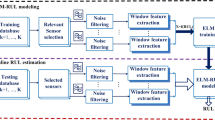
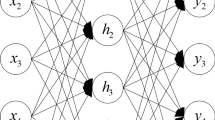
Abstract
Integrated modular avionics is the core system of modern aircraft, which hosts almost all kinds of electrical functions. The performance of integrated modular avionics has an immediate influence on flight mission. Remaining useful life prediction is an effective manner to guarantee the safety and reliability of airplane. To satisfy the real-time requirement of integrated modular avionics, the prediction algorithm should have fast learning speed. This paper proposes an ensemble enhanced online sequential parallel extreme learning machine to predict the remaining useful life of integrated modular avionics. Firstly, a network with parallel hidden layers is designed to improve feature extraction. Secondly, to enhance the learning stability, the input weights of the network are determined by using extreme learning machine autoencoder. Thirdly, an updating method is developed for online prediction and an adaptive weight is designed to construct the ensemble online sequential prediction method. The effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method are verified through the standard datasets. Finally, this paper regards intermittent faults as the feature of integrated modular avionics and builds a degradation model by using Lévy Process. The proposed method is applied to remaining useful life prediction of integrated modular avionics.
























Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Abbreviations
- IMA:
-
Integrated modular avionics
- PHM:
-
Prognostics and health management
- RUL:
-
Remaining useful life
- LSTM:
-
Long short-term memory
- ELM:
-
Extreme learning machine
- OS-ELM:
-
Online sequential-extreme learning machine
- EEOS-PELM:
-
Ensemble enhanced online sequential-parallel extreme learning machine
- ELM-AE:
-
Extreme learning machine autoencoder
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- ReLU:
-
Rectified linear unit
- OFLN:
-
Online fast learning network
- POS-ELM:
-
Parallel online sequential extreme learning machine
- Std:
-
Standard deviation
- MAE:
-
Mean absolute error
- EM:
-
Electromigration
- HCI:
-
Hot carrier injection
References
Zhou T, Xiong H (2012) Design of energy-efficient hierarchical scheduling for integrated modular avionics systems. Chin J Aeronaut 25:109–114
Gao ZH, Ma CB, She ZY, Dong X (2018) An enhanced deep extreme learning machine for integrated modular avionics health state estimation. IEEE Access 6:65813–65823
Matos HLV (2018) Model-based specification of integrated modular avionics systems using object-process methodology. In: 2018 IEEE/AIAA 37th digital avionics systems conference, pp 1–8
Wang Y, Lei H, Hackett R, Beeby M (2019) Safety assessment process optimization for integrated modular avionics. IEEE Aerosp Electron Syst Mag 34:58–67
Zhou Q, Wang J et al (2020) A two-phase multiobjective local search for the device allocation in the distributed integrated modular avionics. IEEE Access 8:1–10
Mathias B, Emil K, Tomas L et al (2018) An optimization approach for pre-runtime scheduling of tasks and communication in an integrated modular avionic system. Optim Eng 19:977–1004
Degtyarev AR, Kiselev SK (2017) Hardware reconfiguration algorithm in multiprocessor systems of integrated modular avionics. Russ Aeronaut 60:116–121
Wan JX, Xiang X, Bai XY et al (2013) Performability analysis of avionics system with multilayer HM/FM using stochastic Petri nets. Chin J Aeronaut 26:363–377
Lu YF, Li Q, Pan ZP, Liang SY (2018) Prognosis of bearing degradation using gradient variable forgetting factor RLS combined with time series model. IEEE Access 6:10986–10995
Wang F, Mamo T (2018) A hybrid model based on support vector regression and differential evolution for remaining useful lifetime prediction of lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 15:49–55
Li X, Ding Q, Sun JQ (2018) Remaining useful life estimation in prognostics using deep convolution neural networks. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 172:1–11
Huang Y, Tang YF, VanZwieten JX, Xiao XC (2019) An adversarial learning approach for machine prognostic health management. In: 2019 international conference on high performance big data and intelligent systems, pp 163–168
Liu JY, Tian Y, Zhang R, Sun YQ, Wang C (2020) A two-stage generative adversarial networks with semantic content constraints for adversarial example generation. IEEE Access 8:205766–205777
Fedosov E, Koverninsky I et al (2017) Use of real-time operating systems in the integrated modular avionics. Procedia Comput Sci 103:384–387
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew C (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70:489–501
Cheng Y, Zhao D, Wang Y, Pei G (2019) Multi-label learning with kernel extreme learning machine autoencoder. Knowl Based Syst 178:1–10
Peng Y, Kong WZ, Yang B (2017) Orthogonal extreme learning machine for image classification. Neurocomputing 266:458–464
Vanli ND, Sayin MO, Delibalta I, Kozat SS (2017) Sequential nonlinear learning for distributed multiagent systems via extreme learning machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn 28:546–558
