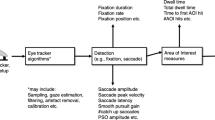
Abstract
In case of driver-driven vehicles, the Adaptive Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) typically focus on providing different driving assistance to the drivers, thereby reducing the load of the drivers. An important aspect that needs to be considered in this design is the real-time assessment of the state of the driver at the time of driving. This is extremely critical for safe driving environment. The common factors for driver’s driveability include measuring driver’s fatigue and distraction level, while driving in different vehicle and traffic environment. In this paper, the state-of-the-art techniques on driver’s driveability is explored through Face and Eye-tracking; while also giving equal importance to the vehicular traffic and the road environment. This paper surveys the advantages and disadvantages of the existing eye and face tracking mechanisms and their integration with the driving performance measures (driveability). Further, a beyond state-of-the-art proposal for head-pose estimation and eye-tracking patterns under controlled environment is presented. The paper throws pen many observations and also opens-up several challenges to further explore in this domain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Onken, R.: DAISY, an adaptive, knowledge-based driver monitoring and warning system. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. (1994)
Ayoob, E.M., Steinfeld, A., Grace, R.: Identification of an ‘appropriate’ drowsy driver detection interface for commercial vehicle operations. Proceedings of Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting. 47(16), 1840–1844 (2003)
Fletcher, L., Petersson, L., Zelinsky, A.: Driver assistance systems based on vision in and out of vehicles. In Proceedings of Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. (2003)
Sayed, R., Eskandarian, A.: Unobtrusive drowsiness detection by neural network learning of driver steering. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Part D, Journal of Automobile Engineering. 215(9), 969–975-5 (2001)
Krajewski, J., Sommer, D., Trutschel, U., Edwards, D., Golz, M.: Steering wheel behavior based estimation of fatigue. 5th International Driving Symposium on Human Factors in Driver Assessment, Training and Vehicle Design, pp. 118–124 (2009)
Ranney, T.A., Mazzae, E., Garrott, R., Goodman, M.J.: NHTSA driver distraction research: past, present, and future. Transp. Res. Center Inc., East Liberty, OH, Technical Report. (2009)
Zhang, H., Smith, M., Dufour, R.: A final report of safety vehicles using adaptive interface technology (Phase II: Task 7c): Visual distraction. In: Delphi Electron. Tech. Report, Safety, Kokomo, IN (2008)
Carsten, O.M.J., Brookhuis, K.: Issues arising from the haste experiments. Transport. Res. F: Traffic Psychol. Behav. 8(2), 191–196 (2005)
Vicente, F., Huang, Z., Xiong, X., Torre, F.D., Zhang, W., Levi, D.: Driver gaze tracking and eyes off the road detection system. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 16(4), 2014–2027 (2015)
STRID, Sub-Group on Fatigue, Canadian operational definition of driver fatigue, Ottawa, ON, Canada, (2006)
Dingus, T.A., Hardee, L., Wierwille, W.W.: Development of impaired driver detection measures. Dept. Ind. Eng. Oper. Res.,Virginia Polytechnic Inst. State Univ., Blacksburg, VA, Tech. Rep., Dept. Rep. 8504, (1985)
Mast, T., Jones, H., Heimstra, N.: Effects of fatigue on performance in a driving device: highway research record. In: Driver Fatigue Research: Development of Methodology, Haworth, Vulcan, Triggs, and Fildes. Accid. Res. Center, Monash Univ. Australia, Victoria, Australia (1989)
Ilkwon, P., Jung-Ho, A., Hyeran, B.: Efficient measurement of eye blinking under various illumination conditions for drowsiness detection systems. Pattern Recognition, ICPR. (2006)
Takei, Y., Furukawa, Y.: Estimate of drivers fatigue through steering motion. IEEE International Conference on Man and Cybernetics. 1765–1770 (2005)
Krajewski, J., et al.: Steering wheel behavior based estimation of fatigue. In Proceeding International Driving Symposium on Human Factors in Driver Assessment, Training and Vehicle Design. (2009)
