Abstract
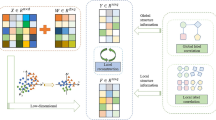
Researchers have considered multi-label learning because of its presence in various real-world applications, in which each entity is associated with more than one class label. Since multi-label data suffers from the curse of high-dimensionality, providing effective feature selection methods is necessary to enhance the learning process. Various multi-label feature selection methods have been proposed so far. However, the existing methods have not yet reached acceptable performance in this research field due to the existence of datasets with various dimensions. This paper proposes a new feature selection algorithm based on subspace learning and a memetic algorithm to provide global and local search in multi-label data. This is the first try that uses a filter-based memetic algorithm for multi-label feature selection. The objective function consists of two conflicting objectives: reconstruction error and sparsity regularization. Finally, nine filter-based multi-label feature selection methods are compared with the proposed method. The comparisons are conducted based on the famous performance evaluation criteria for multi-label classification, such as classification accuracy, hamming-loss, average precision, and one-error. Based on the results obtained in eight real-world datasets, the proposed method is superior to comparing methods according to all evaluation criteria.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Alzubi OA, Alzubi JA, Alweshah M et al (2020) An optimal pruning algorithm of classifier ensembles: dynamic programming approach. Neural Comput Appl 32:16091–16107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04761-6
Bayati H, Dowlatshahi MB, Paniri M (2020a) MLPSO: a filter multi-label feature selection based on particle swarm optimization. In: 2020 25th international computer conference, Computer Society of Iran (CSICC). IEEE, pp 1–6
Bayati H, Dowlatshahi MB, Paniri M (2020) Multi-label feature selection based on competitive swarm optimization. J Soft Comput Inf Technol 9:56–69
Boutell MR, Luo J, Shen X, Brown CM (2004) Learning multi-label scene classification. Pattern Recognit 37:1757–1771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2004.03.009
Cai D, He X, Han J (2007) Spectral regression: a unified approach for sparse subspace learning. In: Proceedings—IEEE international conference on data mining, ICDM. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., pp 73–82
Cai D, Zhang C, He X (2010) Unsupervised feature selection for multi-cluster data. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, pp 333–342
Cai J, Luo J, Wang S, Yang S (2018) Feature selection in machine learning: a new perspective. Neurocomputing 300:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.11.077
Charte F, Charte D (2015) Working with multilabel datasets in R: the mldr package. R J 7:149–162. https://doi.org/10.32614/rj-2015-027
Chen W, Yan J, Zhang B et al (2007) Document transformation for multi-label feature selection in text categorization. In: Proceedings—IEEE international conference on data mining, ICDM, pp 451–456
Deng X, Li Y, Weng J, Zhang J (2019) Feature selection for text classification: a review. Multimed Tools Appl 78:3797–3816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-018-6083-5
Di Martino F, Senatore S (2020) Balancing the user-driven feature selection and their incidence in the clustering structure formation. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106854
Doquire G, Verleysen M (2013) Mutual information-based feature selection for multilabel classification. Neurocomputing. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.06.035
Dowlatshahi MB, Derhami V, Nezamabadi-Pour H (2020) Fuzzy particle swarm optimization with nearest-better neighborhood for multimodal optimization. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 17:7–24. https://doi.org/10.22111/ijfs.2020.5403
Dowlatshahi MB, Kuchaki Rafsanjani M, Gupta BB (2021) An energy aware grouping memetic algorithm to schedule the sensing activity in WSNs-based IoT for smart cities. Appl Soft Comput 108:107473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107473
Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-Pour H (2014) GGSA: a grouping gravitational search algorithm for data clustering. Eng Appl Artif Intell 36:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2014.07.016
Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-Pour H, Mashinchi M (2014) A discrete gravitational search algorithm for solving combinatorial optimization problems. Inf Sci (Ny) 258:94–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2013.09.034
Fan Y, Chen B, Huang W et al (2022) Multi-label feature selection based on label correlations and feature redundancy. Knowl Based Syst 241:108256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108256
Feng S, Duarte MF (2018) Graph autoencoder-based unsupervised feature selection with broad and local data structure preservation. Neurocomputing 312:310–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.117
