Abstract
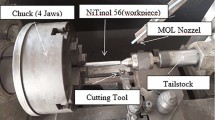
In duplex turning, two-cutting tools as primary-tool is mounted on main tool post and secondary-tool is mounted on indigenous tool post on lathe machine. The objective of present work is to optimize the duplex turning parameters for primary cutting force, secondary cutting force and surface roughness for aerospace material especially Nickel alloy (Ni-718). For this, Taguchi methodology (TM) with response surface methodology (RSM) is utilized for modeling as well as multi-objective optimization of parameters. Firstly, the TM approach has been applied to determine the central value using experimental data, which is used as central value for RSM modeling. The results show that significant improvement in the all responses at optimal data with acceptable limit of errors. It also shows the percentage decrease in primary cutting force = 9.06%, secondary cutting force = 30.91% with improvement in average surface roughness = 1.78% positively.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- V:
-
Cutting velocity (m/min)
- f:
-
Feed rate (mm/rev)
- Dp:
-
Primary-DOC (mm)
- Ds:
-
Secondary-DOC (mm)
- Ra:
-
Average surface roughness (µm)
- Fp:
-
Primary cutting force (N)
- Fs:
-
Secondary cutting force (N)
- n:
-
Number of experiments
- yi :
-
Observed data
- yij :
-
Normalized quality loss
- wi :
-
Associate weight
- Q:
-
Quality loss
- DF:
-
Degree of freedom
- DOC:
-
Depth of cut
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- SS:
-
Sum of squares
- MS:
-
Mean of squares
- PC:
-
Percentage contribution
- TNQL:
-
Total normalized quality loss
- η:
-
Signal to Noise ratio (dB)
- ∑:
-
Summation
References
Aggarwal A, Singh H, Kumar P, Singh M (2008) Optimizing power consumption for CNC turned parts using response surface methodology and Taguchi's technique—a comparative analysis. J Mater Process Technol 200(3):373–384
Ahmed SU, Arora R (2019) Quality characteristics optimization in CNC end milling of A36 K02600 using Taguchi’s approach coupled with artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-019-00796-8
Akincioglu S, Gokkaya H, Uygur I (2016) The effects of cryogenic-treated carbide tools on tool wear and surface roughness of turning of Hastelloy C22 based on Taguchi method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82(1):303–314
Asilturk I, Neseli S (2012) Multi response optimisation of CNC turning parameters via Taguchi method-based response surface analysis. Measurement 45(4):785–794
Balki MK, Sayin C, Sarıkaya M (2016) Optimization of the operating parameters based on Taguchi method in an SI engine used pure gasoline, ethanol and methanol. Fuel 180:630–637
Boucha K, Yallese MA, Mabrouki TM (2010) Statistical analysis of surface roughness and cutting forces using response surface methodology in hard turning of AISI 52100 bearing steel with CBN tool. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 28(3):349–361
Bouzid L, Yallese MA, Chaoui K, Mabrouki T, Boulanouar L (2015) Mathematical modeling for turning of AISI 420 stainless steel using surface response methodology. Proc IMechE Part B: J Eng Manuf 229(1):45–61
Budak E, Ozturk E (2011) Dynamics and stability of parallel turning operations. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 60(1):383–386
Chahal M, Singh V, Garg R (2017) Optimum surface roughness evaluation of dies steel H-11 with CNC milling using RSM with desirability function. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 8(2):432–444
Davoodi B, Hosseini TA (2016) Cutting forces and surface roughness in wet machining of Inconel alloy 738 with coated carbide tool. Proc IMechE Part B: J Eng Manuf 230(2):215–226
Dureja JS, Singh R, Bhatti MS (2014) Optimizing flank wear and surface roughness during hard turning of AISI D3 steel by Taguchi and RSM methods. Prod Manuf Res 2(1):767–783
Galanis NI, Manolakos DE (2010) Surface roughness prediction in turning of femoral head. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 51(1/4):79–86
Gupta MK et al (2019) Parametric optimization and process capability analysis for machining of nickel-based superalloy. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 102(9/12):3995–4009
Kalidasan R, Ramanuj V, Sharma DK, Senthivalen S (2014) Influence of cutting speed and offset distance over cutting tool vibration in multi-tool cutting vibration. Adv Mater Res 984–985:100–105
Kalidasan R, Yatin M, Sarma DK, Senthilvelan S, Dixit US (2016) An experimental study of cutting forces and temperature in multi-tool turning of grey cast iron. Int J Mach Mach Mater 18(5/6):540–551
Kalidasan R, Senthilvelan S, Dixit US (2017) An experimental study of surface roughness in double tool turning process. Int J Add Sub Mater Manuf 1(3/4):310–327