Farid, M., et al.: Methods to develop a driver observation system used in an active safety system. VDI Ber. 1960, 639–650 (2006)
Zhong, Y.J., et al.: Localized energy study for analyzing driver fatigue state based on wavelet analysis. In International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition. 1843–1846 (2007)
Hansen, D.W., Ji, Q.: In the eye of the beholder: a survey of models for eyes and gaze. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(3), 478–500 (2010)
Yoo, D.H., Chung, M.J.: A novel non-intrusive eye gaze estimation using cross-ratio under large head motion. CVIU. (2005)
Zhu, Z., Ji, Q.: Eye gaze tracking under natural head movements. CVPR. (2005)
Zhu, Z., Ji, Q., Bennett, K.P.: Nonlinear eye gaze mapping function estimation via support vector regression. In Pattern Recognition Letters. (2006)
Chen, J., Ji, Q.: 3D gaze estimation with a single camera without IR illumination. ICPR (2008)
Valenti, R., Sebe, N., Gevers, T.: Combining head pose and eye location information for gaze estimation. TIP. (2012)
Reale, M., Canavan, S., Yin, L., Hu, K., Hung, T.: A multi-gesture interaction system using a 3-d iris disk model for gaze estimation and an active appearance model for 3-d hand pointing. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia. 13(3), 474–486, 2012 (2011)
Valenti, R., Sebe, N., Gevers, T.: What are you looking at? IJCV. 98(3), 324–334 (2012)
http://www.smarteye.se – Last accessed on April 27th, 2019
Last accessed on April. 27th (2019). http://www.eyealert.com
Jeni, L.A., Hashimoto, H., Kubota, T.: Robust facial expression Recognition using near infrared cameras. Journal of Advanced Computational Intelligence and Intelligent Informatics. (2012)
Martin, S., Tran, C., Tawari, A., Kwan, J., Trivedi, M.M.: Optical flow based head movement and gesture analysis in automotive environment. In: 15th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (2012)
Tiwari, A., Martin, S., Trivedi, M.M.: Continuous head movement estimator for driver assistance: issues, algorithms, and on-road evaluations. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 15(2), (2012)
Imabuchi, T., Prima, O.D.A., Ito, H.: Visible spectrum eye tracking for safety driving assistance, pp. 428–434. Springer International Publishing Switzerland (2016)
Liu, T., Yang, Y., Huang, G.B., Yeo, Y.K., Lin, Z.: Driver distraction detection using semi-supervised machine learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015,
Jha, S., Busso, C.: Analyzing the relationship between head pose and gaze to model driver visual attention. In: IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (2014)
Yuille, A.L., Hallinan, P.W., Cohen, D.S.: Feature extraction from faces using deformable templates. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 8(2), 99–111 (1992)
Rahayfeh, A.A., Faezipour, M.: Eye tracking and head movement detection: a state-of-art survey. IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine. (2013)
Tiwari, A., Martin, S., Trivedi, M.M.: Continuous head movement estimator for driver assistance: issues, algorithms, and on-road evaluations. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 15(2), (2014)
Moeslund, T., Hilton, A., Kruger, V.: A survey of computer vision-based human motion capture. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 81(3), 231–268 (2001)
Moeslund, T., Hilton, A., Kruger, V.: A survey of advances in vision-based human motion capture and analysis. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 104(2), 90–126 (2006)
Hjelmas, E., Lowx, B.: Face detection: a survey. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 83(3), 236–274 (2001)
Horprasert, T., Yacoob, Y., Davis, L.: An anthropometric shape model for estimating head orientation. In: Proc. Third Intl Workshop Visual Form, pp. 247–256 (1997)
Zhao, W., Chellappa, R., Phillips, P., Rosenfeld, A.: Face recognition: A literature survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 35(4), 399–458 (2001)
Fasel, B., Luettin, J.: Automatic facial expression analysis: a survey. Pattern Recogn. 36(1), 259–275 (2003)