Hashemi A, Bagher Dowlatshahi M, Nezamabadi-pour H (2021) A pareto-based ensemble of feature selection algorithms. Expert Syst Appl 180:115130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115130
Hashemi A, Bagher Dowlatshahi M, Nezamabadi-pour H (2021) An efficient Pareto-based feature selection algorithm for multi-label classification. Inf Sci (Ny) 581:428–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.09.052
Hashemi A, Dowlatshahi MB (2020) MLCR: a fast multi-label feature selection method based on K-means and L2-norm. In: 2020 25th international computer conference, Computer Society of Iran (CSICC). IEEE, pp 1–7
Hashemi A, Dowlatshahi MB (2022) An ensemble of feature selection algorithms using OWA operator. In: 2022 9th Iranian joint congress on fuzzy and intelligent systems (CFIS). IEEE, pp 1–6
Hashemi A, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-pour H (2020) MGFS: a multi-label graph-based feature selection algorithm via PageRank centrality. Expert Syst Appl 142:113024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.113024
Hashemi A, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-pour H (2021) VMFS: a VIKOR-based multi-target feature selection. Expert Syst Appl 182:115224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115224
Hashemi A, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-pour H (2022) Ensemble of feature selection algorithms: a multi-criteria decision-making approach. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 13:49–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01347-z
Hashemi A, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-pour H (2020) MFS-MCDM: multi-label feature selection using multi-criteria decision making. Knowl Based Syst 206:106365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106365
Hashemi A, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-pour H (2021) Gravitational search algorithm. In: Handbook of AI-based metaheuristics, p 32
Hashemi A, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-Pour H (2021) A bipartite matching-based feature selection for multi-label learning. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 12:459–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-020-01180-w
Hashemi A, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-Pour H (2021) Minimum redundancy maximum relevance ensemble feature selection: a bi-objective Pareto-based approach. J Soft Comput Inf Technol
Hashemi A, Joodaki M, Joodaki NZ, Dowlatshahi MB (2022) Ant colony optimization equipped with an ensemble of heuristics through multi-criteria decision making: a case study in ensemble feature selection. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109046
Hashemi A, Pajoohan M-R, Dowlatshahi MB (2022) Online streaming feature selection based on Sugeno fuzzy integral. In: 2022 9th Iranian joint congress on fuzzy and intelligent systems (CFIS). IEEE, pp 1–6
Hu G, Du B, Wang X, Wei G (2022) An enhanced black widow optimization algorithm for feature selection. Knowl Based Syst 235:107638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107638
Huang R, Jiang W, Sun G (2018) Manifold-based constraint Laplacian score for multi-label feature selection. Pattern Recognit Lett 112:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2018.08.021
Jha K, Saha S (2020) Incorporation of multimodal multiobjective optimization in designing a filter based feature selection technique. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106823
Joodaki M, Dowlatshahi MB, Joodaki NZ (2021) An ensemble feature selection algorithm based on PageRank centrality and fuzzy logic. Knowl Based Syst 233:107538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107538
Kashef S, Nezamabadi-pour H, Nikpour B (2018) Multilabel feature selection: a comprehensive review and guiding experiments. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Data Min Knowl Discov 8:e1240. https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.1240
Kumar M, Husain M, Upreti N, Gupta D (2020) Genetic algorithm: review and application. SSRN Electron J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3529843
Lee J, Kim DW (2015) Memetic feature selection algorithm for multi-label classification. Inf Sci (Ny) 293:80–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.09.020
Lee J, Yu I, Park J, Kim DW (2019) Memetic feature selection for multilabel text categorization using label frequency difference. Inf Sci (Ny) 485:263–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.02.021
Li J, Cheng K, Wang S et al (2017) Feature selection: a data perspective. ACM Comput Surv. https://doi.org/10.1145/3136625
Li X, Zhang H, Zhang R et al (2019) Generalized uncorrelated regression with adaptive graph for unsupervised feature selection. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30:1587–1595. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2868847
Lin Y, Hu Q, Liu J et al (2016) Multi-label feature selection based on neighborhood mutual information. Appl Soft Comput J 38:244–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.10.009
Lipovetsky S (2009) PCA and SVD with nonnegative loadings. Pattern Recognit 42:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2008.06.025