Lv F, Han M (2019) Hyperspectral image classification based on multiple reduced kernel extreme learning machine. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10:3397–3405
Wang H, Liu X, Song P, Tu X (2019) Sensitive time series prediction using extreme learning machine. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10:3371–3386
Kamran J, Rafael G, Noureddine Z (2015) A new multivariate approach for prognostics based on extreme learning machine and fuzzy clustering. IEEE Trans Cybern 12:2626–2639
Liu Z, Cheng Y et al (2018) A method for remaining useful life prediction of crystal oscillators using the Bayesian approach and extreme learning machine under uncertainty. Neurocomputing 305:27–38
Roozbeh R, Shiladitya C, Mehrdad S (2017) Multi-step parallel-strategy for estimating the remaining useful life of batteries. In: 2017 IEEE 30th canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering, pp 1–4
Lu F, Wu J, Huang J, Qiu X (2019) Aircraft engine degradation prognostics based on logistic regression and novel OS-ELM algorithm. Aerosp Sci Technol 84:661–671
Gao ZH, Ma CB, Song D, Liu Y (2019) Deep quantum inspired neural network with application to aircraft fuel system fault diagnosis. Neurocomputing 238:13–23
Zhao L, Zhu J (2019) Learning from correlation with extreme learning machine. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10:3635–3645
Nguyen TV, Mirza B (2018) Dual-layer kernel extreme learning machine for action recognition. Neurocomputing 260:123–130
Kasun LLC, Zhou H, Huang GB, Chi MV (2013) Representational learning with ELMs for big data. IEEE Intell Syst 28:31–34
Li S, Jiang H, Bai J, Liu Y, Yao Y (2019) Stacked sparse autoencoder and case-based postprocessing method for nucleus detection. Neurocomputing 351:167–179
Tang JX, Deng CW, Huang GB (2016) Extreme learning machine for multilayer perceptron. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27:809–821
Khatab ZE, Hajihoseini A, Ghorashi SA (2018) A fingerprint method for indoor localization using autoencoder based deep extreme learning machine. IEEE Sens Lett 65:1–4
Zeng NY, Zhang H (2017) A switching delayed PSO optimized extreme learning machine for short-term load forecasting. Neurocomputing 240:175–182
Gao ZH, Ma CB, Zhang JF, Xu WJ (2019) Enhanced online sequential parallel extreme learning machine and its application in remaining useful life prediction of integrated modular avionics. IEEE Access 7:183479–183488
Corchs S, Fersini E, Gasparini F (2019) Ensemble learning on visual and textual data for social image emotion classification. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10:2057–2070
Shao HD, Jiang HK, Lin Y, Li XQ (2018) A novel method for intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling bearings using ensemble deep auto-encoders. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 102:278–297
Modi S, Lin Y, Cheng L, Yang G, Liu L, Zhang WJ (2011) A socially inspired framework for human state inference using expert opinion integration. IEEE-ASME Trans Mechatron 16:874–878
Cai M, Yu XJ, Han B (2015) Adaptive natural gradient learning algorithms for Mackey-Glass chaotic time prediction. Neurocomputing 175:41–45
Zhao JS, Yu XJ (2015) Adaptive natural gradient learning algorithms for Mackey-Glass chaotic time prediction. Neurocomputing 175:41–45
Niu PF, Chen K, Ma YP (2017) Model turbine heat rate by fast learning network with tuning based on ameliorated krill herd algorithm. Knowl Based Syst 118:80–92
Tavares LD, Saldanha RR, Vieira DAG (2015) Extreme learning machine with parallel layer perceptrons. Neurocomputing 166:164–171
Deng GQ, Qiu J, Liu GJ (2014) A stochastic automaton approach to discriminate intermittent from permanent faults. Proc Inst Mech Eng G J Aerosp Eng 228(6):880–888
Gao ZH, Ma CB (2017) An IMA degradation model with intermittent faults for RUL prediction. In: 2017 Prognostics and system health management conference, pp 1–6
Niemiro W (2019) Fixed relative precision estimators of growth rate for compound Poisson and Lévy processes. Stat Probab Lett 153:151–156
Vladimir U, Irina T (2017) Availability assessment of a telecommunications system with permanent and intermittent faults. In: 2017 IEEE first Ukraine conference on electrical and computer engineering, pp 908–911
Hainaut D (2010) Mutual information for stochastic signals and Lévy processes. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 56:18–24
Liao PJ, Chen CL (2008) A new on-state drain-bias TDDB lifetime model and HCI effect on drain-bias TDDB of ultra thin oxide. In: 2008 IEEE international reliability physics symposium, pp 210–214
Adarsh B, Jennifer MP (2017) Electromigration: lognormal versus Weibull distribution. In: 2017 IEEE international integrated reliability workshop, pp 1–4
Kim NH, Dawn A, Choi JH (2016) Prognostics and health management of engineering systems: an introduction. Springer, Berlin
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zehai, G., Cunbao, M., Jianfeng, Z. et al. Remaining useful life prediction of integrated modular avionics using ensemble enhanced online sequential parallel extreme learning machine. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 12, 1893–1911 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01283-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01283-y