Abstract
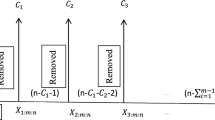
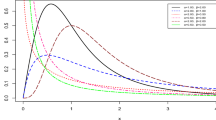
This paper proposes a Poisson-inverse exponential distribution (PIED) as a lifetime model with initially increasing then decreasing failure model. Its statistical characteristics and important distributional properties are discussed along with its reliability and failure rate function. The maximum likelihood estimators (MLEs) and Bayes estimators of parameters of PIED under symmetric and asymmetric loss functions for progressive type-II censored data with binomial removals have been obtained. The MLEs and corresponding Bayes estimators are compared in terms of their simulated risks. The proposed methodology is illustrated through a real data set of bladder cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balakrishnan N (2007) Progressive methodology: an appraisal (with discussion). Test 16(2):211–259
Balakrishnan N, Cramer E, Kamps U (2001) Bounds for means and variances of progressive type-II censored order statistics. Stat Probab Lett 54:301–315
Balakrishnan N, Sandhu RA (1995) A simple simulational algorithm for generating progressive type-II censored samples. Am Stat 49(2):229–230
Barreto-Souza W, Cribari-Neto F (2009) A generalization of the exponential-Poisson distribution. Stat Probab Lett 79(24):2493–2500
Calabria R, Pulcini G (1996) Point estimation under-asymmetric loss functions for life -truncated exponential samples. Commun Stat Theory Methods 25(3):585–600
Cancho GV, Louzada-Neto F, Gladys D C Barriga (2011) The Poisson-exponential lifetime distribution. Comput Stat Data Anal 55(1):677–686
Chib S, Greenberg E (1995) Understanding the metropolis-hastings algorithm. J Am Stat Assoc 49(2):327–335
Childs A, Balakrishnan N (2000) Conditional inference procedures for the Laplace distribution when the observed samples are progressively censored. Metrika 52(3):253–265
Cohen AC (1963) Progressively censored samples in life testing. Technometrics 5(3):327–339
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Methodol) 39(1):1–38
Dey DK, Ghosh M, Srinivasan C (1987) Simultaneous estimation of parameters under entropy loss. J Stat Plan Inference 15(3):347–363
Gelfand A E, Hills S E, Poon A Racine, Smith A F M (1990) Illustration of Bayesian inference in normal data models using Gibbs sampling. J Am Stat Assoc 85(412):972–985
Hogg RV, Mckean JW, Craig AT (2009) Introduction to mathematical statistics, 6th edn. Macmillan Publishing, New York
Kalbfleisch JD, Lawless JF (1989) Inference based on retrospective ascertainment: an analysis of the data on transfusion related AIDS. J Am Stat Assoc 84(406):360–372
Kamps U, Cramer E (2001) On distributions of generalized order statistics. Statistics 35(3):269–280
Krishnan T, McLachlan G (1997) The EM algorithm and extensions. Wiley, New York
Kus C (2007) A new lifetime distributions. Comput Stat Data Anal 51(9):4497–4509
Lawless JF (1982) Statistical models and methods for lifetime data, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Lee ET, Wang JW (2003) Statistical methods for survival data analysis, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Lin CT, Duran BS, Lewis TO (1989) Inverted gamma as life distribution. Microelectron Reliab 29(4):619–629
Louzada F, Cancho V G, Barriga Gladys D C (2012) The Poisson-exponential regression model under different latent activation schemes. Comput Appl Math 31(3):617–632
Louzada-Neto F, Cancho VG, Barriga GD (2011) The poisson-exponential distribution: a Bayesian approach. J Appl Stat 38(6):1239–1248
Nassar MM, Eissa FH (2004) Bayesian estimation for the exponentiated Weibull model. Commun Stat Theory Methods 33(10):2343–2362
Ng HKT, Chan PS, Balakrishnan N (2002) Estimation of parameters from progressively censored data using an algorithm. Comput Stat Data Anal 39(4):371–386
Schabe H (1991) Bayes estimates under asymmetric loss. IEEE Trans Reliab 40(1):63–67
Singh SK, Singh U, Kumar M (2013a) Estimation of parameters of exponentiated Pareto distribution for progressive type-ii censored data with binomial random removals scheme. Electron J Appl Stat 06(2):130–148
Singh SK, Singh U, Kumar M (2013b) Estimation of parameters of generalized inverted exponential distribution for progressive type-II censored sample with binomial removals. J Probab Stat 2013:1–12
Singh SK, Singh U, Kumar M (2014a) Bayesian estimation for Poission-exponential model under progressive type-II censoring data with binomial removal and its application to ovarian cancer data. Commun Stat Simul Comput 45(9):3457–3475
Singh SK, Singh U, Kumar M (2014b) Bayesian inference for exponentiated Pareto model with application to bladder cancer remission time. Stat Transit 15(3):403–426
Singh SK, Singh U, Kumar M (2014c) Estimation for the parameter of Poisson-exponential distribution under Bayesian paradigm. J Data Sci 12(2014):157–173
Smith AFM (1991) Bayesian computational methods. Philos Trans Phys Sci Eng 337(1647):369–386
Tomazella VLD, Cancho VG, Louzada F (2013) The Bayesian reference analysis for the Poisson-exponential lifetime distribution. Chil J Stat 4(1):99–113
Tse SK, Yang C, Yuen HK (2000) Statistical analysis of Weibull distributed life time data under type ii progressive censoring with binomial removals. J Appl Stat 27(8):1033–1043
Zea LM, Silva RB, Bourguignon M, Santos AM, Cordeiro GM (2012) The Beta exponentiated Pareto distribution with application to bladder cancer susceptibility. Int J Stat Probab 1(2):8–19
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank editors and referees for there constructive comments and suggestions which improved and enriched the presentation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1: Proof of Theorem
The conditional density of the random variable \(X = max(Y_{1, 2, \ldots ,} Y_{N})\) is given by
Then the joint distribution of X and N is given by:
The marginal pdf of X can be easily obtained as follows:
Appendix 2: Proof for h(0) and \(h(\infty ) = 0\)
Since the failure rate function with \(\lim _{x\rightarrow 0} h(x; \lambda , \theta )\) and \(\lim _{x\rightarrow \infty } h(x; \lambda , \theta )\) are given as
and
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Singh, S.K. & Singh, U. Bayesian inference for Poisson-inverse exponential distribution under progressive type-II censoring with binomial removal. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 9, 1235–1249 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-018-0704-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-018-0704-2