Abstract
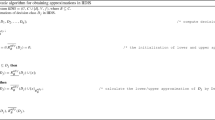
As a typical generalization of classical rough set, variable precision fuzzy neighborhood rough set (VPFNRS) can effectively handle the datasets with noise. At the same time, the three-way regions induced by VPFNRS can determine some decision rules. However, data usually changes over time in real life, such as the addition of new objects and the removal of obsolete objects. Therefore, the rules determined by the three-way regions may change with time. To address this issue, we investigate the dynamic maintenance of the variable precision fuzzy neighborhood three-way regions under the background of interval-valued fuzzy decision system (IvFDS), aiming to effectively update the three-way regions in dynamic environment. Firstly, the \(\delta\)-fuzzy neighborhood relation and its induced \(\delta\)-fuzzy neighborhood class are defined. On this basis, a novel VPFNRS model suitable for IvFDS is proposed. Secondly, the variable precision fuzzy neighborhood three-way regions induced by the proposed model and its matrix representations are introduced. Subsequently, the matrix-based incremental mechanisms to update the three-way regions when the objects change are constructed. Meanwhile, corresponding incremental algorithms are designed. Finally, a series of numerical comparative experiments are executed on nine datasets, and the results indicate that incremental algorithms are not only effective, but also highly efficient under the dynamic data environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao YY (2010) Three-way decisions with probabilistic rough sets. Inf Sci 180(3):341–353
Yao YY (2011) The superiority of three-way decisions in probabilistic rough set models. Inf Sci 181(6):1080–1096
Lang GM, Miao DQ, Fujita H (2020) Three-way group conflict analysis based on pythagorean fuzzy set theory. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(3):447–461
Lang GM (2020) A general conflict analysis model based on three-way decision. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11(5):1083–1094
Wang WJ, Zhan JM, Zhang C (2021) Three-way decisions based multi-attribute decision making with probabilistic dominance relations. Inf Sci 559:75–96
Deng XF, Yao YY (2014) A multifaceted analysis of probabilistic three-way decisions. Fundam Inform 132(3):291–313
Yao YY (2018) Three-way decision and granular computing. Int J Approx Reason 103:107–123
Yao YY (2021) The geometry of three-way decision. Appl Intell 51(9):6298–6325
Yao YY (2021) Set-theoretic models of three-way decision. Granul Comput 6:133–148
Yang B, Li JH (2020) Complex network analysis of three-way decision researches. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11(5):973–987
Yao YY, Wong SKM (1992) A decision theoretic framework for approximating concepts. Int J Man-Mach Stud 37(6):793–809
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Roy S, Shivakumara P, Jain N, Khare V, Dutta A, Pal U, Lu T (2018) Rough-fuzzy based scene categorization for text detection and recognition in video. Pattern Recognit 80:64–82
Wei W, Liang JY (2019) Information fusion in rough set theory : an overview. Inf Fusion 48:107–118
Tan AH, Wu WZ, Qian YH, Liang JY, Chen JK, Li JJ (2019) Intuitionistic fuzzy rough set-based granular structures and attribute subset selection. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(3):527–539
Pei DW (2005) A generalized model of fuzzy rough sets. Int J Gen Syst 34(5):603–613
Guo YT, Tsang ECC, Xu WH, Chen DG (2019) Local logical disjunction double-quantitative rough sets. Inf Sci 500:87–112
Sang BB, Yang L, Chen HM, Xu WH, Guo YT, Yuan Z (2019) Generalized multi-granulation double-quantitative decision-theoretic rough set of multi-source information system. Int J Approx Reason 115:157–179
Xu WH, Yu JH (2017) A novel approach to information fusion in multi-source datasets: a granular computing viewpoint. Inf Sci 378:410–423
Hu QH, Yu DR, Liu JF, Wu CX (2008) Neighborhood rough set based heterogeneous feature subset selection. Inf Sci 178(18):3577–3594
Dubois D, Prade H (1990) Rough fuzzy sets and fuzzy rough sets. Int J Gen Syst 17(2–3):191–209
Wang CZ, Shao MW, He Q, Qian YH, Qi YL (2016) Feature subset selection based on fuzzy neighborhood rough sets. Knowl Based Syst 111:173–179
D’Urso P, Leski JM (2016) Fuzzy c-ordered medoids clustering for interval-valued data. Pattern Recogni 58:49–67
Guru DS, Kiranagi BB, Nagabhushan P (2004) Multivalued type proximity measure and concept of mutual similarity value useful for clustering symbolic patterns. Pattern Recognit Lett 25(10):1203–1213
Lang GM, Miao DQ, Yang T, Cai MJ (2016) Knowledge reduction of dynamic covering decision information systems when varying covering cardinalities. Inf Sci 346–347:236–260
Yu JH, Xu WH (2017) Incremental knowledge discovering in interval-valued decision information system with the dynamic data. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 8(3):849–864
Guo YT, Tsang ECC, Hu M, Lin XX, Chen DG, Xu WH, Sang BB (2020) Incremental updating approximations for double-quantitative decision-theoretic rough sets with the variation of objects. Knowl Based Syst. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.105082
Yang L, Qin KY, Sang BB, Xu WH (2021) Dynamic fuzzy neighborhood rough set approach for interval-valued information systems with fuzzy decision. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107679