Maruyama S, Tatsukawa T (2017) A parametric study of crossover operators in Pareto-based multiobjective evolutionary algorithm. In: Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics). Springer Verlag, pp 3–14
Melo A, Paulheim H (2019) Local and global feature selection for multilabel classification with binary relevance. Artif Intell Rev 51:33–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9556-4
Miao J, Niu L (2016) A survey on feature selection. In: Procedia computer science, pp 919–926
Moscato P (2000) On evolution, search, optimization, genetic algorithms and martial arts-towards memetic algorithms
Movassagh AA, Alzubi JA, Gheisari M et al (2021) Artificial neural networks training algorithm integrating invasive weed optimization with differential evolutionary model. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02623-6
Paniri M, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-pour H (2021) Ant-TD: ant colony optimization plus temporal difference reinforcement learning for multi-label feature selection. Swarm Evol Comput 64:100892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2021.100892
Paniri M, Dowlatshahi MB, Nezamabadi-pour H (2020) MLACO: a multi-label feature selection algorithm based on ant colony optimization. Knowl Based Syst 192:105285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.105285
Pereira RB, Plastino A, Zadrozny B, Merschmann L (2016) Categorizing feature selection methods for multi-label classification. Artif Intell Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-016-9516-4
Qian W, Long X, Wang Y, Xie Y (2020) Multi-label feature selection based on label distribution and feature complementarity. Appl Soft Comput 90:106167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106167
Read J (2008) A pruned problem transformation method for multi-label classification
Read J, Pfahringer B, Holmes G (2008) Multi-label classification using ensembles of pruned sets. In: Proceedings—IEEE international conference on data mining, ICDM, pp 995–1000
Rey D, Neuhäuser M (2011) Wilcoxon-signed-rank test. International encyclopedia of statistical science. Springer, Berlin, pp 1658–1659
Reyes O, Morell C, Ventura S (2015) Scalable extensions of the ReliefF algorithm for weighting and selecting features on the multi-label learning context. Neurocomputing. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2015.02.045
Sheikhpour R, Sarram MA, Gharaghani S, Chahooki MAZ (2017) A Survey on semi-supervised feature selection methods. Pattern Recognit 64:141–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.11.003
Solorio-Fernández S, Carrasco-Ochoa JA, Martínez-Trinidad JF (2020) A review of unsupervised feature selection methods. Artif Intell Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09682-y
Talbi E-G (2009) Metaheuristics from design to implementation
Talbi E-G (2009) Metaheuristics. Wiley, Hoboken
Tsoumakas G, Katakis I, Vlahavas I (2011) Random k-labelsets for multilabel classification. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 23:1079–1089. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2010.164
Wang S, Tang J, Liu H (2015) Embedded unsupervised feature selection. Proc Natl Conf Artif Intell 1:470–476
Wang Y, Zheng W, Cheng Y, Zhao D (2020) Two-level label recovery-based label embedding for multi-label classification with missing labels. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106868
Xue B, Zhang M, Browne WN (2013) Particle swarm optimization for feature selection in classification: a multi-objective approach. IEEE Trans Cybern 43:1656–1671. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2227469
Zhang J, Luo Z, Li C et al (2019) Manifold regularized discriminative feature selection for multi-label learning. Pattern Recognit 95:136–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.003
Zhang ML, Zhou ZH (2007) ML-KNN: a lazy learning approach to multi-label learning. Pattern Recognit 40:2038–2048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2006.12.019
Zhang P, Liu G, Gao W (2019) Distinguishing two types of labels for multi-label feature selection. Pattern Recognit 95:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.06.004
Zhang R, Nie F, Li X, Wei X (2019) Feature selection with multi-view data: a survey. Inf Fusion 50:158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2018.11.019
Zhang Y, Ma Y (2022) Non-negative multi-label feature selection with dynamic graph constraints. Knowl Based Syst 238:107924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107924
Zhu P, Zuo W, Zhang L et al (2015) Unsupervised feature selection by regularized self-representation. Pattern Recognit 48:438–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2014.08.006
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bayati, H., Dowlatshahi, M.B. & Hashemi, A. MSSL: a memetic-based sparse subspace learning algorithm for multi-label classification. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 13, 3607–3624 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-022-01616-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-022-01616-5