Abstract
Partitioning a heterogeneous road network into homogenous subnetworks is one way of solving the problem of high scattering or a hysteresis loop that may be inherent in the empirics of a macroscopic fundamental diagram. This study conducts cross-comparison analysis of two well-studied partitioning methods—(i) community detection through modularity maximization and (ii) normalized cut graph partitioning—to investigate the applicability of these methods. Through a case study using real traffic data recorded by an enormous number of detectors in the Tokyo central business district, we found that both methods work well for the test transportation network; however, undesirable results may be obtained if there is only one bottleneck in a subnetwork, or if there is a drastic change in traffic conditions between adjacent links.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
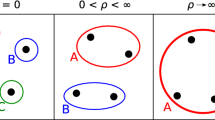
For example, if we choose a value of 100 as the bandwidth, the average is 0.168 and the standard deviation is 0.313, which is low. In such a case, almost all links are disconnected. Meanwhile, a bandwidth of 10,000 leads to an average of 0.992 and standard deviation of 0.018, which would generate almost the same results as the unweighted network. These values would therefore yield undesirable results.
References
Daganzo, C.F.: Urban gridlock: macroscopic modeling and mitigation approaches. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 41(1), 49–62 (2007)
Geroliminis, N., Daganzo, C.F.: Existence of urban-scale macroscopic fundamental diagrams: some experimental findings. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 42(9), 759–770 (2008)
Aboudolas, K., Geroliminis, N.: Perimeter and boundary flow control in multi-reservoir heterogeneous networks. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 55, 265–281 (2013)
Geroliminis, N., Haddad, J., Ramezani, M.: Optimal perimeter control for two urban regions with macroscopic fundamental diagrams: a model predictive approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 14(1), 348–359 (2012)
Zheng, N., Waraich, R.A., Axhausen, K.W., Geroliminis, N.: A dynamic cordon pricing scheme combining the macroscopic fundamental diagram and an agent-based traffic model. Transp. Res. A Policy Pract. 46(8), 1291–1303 (2012)
Zheng, N., Rérat, G., Geroliminis, N.: Time-dependent area-based pricing for multimodal systems with heterogeneous users in an agent-based environment. Trans. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 62, 133–148 (2016)
Geroliminis, N., Zheng, N., Ampountolas, K.: A three-dimensional macroscopic fundamental diagram for mixed bi-modal urban networks. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 42, 168–181 (2014)
Chiabaut, N.: Evaluation of a multimodal urban arterial: the passenger macroscopic fundamental diagram. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 81, 410–420 (2015)
Zheng, N., Dantsuji, T., Wang, P., Geroliminis, N.: Macroscopic approach for optimizing road space allocation of bus lanes in multimodal urban networks through simulation analysis. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board. 2651, 42–51 (2017)
Loder, A., Ambühl, L., Menendez, M., Axhausen, K.W.: Empirics of multi-modal traffic networks – using the 3D macroscopic fundamental diagram. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 82, 88–101 (2017)
Dantsuji, T.: Simulation-based joint optimization framework for congestion mitigation in multimodal urban network: a macroscopic approach. Presented at 15th world conference on transport research, Mumbai (2019)
Buisson, C., Ladier, C.: Exploring the impact of homogeneity of traffic measurements on the existence of macroscopic fundamental diagrams. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board. 2124(1), 127–136 (2009)
Geroliminis, N., Sun, J.: Properties of a well-defined macroscopic fundamental diagram for urban traffic. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 45(3), 605–617 (2011)
Ji, Y., Geroliminis, N.: On the spatial partitioning of urban transportation networks. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 46(10), 1639–1656 (2012)
Ge, Q., Fukuda, D.: A macroscopic dynamic network loading model for multiple-reservoir system. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 126, 502–527 (2019)
Ge, Q., Fukuda, D., Han, K., Song, W.: Reservoir-based surrogate modeling of dynamic user equilibrium. Transp. Res. Procedia. 38, 772–791 (2019)
Saeedmanesh, M., Geroliminis, N.: Dynamic clustering and propagation of congestion in heterogeneously congested urban traffic networks. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 105, 193–211 (2017)
An, K., Chiu, Y.C., Hu, X., Chen, X.: A network partitioning algorithmic approach for macroscopic fundamental diagram-based hierarchical traffic network management. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 19(4), 1130–1139 (2018)
Ambühl, L., Loder, A., Zheng, N., Menendez, M.: Approximative network partitioning for MFDs from stationary sensor data. In: Proceedings of the 18th Swiss Transport Research Conference (2018)
Ge, Q., Wang, P., Fukuda, D.: A community detection for identifying neighborhoods. In: Proceedings of the 21st Hong Kong Society for Transportation Studies Conference (2016)
Newman, M.E.: Spectral methods for community detection and graph partitioning. Phys. Rev. E. 88(4), 042822 (2013)
Shi, J., Malik, J.: Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(8), 888–905 (2000)
Newman, M.E., Girvan, M.: Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E. 69(2), 026113 (2004)
Blondel, V.D., Guillaume, J.L., Lambiotte, R., Lefebvre, E.: Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theor. Exp. 2008(10), P10008 (2008)
Fortunato, S.: Community detection in graphs. Phys. Rep. 486(3–5), 75–174 (2010)
Eom, J., Park, M., Heo, T.Y., Huntsinger, L.: Improving the prediction of annual average daily traffic for nonfreeway facilities by applying a spatial statistical method. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board. 1968, 20–29 (2006)
Bae, B., Kim, H., Lim, H., Liu, Y., Han, L.D., Freeze, P.B.: Missing data imputation for traffic flow speed using spatio-temporal cokriging. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 88, 124–139 (2018)
Mazloumian, A., Geroliminis, N., Helbing, D.: 2010. The spatial variability of vehicle densities as determinant of urban network capacity. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society a: mathematical. Phys. Eng. Sci. 368, 4627–4647 (1928)
Wada, K., Satsukawa, K., Smith, M., Akamatsu, T.: Network throughput under dynamic user equilibrium: queue spillback, paradox and traffic control. Transp. Res. B Methodol. 126, 391–413 (2019)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI under grant number JP 18 J15178 and by the Committee on Advanced Road Technology, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism, Japan under grant number #28-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dantsuji, T., Hirabayashi, S., Ge, Q. et al. Cross Comparison of Spatial Partitioning Methods for an Urban Transportation Network. Int. J. ITS Res. 18, 412–421 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-019-00209-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-019-00209-x