2013) An improvement to the nearest neighbor classifier and face recognition experiments. Int J Innov Comput Inf Control 9(2):543–554
Kim SJ, Koh K, Lustig M, Boyd S, Gorinevsky D (2008) An interior-point method for large-scale l1-regularized least squares. IEEE J Sel Top Signal Process 1(4):606–617
Zouari M, Masmoudi AD, Masmoudi DS (2014) A non linear stretching image enhancement technique for microcalcification detection. In: 2014 1st international conference on advanced technologies for signal and image processing (ATSIP). IEEE, pp 193–197
Dan C, Qi Z, Hui W, Feng S (2015) A novel color image contrast enhancement algorithm using saturation-lightness combined stretching in the hsl color space for amoled applications. In: IEEE international conference on solid-state & integrated circuit technology
Nagaoka T, Nakamura A, Aizawa K, Kanazawa M, Kezuka T, Miura M, Usui M, Ohtsubo S, Sota T (2007) Application of decorrelation stretching method to hyperspectral fundus image processing. Proc SPIE 6426:526–533
Karvelis PS, Fotiadis DI (2008) A region based decorrelation stretching method: application to multispectral chromosome image classification. In: IEEE international conference on image processing
http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/research/dtg/attarchive/facedatabase.html
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Major Research Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.91746116, the Major Applied Basic Research Program of Guizhou Province under Grant No. JZ20142001 and the Major Special Science and Technology Projects of Guizhou Province under Grant No. [2017]3002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Y., Sun, L. & Xu, Y. Exploring of alternative representations of facial images for face recognition. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 11, 2289–2295 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01116-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01116-4