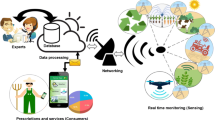
Abstract
In this paper we propose a model for the application of radio frequency identification (RFID) technology and wireless sensors in food logistics to ensure the products’ quality and the traceability along the supply chain, from farms to consumers. The wireless sensors can detect the conditions of the food quality and transmit the information to the RFID tags. The RFID tags can also record other information such as the expired date and communicate with the computer system through the RFID reader. Once the low qualities of products or bad conditions of storage environment are detected, some reactions such as enhancing the package or removing the bad products can be taken immediately in the distribution centers. According to the information on the smart tags, the distribution and the vehicle routing plans are determined to maintain better qualities of the food products when they arrive at the retailers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catarinucci, L., Cappelli, M., Colella, R., Tarricone, L.: A novel low-cost multisensor-tag for RFID applications in healthcare. Microw Opt Technol Lett 50(11), 2877–2880 (2008)
Cho, J., Shim, Y., Kwon, T., Choi, Y., Pack, S., Kim, S.: SARIF: a novel framework for integrating wireless sensor and RFID networks. IEEE Wirel Commun 14(6), 50–56 (2007)
Gupta, A.: Enterprise resource planning: the emerging organizational value systems. Ind Manage Data Syst 100(3), 114–118 (2000)
Hamrita, T.K., Hoffacker, E.C.: Development of a “smart” wireless soil monitoring sensor prototype using RFID technology. Appl Eng Agric 21(1), 139–143 (2005)
Jedermann, R., Behrens, C., Westphal, D., Lang, W.: Applying autonomous sensor systems in logistics-Combining sensor networks, RFIDs and software agents. Sens Actuators, A, Phys 132(1), 370–375 (2006)
Kerry, J.P., O’Grady, M.N., Hogan, S.A.: Past current and potential utilisation of active and intelligent packaging systems for meat and muscle-based products: a review. Meat Sci 74, 113–130 (2006)
Marrocco, G., Mattioni, L., Calabrese, C.: Multiport sensor RFIDs for wireless passive sensing of objects—Basic theory and early results. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 56(8), 2691–2702 (2008)
Ohashi, K., Kurihara, Y., Watanabe, K., Tanaka, H.: Safe patient transfer system with monitoring of location and vital signs. J Med Dent Sci 55(1), 33–41 (2008)
Roberts, C.M.: Radio frequency identification (RFID). Comput Secur 25, 18–26 (2006)
Smaros, J., Holmstrom, J.: Viewpoint: reaching the consumer through grocery VMI. Int J Retail Distrib Manag 28(2), 55–61 (2000)
Spieß, P., Bornhövd, C., Lin, T., Haller, S., Schaper, J.: Going beyond auto-ID: a service-oriented smart items infrastructure. J Enterprise Inform Manag 20(3), 356–370 (2007)
Vellidis, G., Tucker, M., Perry, C., Kvien, C., Bednarz, C.: A real-time wireless smart sensor array for scheduling irrigation. Comput Electron Agric 61(1), 44–50 (2008)
Wang, N., Zhang, N., Wang, M.: Wireless sensors in agriculture and food industry—recent development and future perspective. Comput Electron Agric 50, 1–14 (2006)
Yuan, L., Zhu, Y.: Integrated RFID and wireless sensor network architecture for transportation monitoring. J Harbin Inst Technol (New Series) 14(2), 166–170 (2007)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referees for their helpful comments and the National Science Council, Taiwan, for financially supporting this work. (NSC 96-2221-E-231-020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsueh, CF., Chang, MS. A Model for Intelligent Transportation of Perishable Products. Int. J. ITS Res. 8, 36–41 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-009-0004-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-009-0004-y