Abstract
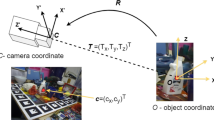
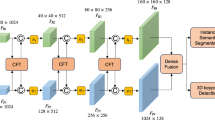
Accurate six degrees of freedom (6-DoF) pose estimation is crucial for robust visual perception in fields such as smart manufacturing. Traditional RGB-based methods, though widely used, often face difficulties in adapting to dynamic scenes, understanding contextual information, and capturing temporal variations effectively. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel multi-modal 6-DoF pose estimation framework. This framework uses RGB images as the primary input and integrates spatial cues, including keypoint heatmaps and affinity fields, through a spatially aligned approach inspired by the Trans-UNet architecture. Our multi-modal method enhances both contextual understanding and temporal consistency. Experimental results on the Objectron dataset demonstrate that our approach surpasses existing algorithms across most categories. Furthermore, real-world tests confirm the accuracy and practical applicability of our method for robotic tasks, such as precision grasping, highlighting its effectiveness for real-world applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
Data supporting this study are available on request from the authors.
References
Fan Z, Zhu Y, He Y, Sun Q, Liu H, He J (2022) Deep learning on monocular object pose detection and tracking: a comprehensive overview. ACM Comput Surv 55(4):1–40
Rad M, Lepetit V (2017) Bb8: a scalable, accurate, robust to partial occlusion method for predicting the 3d poses of challenging objects without using depth. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 3828–3836
Kehl W, Manhardt F, Tombari F, Ilic S, Navab N (2017) Ssd-6d: making rgb-based 3d detection and 6d pose estimation great again. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 1521–1529
Xiang Y, Schmidt T, Narayanan V, Fox D (2017) Posecnn: A convolutional neural network for 6d object pose estimation in cluttered scenes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.00199
Li B, Ouyang W, Sheng L, Zeng X, Wang X (2019) Gs3d: an efficient 3d object detection framework for autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1019–1028
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 28
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C-Y, Berg AC (2016) Ssd: single shot multibox detector. In: Computer vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11–14, 2016, Proceedings, Part I 14. Springer, pp 21–37
Weng X, Wang J, Held D, Kitani K (2020) 3d multi-object tracking: a baseline and new evaluation metrics. In: 2020 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems. IEEE, pp 10359–10366
Weng X, Yuan Y, Kitani K (2020) Joint 3d tracking and forecasting with graph neural network and diversity sampling. 2(6.2):1. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.07847
Fu Q, Xie K, Wen C, He J, Zhang W, Tian H, Yang S (2024) Adaptive occlusion hybrid second-order attention network for head pose estimation. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 15(2):667–683
Trabelsi A, Chaabane M, Blanchard N, Beveridge R (2021) A pose proposal and refinement network for better 6d object pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, pp 2382–2391
Hodan T, Barath D, Matas J (2020) Epos: estimating 6d pose of objects with symmetries. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 11703–11712
Tremblay J, To T, Sundaralingam B, Xiang Y, Fox D, Birchfield S (2018) Deep object pose estimation for semantic robotic grasping of household objects. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.10790
Cao Z, Simon T, Wei S.-E, Sheikh Y (2017) Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7291–7299
Lin Y, Tremblay J, Tyree S, Vela P.A, Birchfield S (2022) Keypoint-based category-level object pose tracking from an rgb sequence with uncertainty estimation. In: 2022 International conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 1258–1264
Yu F, Wang D, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2018) Deep layer aggregation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2403–2412
Wang Z, Zhou X, Wang W, Liang C (2020) Emotion recognition using multimodal deep learning in multiple psychophysiological signals and video. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11(4):923–934
Wang S, Zhang X, Luo Z, Wang Y (2023) Multimodal sparse support tensor machine for multiple classification learning. Int J Mach Learn Cybern:1–13
He Y, Huang H, Fan H, Chen Q, Sun J (2021) Ffb6d: a full flow bidirectional fusion network for 6d pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 3003–3013
Deilamsalehy H, Havens TC (2016) Sensor fused three-dimensional localization using imu, camera and lidar. In: 2016 IEEE sensors. IEEE, pp 1–3
Tsai Y-HH, Bai S, Liang PP, Kolter JZ, Morency L-P, Salakhutdinov R (2019) Multimodal transformer for unaligned multimodal language sequences. In: Proceedings of the conference association for computational linguistics meeting, vol 2019. NIH Public Access, p 6558
Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Dehghani M, Minderer M, Heigold G, Gelly S et al (2020) An image is worth 16 \(\times\) 16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929
Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, Usunier N, Kirillov A, Zagoruyko (2020) End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 213–229
Zheng S, Lu J, Zhao H, Zhu X, Luo Z, Wang Y, Fu Y, Feng J, Xiang T, Torr PH et al (2021) Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 6881–6890
Zhou L, Zhou Y, Corso JJ, Socher R, Xiong C (2018) End-to-end dense video captioning with masked transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 8739–8748
Yin J, Shen J, Gao X, Crandall DJ, Yang R (2021) Graph neural network and spatiotemporal transformer attention for 3d video object detection from point clouds. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 45(8):9822–9835
Jantos T.G, Hamdad M.A, Granig W, Weiss S, Steinbrener J (2023) Poet: pose estimation transformer for single-view, multi-object 6d pose estimation. In: Conference on robot learning. PMLR, pp 1060–1070
Yu S, Zhai D-H, Xia Y, Li D, Zhao S (2024) Cattrack: single-stage category-level 6d object pose tracking via convolution and vision transformer. IEEE Trans Multimedia 26:1665–1680. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2023.3284598
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th international conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer, pp 234–241
Chen J, Lu Y, Yu Q, Luo X, Adeli E, Wang Y, Lu L, Yuille AL, Zhou Y (2021) Transunet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306
Abdel-Aziz YI, Karara HM, Hauck M (2015) Direct linear transformation from comparator coordinates into object space coordinates in close-range photogrammetry. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 81(2):103–107
Ahmadyan A, Zhang L, Ablavatski A, Wei J, Grundmann M (2021) Objectron: a large scale dataset of object-centric videos in the wild with pose annotations. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7822–7831
Hou T, Ahmadyan A, Zhang L, Wei J, Grundmann M (2020) Mobilepose: real-time pose estimation for unseen objects with weak shape supervision. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.03522
Tan M, Le Q (2019) Efficientnet: rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In: International conference on machine learning. PMLR, pp 6105–6114
Lin Y, Tremblay J, Tyree S, Vela PA, Birchfield S (2022) Single-stage keypoint-based category-level object pose estimation from an rgb image. In: International conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 1547–1553
Wang C, Martín-Martín R, Xu D, Lv J, Lu C, Fei-Fei L, Savarese S, Zhu Y (2020) 6-pack: category-level 6d pose tracker with anchor-based keypoints. In: 2020 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 10059–10066
Lin Y, Tremblay J, Tyree S, Vela PA, Birchfield S (2022) Single-stage keypoint-based category-level object pose estimation from an rgb image. In: 2022 International conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 1547–1553
Issac J, Wüthrich M, Cifuentes CG, Bohg J, Trimpe S, Schaal S (2016) Depth-based object tracking using a robust gaussian filter. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). IEEE, pp 608–615
Loshchilov I, Hutter F (2018) Fixing weight decay regularization in adam. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05101
Zhou X, Koltun V, Krähenbühl P (2020) Tracking objects as points. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 474–490
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Key R &D Program of China under Grant 2021YFB1714800, in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 62173034, 61925303, 62088101, and by the Chongqing Natural Science Foundation under Grant 2021ZX4100027.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1. Implementation of keypoint heatmaps and affinity fields
Appendix 1. Implementation of keypoint heatmaps and affinity fields
The implementation of keypoint heatmaps and affinity fields in our approach plays a crucial role in identifying object keypoints and encoding their spatial relationships. Keypoint heatmaps are utilized to locate the projections of an object’s 3D keypoints, while affinity fields capture the directional connections between each keypoint and the center point, thereby encoding the object’s structural topology. During the training process, we employ Algorithm 2 to generate 9 keypoint heatmaps and Algorithm 3 to produce 16 affinity fields per frame.
The affinity fields are specifically designed to capture the directional influences along the x and y axes from the 8 corner keypoints, excluding the center point. Both the keypoint heatmaps and affinity fields are sized \(H \times W\) to ensure spatial alignment with the input frame. An adaptive factor r is introduced to adjust the feature region based on the relative size of the target object. The keypoint coordinates \({(i_{(k, n)}, j_{(k, n)})}\) are derived from the pose annotations available in the Objectron dataset.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mei, Y., Wang, S., Li, Z. et al. Multi-modal 6-DoF object pose tracking: integrating spatial cues with monocular RGB imagery. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 16, 1327–1340 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-024-02336-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-024-02336-8