Li WT, Xu WH, Zhang XY, Zhang J (2021) Updating approximations with dynamic objects based on local multigranulation rough sets in ordered information systems. Artif Intell Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10053-9
Yu JH, Chen MH, Xu WH (2017) Dynamic computing rough approximations approach to time-evolving information granule interval-valued ordered information system. Appl Soft Comput 60:18–29
Li TR, Ruan D, Wets G, Song J, Xu Y (2007) A rough sets based characteristic relation approach for dynamic attribute generalization in data mining. Knowl Based Syst 20(5):485–494
Hu CX, Liu SX, Huang XL (2017) Dynamic updating approximations in multigranulation rough sets while refining or coarsening attribute values. Knowl Based Syst 130:62–73
Zeng AP, Li TR, Hu J, Chen HM, Luo C (2017) Dynamical updating fuzzy rough approximations for hybrid data under the variation of attribute values. Inf Sci 378:363–388
Wang S, Li TR, Luo C, Hu J, Fujita H, Huang TQ (2020) A novel approach for efficient updating approximations in dynamic ordered information systems. Inf Sci 507:197–219
Wang S, Li TR, Luo C, Chen HM, Fujita H (2019) Domain-wise approaches for updating approximations with multi-dimensional variation of ordered information systems. Inf Sci 478:100–124
Wang S, Li TR, Luo C, Fujita H (2016) Efficient updating rough approximations with multi-dimensional variation of ordered data. Inf Sci 372:690–708
Sang BB, Chen HM, Li TR, Xu WH, Yu H (2020) Incremental approaches for heterogeneous feature selection in dynamic ordered data. Inf Sci 541:475–501
Zhang YY, Li TR, Luo C, Zhang JB, Chen HM (2016) Incremental updating of rough approximations in interval-valued information systems under attribute generalization. Inf Sci 373:461–475
Liu D, Li TR, Zhang JB (2014) A rough set-based incremental approach for learning knowledge in dynamic incomplete information systems. Int J Approx Reason 55(8):1764–1786
Lin BY, Zhang XY, Xu WH, Wu YX (2020) Dynamically updating approximations based on multi-threshold tolerance relation in incomplete interval-valued decision information systems. Knowl Inf Syst 62(3):1063–1087
Chen HM, Li TR, Ruan D, Lin JH, Hu CX (2013) A rough-set-based incremental approach for updating approximations under dynamic maintenance environments. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(2):274–284
Hu J, Li TR, Luo C, Fujita H, Li SY (2017) Incremental fuzzy probabilistic rough sets over two universes. Int J Approx Reason 81:28–48
Huang QQ, Li TR, Huang YY, Yang X, Fujita H (2020) Dynamic dominance rough set approach for processing composite ordered data. Knowl Based Syst 187:104829
Huang YY, Li TR, Luo C, Fujita H, Horng S (2017) Matrix-based dynamic updating rough fuzzy approximations for data mining. Knowl Based Syst 119:273–283
Sang BB, Chen HM, Yang L, Zhou DP, Li TR, Xu WH (2020) Incremental attribute reduction approaches for ordered data with time-evolving objects. Knowl Based Syst 212:106583
Cai MJ, Lang GM, Fujita H, Li ZY, Yang T (2019) Incremental approaches to updating reducts under dynamic covering granularity. Knowl Based Syst 172:130–140
Wei W, Wu XY, Liang JY, Cui JB, Sun YJ (2018) Discernibility matrix based incremental attribute reduction for dynamic data. Knowl Based Syst 140:142–157
Luo C, Li TR, Yi Z, Fujita H (2016) Matrix approach to decision-theoretic rough sets for evolving data. Knowl Based Syst 99:123–134
Yang X, Li TR, Fujita H, Liu D, Yao YY (2017) A unified model of sequential three-way decisions and multilevel incremental processing. Knowl Based Syst 134:172–188
Sang YL, Liang JY, Qian YH (2016) Decision-theoretic rough sets under dynamic granulation. Knowl Based Syst 91:84–92
Luo C, Li TR, Huang YY, Fujita H (2019) Updating three-way decisions in incomplete multi-scale information systems. Inf Sci 476:274–289
Zhang QH, Lv GX, Chen YH, Wang GY (2018) A dynamic three-way decision model based on the updating of attribute values. Knowl Based Syst 142:71–84
Hu CX, Zhang L (2020) Incremental updating probabilistic neighborhood three-way regions with time-evolving attributes. Int J Approx Reasn 120:1–23
Yang X, Li TR, Liu D, Chen HM, Luo C (2017) A unified framework of dynamic three-way probabilistic rough sets. Inf Sci 420:126–147
Huang QQ, Li TR, Huang YY, Yang X (2020) Incremental three-way neighborhood approach for dynamic incomplete hybrid data. Inf Sci 541:98–122
Yang XB, Qi Y, Yu DJ, Yu HL, Yang JY (2015) \(\alpha\)-dominance relation and rough sets in interval-valued information systems. Inf Sci 294:334–347
Chen ZC, Qin KY (2009) Attribute reduction of interval-valued information system based on variable precision tolerance relation. Comput Sci 36(3):163–166 (in Chinese)
Leung Y, Fischer MM, Wu WZ, Mi JS (2008) A rough set approach for the discovery of classification rules in interval-valued information systems. Int J Approx Reason 47(2):233–246
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61976130).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Qin, K., Sang, B. et al. Dynamic maintenance of variable precision fuzzy neighborhood three-way regions in interval-valued fuzzy decision system. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 13, 1797–1818 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01489-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01489-0