Abstract
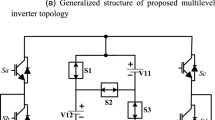
The quality of power generation from various energy sources is essential for industrial and household applications. To achieve the quality of power by reducing the Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) through multilevel inverters (MLIs) is an attractive solution. MLIs have drawn tremendous performance as compared to the classical two-level inverter for reducing the %THD and lower electromagnetic interference. However, MLIs having more device count and intricacy of the circuitry and reducing the THD further might affect the cost, size, and complexity of the circuit. In this paper, a new inverter topology is proposed to have a low level of THD and reduced part count. The proposed topology consists of a combination of the synchronous buck converter and cascaded with an H-bridge. This approach reduces the requirement of the number of isolated dc voltage sources, switches, and other components in addition to low %THD. More specifically, the proposed inverter does not need dc voltage sources of different values, minimizes the cost and size of the system as compared with the conventional and hybrid topologies. The effectiveness of the proposed converter is validated using the results of both simulations and experiments on the laboratory prototype of the 150 W converter.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alishah RS, Nazarpour D, Hosseini SH, Sabahi M (2014) Switched-diode structure for multilevel converter with reduced number of power electronic devices. IET Power Electron 7(3):648–656
Alishah RS, Nazarpour D, Hosseini SH, Sabahi M (2014) Novel topologies for symmetric, asymmetric, and cascade switched-diode multilevel converter with minimum number of power electronic components. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(10):5300–5310
Alishah RS, Nazarpour D, Hosseini SH, Sabahi M (2015) Reduction of power electronic elements in multilevel converters using a new cascade structure. IEEE Trans on Ind Electron 62(1):256–269
Anand V, Singh V (2020) Compact symmetrical and asymmetrical multilevel inverter with reduced switches. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/2050-7038.12458
Babaei E, Laali S, Bayat Z (2015) A single-phase cascaded multilevel inverter based on a new basic unit with reduced number of power switches. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(2):922–929
Babaei E, Hosseini SH (2007) “Charge balance control methods for asymmetrical cascade multilevel converters, In: Proceeding of international conference on electrical machines and systems, Korea.
Dhananjaya M, Pattnaik S (2018) “Design and analysis of a novel universal power converter”, In: Proceeding of internatinal conference power, instrumentation, control and computing (PICC), pp. 1–6, Thrissur, India.
Du Z, Ozpineci B, Tolbert LM, Chiasson JN (2009) DC–AC cascaded H-bridge multilevel boost inverter with no inductors for electric/hybrid electric vehicle applications”. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 45(3):963–970
Espinoza JR (2001) “Inverters,” Power electronics handbook, Rashid MH, Ed. New York, NY, USA: Elsevier, pp. 225–269.
Gautam SP, Kumar L, Gupta S (2015) Hybrid topology of symmetrical multilevel inverter using less number of devices. IET Power Electron 8(11):2125–2135
Gupta KK, Jain S (2013) Multilevel inverter topology based on series connected switched sources. IET Power Electron 6(1):164–174
Gupta KK, Jain S (2014) A novel multilevel inverter based on switched DC sources. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(7):3269–3278
Kangarlu MF (2013) A generalized cascaded multilevel inverter using series connection of submultilevel inverters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(2):625–636
Kangarlu MF, Babaei E (2013) A generalized cascaded multilevel inverter using series connection of submultilevel inverters. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(2):625–636
Kirthika Devi VS, Srivani SG (2017) “Modified phase shifted PWM for cascaded H-bridge multilevel inverter," In: Proceeding of AEEICB17, pp. 89–94.
Kumar A, Sensarma P (2017) A four-switch single-stage single-phase buck-boost inverter. IEEE Trans Power electron 32(7):5282–5292
Kumari M, Siddique MD, Sarwar A, Tariq M, Mekhilef S, Iqbal A (2021) Recent trends and review on switched-capacitor-based single-stage boost multilevel inverter. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/2050-7038.12730
Marian K, Czuk K (2008) Pulse-width modulated DC–DC power converters. Wiley, New York, NY, USA
Mohamad AS, Mariun N, Nasri Sulaiman, Radzi MAM (2015) A new cascaded multilevel inverter topology with minimum number of conducting switches," In: IEEE (ISGT ASIA), ASIA.
Raman SR, Cheng KWE, Ye Y (2018) Multi-input switched-capacitor multilevel inverter for high-frequency AC power distribution”. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(7):5937–5948
Rani PS, Prasadarao VS, Koppineni K, Subbarao RNV (2014) Comparison of symmetrical and asymmetrical multilevel inverter topologies with reduced number of switches," In: Proceeding of IEEE.
Rashid MH (2006) Power electronics circuits, devices, and applications, 3rd ed., published by Pearson education, South Asia.
Singh V, Pattnaik S, Gupta S, Santosh B (2016) A single-phase cell-based asymmetrical cascaded multilevel inverter. J Power Electron 16(2):532–541
Singh J, Dahiya R, Saini LM (2018) Buck converter–based cascaded asymmetrical multilevel inverter with reduced components. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst 28(3):e2501
Zaragoza J, Pou J, Ceballos S, Robles E, Ibanez P, Villate JL (2009) A comprehensive study of a hybrid modulation technique for the neutral-point-clamped converter. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 56(2):294–304
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhananjaya, M., Pattnaik, S. & Potnuru, D. Design and implementation of a new inverter topology with reduced THD and part count. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 13, 1410–1418 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01486-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-021-01486-0