Kumar S, Yadav RN, Kumar R (2017) Experimental studies on duplex turning of titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V). In: The proceedings of IEEE international conference on advances in mechanical industrial automation and management system, vol 01, pp 337–341
Meral G, Sarıkaya M, Dilipak H, Seker U (2015) Multi-response optimization of cutting parameters for hole quality in drilling of AISI 1050 steel. Arab J Sci Eng 40(12):3709–3722
Mia M, Dey PR, Hossain MS, Arafat MT, Asaduzzaman M, Ullah MS, Zobaer ST (2018) Taguchi S/N based optimization of machining parameters for surface roughness, tool wear and material removal rate in hard turning under MQL cutting condition. Measurement 122(1):380–391
Montgomery DC (2017) Design and analysis of experiments. Wiley, New York
Nalbant M, Gokkaya H, Sur G (2007) Application of Taguchi method in the optimization of cutting parameters for surface roughness in turning. Mater Des 28(4):1379–1385
Noordin MY, Venkatesh VC, Sharif S, Elting S, Abdullah A (2004) Application of response surface methodology in describing the performance of coated carbide tools when turning AISI 1045 steel. J Mater Process Technol 145(1):46–58
Ozcelik Y, Engine IC (2017) Development of cuttability abacuses in abrasive water jet cutting with regards to depth of cut and roughness of cut surfaces. J Test Eval 45(5):1809–1819
Patole PB, Kulkarni VV (2018) Optimization of process parameters based on surface roughness and cutting force in MQL turning of AISI 4340 using nano fluid. Mater Today: Proc 5(1):104–112
Phadke MS (1989) Quality engineering using robust design. Prentice-Hill, Englewood Cliffs
Puri AB, Bhattacharyya B (2005) Modeling and analysis of white layer depth in a wire-cut EDM process through response surface methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25(3/4):301–307
Ramana MV, Aditya YS (2017) Optimization and influence of process parameters on surface roughness in turning of titanium alloy. Mater Today: Proc 4(2):1843–1851
Sait AN, Aravindan S, Haq AN (2009) Optimisation of machining parameters of glass-fiber-reinforced plastic (GFRP) pipes by desirability function analysis using Taguchi technique. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 43(1):581–589
Sarıkaya M, Gullu A (2014) Taguchi design and response surface methodology based analysis of machining parameters in CNC turning under MQL. J Clean Prod 65:604–616
Sarıkaya M, Gullu A (2015) Multi-response optimization of minimum quantity lubrication parameters using Taguchi-based grey relational analysis in turning of difficult-to-cut alloy Haynes 25. J Clean Prod 91(1):347–357
Sarıkaya M, Yılmaz V, Gullu A (2016) Analysis of cutting parameters and cooling/lubrication methods for sustainable machining in turning of Haynes 25 superalloy. J Clean Prod 133(1):172–181
Selvaraj DP, Chandramohan P, Mohanraj M (2014) Optimization of surface roughness, cutting force and tool wear of nitrogen alloyed duplex stainless steel in a dry turning process using Taguchi method. Measurement 49:205–215
Shinde R, Sonawane SA (2018) Effect of speed, feed and depth of cut on vibration and surface roughness during turning operation. J Mech Prod Eng Res Dev 8(4):819–826
Tang L, Landers RG, Balakrishnan SN (2008) Parallel turning process parameter optimization based on a novel heuristic approach. J Manuf Sci Eng 130(3):031002
Yadav RN (2017a) Development and experimental investigation of duplex turning process. Adv Manuf 5(2):149–157
Yadav RN (2017b) A hybrid approach of Taguchi-Response surface methodology for modeling and optimization of duplex turning process. Measurement 100(1):131–138
Yadav RN (2018) An experimental study and parameters optimization on duplex turning of titanium alloy. Mater Perform Charact 7:423–444
Yildirim CV, Sarikaya M, Kivak T, Sirin S (2019) The effect of addition of hBN nanoparticles to nano fluid-MQL on tool wears patterns, tool life, roughness and temperature in turning of Ni-based Inconel 625. Tribol Int 134:443–456
Zhang Q, Zhang S, Shi W (2018) Modeling of surface topography based on relationship between feed per tooth and radial depth of cut in ball-end milling of AISI H13 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 95(9/12):4199–4209
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Yadav, R.N. & Kumar, R. Empirical modeling and multi-response optimization of duplex turning for Ni-718 alloy. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 11, 126–139 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-019-00931-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-019-00931-5