Abstract
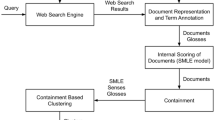
Information retrieval (IR) is the process of finding relevant information from the millions of unstructured documents on the web. Despite of all the success in IR, it faces many problems such as lexical ambiguity, compound word formation and language morphology etc. To address the ambiguity problem, in this paper the authors proposed a graph based soft clustering method which improves the performance of IR system. Initially text snippet words are taken for constructing a co-occurrence graph corresponding to the Hindi query given by a user. Then other words (relevant to the query terms) present in the text corpus are added on the basis of the dice coefficient. For each interpretation of the user query, we retrieve results in the form of a web cluster. Sometimes more than one interpretation of the query are closely related, therefore many results returned from IR corresponding to these interpretations are common. This type of issue can be better dealt by using soft clustering method, so we use Max–Max soft clustering approach. We use various similarity measures like word overlap, degree overlap, token overlap and average similarity respectively for ranking the results within each cluster. This is the first attempt to fuzzy IR for a query in Hindi language, experimental evaluations shows promising results.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biemann C (2006) Chinese whispers—an efficient graph clustering algorithm and its application to natural language processing problems. In: Proceedings of the 1st workshop on graph-based algorithms for natural language processing, New York, pp 73–80
Clough P, Mark S, Murad A, Sergio N, Monica LP (2009) Multiple approaches to analysing query diversity. In: Proceedings of the 32nd annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, Boston, pp 734–735
David H, Bill K (2013) Max–Max: a graph-based soft clustering algorithm applied to word sense induction. In: Gelbukh A (ed) CICLing Part 1. LNCS, vol. 7816. Springer, Berlin, pp 368–381
Devendra KT, Amita J, Neha D, Shuchi G (2014) MetaSurfer: a new metasearch engine based on FAHP and modified EOWA operator. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 99:1–13
Dwivedi KS (2008) An entropy based method for removing web query ambiguity in Hindi language. J Comput Sci 4(9):762–767
Fellbaum C (1998) WordNet: an electronic database. MIT Press, Cambridge
Frakes WB (1992) Stemming algorithms. In: Information retrieval: data structures & algorithms. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, pp 131–160
Furnas GW, Landauer TK, Gomez LM, Dumais ST (1987) The vocabulary problem in human–system communication. Commun ACM 30(11):964–971
Iadh O, Gianni A, Vassilis P, Ben H, Craig M, Douglas J (2005) Terrier information retrieval platform. In: Proceedings of the 27th European conference on information retrieval. Springer, Berlin
Iadh O, Gianni A, Vassilis P, Ben H, Craig M, Christina L (2006) Terrier: a high performance and scalable information retrieval platform. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGIR’06 workshop on open source information retrieval, Seattle, 10 Aug 2006
Iadh O, Christina L, Craig M, Vassilis P (2007) Research directions in terrier: a search engine for advanced retrieval on the Web. In: Novatica/UPGRADE special issue on next generation web search, vol 8. pp 849–56
Jain A, Yadav SK, Tayal D (2013) Measuring context-meaning for open class words in Hindi language. In: 6th International conference on contemporary computing (IEEE), 8–10 Aug 2013 , Noida, India, vol 8, pp 118–123
Kamvar M, Baluja S (2006) A large scale study of wireless search behavior: google mobile search. In: Proceedings of the 2006 conference on human factors in computing systems, Montreal, pp 701–709
Klapaftis I, Manandhar S (2008) Word sense induction using graphs of collocations. In: Proceedings of the 2008 conference on ECAI, pp 298–302
Kumar S (2012a) An experimental analysis on the influence of English on Hindi language information retrieval. Int J Comput Appl 41(11):30–35
Kumar S (2012b) Query optimization: a solution for low recall problem in Hindi language information retrieval. Int J Comput Appl 55(17):6–17
Lakshmikant U, Sachidanand S (2014) Hindi dictionary
Lesk M (1986) Automatic sense disambiguation using machine readable dictionaries: how to tell a pine cone from an ice cream cone. In: Proceedings of the 5th annual international conference on systems documentation. ACM Press, New York, pp 24–26
Marco D, Roberto N (2013) Clustering and diversifying search results with graph-based WSI. Comput Linguist 39(3):709–754
Miller GA, Beckwith R, Fellbaum C, Gross D, Miller KJ (1990) Introduction to wordnet: an on-line lexical database. Int J Lexicogr 3(4):235–244
Rakesh A, Sreenivas G, Alan H, Samuel L (2009) Diversifying search results. In: Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on web search and web data mining, Barcelona, pp 5–14
Roberto N (2009) Word sense disambiguation: a survey. ACM Comput Surv 41(2):10
Sanderson M (2008) Ambiguous queries: test collections need more sense. In: Proceedings of the 31st annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, Singapore, pp 499–506
Siddiqui T, Tiwari US (2010) Natural language processing and information retrieval. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Sinha M, Bhattacharya RP (2008) Hindi word sense disambiguation. In: Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Indian Institute of Information Technology, Mumbai
Song R, Luo Z, Nie J.-Y, Yong Y, Hon H.-W (2009) Identification of ambiguous queries in web search. Inf Process Manag 45:216–229
Swaminathan A, Cherian VM, Darko K (2009) Essential pages. In: Proceedings of 2009 IEEE/WIC/ACM international conference on web intelligence. IEEE Computer Society, Milan, pp 173–182
Wittgenstein L (1953) Philosophical investigations. Blackwell, Oxford
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Glossary
- विडियोगेम
-
Name of a game
- मॅक
-
Name of an operating system
- पशु
-
Animal
- अनुकरण
-
Simulation/Imitation
- प्रोधौगिकी
-
Technology
- टाइगर
-
Tiger (name of an animal)/name of an operating system
- सोफ्टवेयर
-
Software
- एप्पल
-
Name of a brand/name of a fruit
- जग
-
Jug
- संसार, दुनिया, विश्व
-
World
- एप्पल
-
Name of a brand/name of a fruit
- फोन
-
Phone
- बिल्ली
-
Cat
- विडालवंशी
-
Carnivorous
- थार
-
Name of a desert
- राजस्थान
-
Name of a Indian state
- परभक्षी
-
Predator
- एप्पल
-
Name of a brand/name of a fruit
- बर्तन
-
Utensils
- जुर्माना, जुरमाना
-
Fine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, A., Tayal, D.K. & Yadav, S. Retrieving web search results using Max–Max soft clustering for Hindi query. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 7 (Suppl 1), 70–81 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-014-0307-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-014-0307-5