Chutorian, E.M., Trivedi, M.M.: Head pose estimation in computer vision: a survey. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 31(4),
Ng, J., Gong, S.: Composite support vector Machines for Detection of faces across views and pose estimation. Image Vis. Comput. 20(5–6), 359–368 (2002) 2009
Duda, R., Hart, P., Stork, D.: Pattern classification, second edn. John Wiley & Sons (2001)
Raytchev, I.Y., Sakaue, K.: Head pose estimation by nonlinear manifold learning. Proc. 17th Intl Conf. Pattern Recogn. 462–466 (2004)
Hansen, D., Ji, Q.: In the eye of the beholder: a survey of models for eyes and gaze. IEEE Trans. PAMI. 32(3), 478–500 (2010)
Bohme, M., Meyer, A., Martinetz, T., Barth, E.: Remote eye tracking: state of the art and directions for future development. In: The 2nd Conf. On Communication by Gaze Interaction, COGAIN, Turin, Italy, pp. 10–15 (2006)
http://www.eyegaze.com/ - Last accessed on June 4th, 2019
Ohno, T.: One-point calibration gaze tracking method. In: Proc. Symp. Eye Tracking Research and Applications, pp. 34–34 (2006)
Morimoto, C.H., Amir, A., Flickner, M.: Detecting eye position and gaze from a single camera and 2 light sources. In Proc. of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition. (2002)
Coutinho, F.L., Morimoto, C.H.: Improving head movement tolerance of cross-ratio based eye trackers. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (2012)
Zhang, K., Zhao, X., Ma, Z., Man, Y.: A simplified 3D gaze tracking technology with stereo vision. In: International Conference on Optoelectronics and Image Processing, pp. 131–134 (2012)
Hung, R.M., Yin, L.: Pointing with the eyes: gaze estimation using a static/active camera system and 3D iris disk model. IEEE Intl. Conf. on Multimedia and Expo. 280–285 (2010)
https://www.fondriest.com/environmentalmeasurements/parameters/weather/photosynthetically-active-radiation/- last Accessed on June 4th, 2019
https://www.creativeplanetnetwork.com/news-features/dv101-makinginvisible-visible-understanding-infrared-filtration-423128- last Accessed on June4, 2019
Last Accessed on June. 4th (2019). https://spectrum.ieee.org/transportation/advanced-cars/bmw-laserheadlights-slice-through-the-dark
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-23265-x last Accessed on June 4th, 2019
http://www.phys.uconn.edu/gibson/Notes/Section5-3/Sec5-3 - last Accessed on June 4th, 2019
hhttp://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/geoopt/lenseq.html- last Accessed on June 4, 2019
https://www.vsp.com/eyeglasses-lenses.html- Accessed on June 4th, 2019
Kummerer, M., Wallis, T.S.A., Bethge, M.: DeepGaze II: Reading fixations from deep features trained on object recognition. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). (2016)
https://www.kaggle.com/kmader/biwi-kinect-head-pose-database - Accessed on June 13th, 2019
https://www.tugraz.at/institute/icg/research/team-bischof/lrs/downloads/aflw/-last Accessed on July 27, 2019
Venkataraman, H., Assfalg, R.: Driver performance detection & recommender system in vehicular environment using video streaming analytics. IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM). 1–3 (2017)
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.zihua.android.mytracks&hl=en_IN, last Accessed May 28th, 2019
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.peterhohsy.gsensor_debug, last accessed May 28th, 2019
https://www.kaggle.com/c/tut-head-pose-estimation-challenge - Last accessed on 6th July, 2019
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of Department of Science and Technology (DST) Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB). Also, the authors thank the Indo-German DST-DAAD agency for their research and travel support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Addanki, S.C., Jaswanth, N., Assfalg, R. et al. Analysis of Traffic Related Factors and Vehicle Environment in Monitoring Driver’s Driveability. Int. J. ITS Res. 18, 277–287 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-019-00198-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-019-00198-x