Abstract
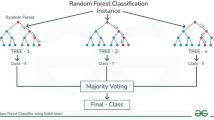
Use of smokeless tobacco (SLT) in women is very high and serious public health issue in the northeast states, India. Prediction on status of SLT use among women is a key to policy making and resource planning at district and community level in this region. This study aims to predict the status of smokeless tobacco use among women in northeast states of India by applying several machine learning (ML) algorithms. We used publicly available National Family Health Survey, 2015–16 data. Eight ML algorithms were used for the prediction on status of SLT use. Precision, specificity, sensitivity, accuracy, and Cohen’s kappa statistic were performed as a part of the systematic assessment of the algorithms. Result of this study reveals that the best classification performance was accomplished with random forest (RF) algorithm accuracy of 79.51% [77.65–81.37], sensitivity of 87.75% [86.55–88.95], specificity of 65.19% [65.18–65.20], precision of 81.39%, F-measure of 84.35 and Cohen’s Kappa was 0.545 [0.529–0.558]. It was concluded that the algorithm of random forest was found superior and performed much better as compared to the rest ML algorithms in predicting the status on smokeless tobacco use in women of northeast states, India. Finally, this research finding recommends application of RF algorithm for classification and feature selection to predict the status of smokeless tobacco as a core interest.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agresti A (2018) An introduction to categorical data analysis. Wiley, New Jersey
Altman NS (1992) An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am Stat 46(3):175–185. https://doi.org/10.1080/00031305.1992.10475879
Balakrishnama S, Ganapathiraju A (1998) Linear discriminant analysis-a brief tutorial. Inst Signal Inf Process 18(1998):1–8
Bergström J, Preber H (1994) Tobacco use as a risk factor. J Periodontol 65:545–550. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.1994.65.5s.545
Boyle P, Gray N, Henningfield J, Seffrin J, Zatonski W (eds) (2010) Tobacco: science, policy and public health. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199566655.001.0001
Cagala T (2017) Improving data quality and closing data gaps with machine learning (Vol. 46). Bank for International Settlements
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20(3):273–297
Desalu OO, Iseh KR, Olokoba AB, Salawu FK, Danburam A (2010) Smokeless tobacco use in adult Nigerian population. Niger J Clin Pract, 13(4)
Efron B (1983) Estimating the error rate of a prediction rule: improvement on cross-validation. J Am Stat Assoc 78(382):316–331. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1983.10477973
Fix E, Hodges JL (1989) Discriminatory analysis. Nonparametric discrimination: consistency properties. Int Stat Rev/revue Int Stat 57(3):238–247
Gandhi R (2018) Support vector machine—introduction to machine learning algorithms. Towards Data Science, 7
Gomes HM, Bifet A, Read J, Barddal JP, Enembreck F, Pfharinger B, Abdessalem T (2017) Adaptive random forests for evolving data stream classification. Mach Learn 106(9):1469–1495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-017-5642-8
Gupta R, Gurm H, Bartholomew JR (2004) Smokeless tobacco and cardiovascular risk. Arch Intern Med 164(17):1845–1849
Haobijam N, Nair S, Devi AS, Singh SR, Hijam M, Alee NT, Rao MVV (2021) Smokeless tobacco use among women in northeastern states, India: a study of spatial clustering and its determinants using National Family Health Survey-4 data. Clin Epidemiol Global Health 12:100840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100840
Ho TK (1998) C4. 5 decision forests. In: Proceedings fourteenth international conference on pattern recognition (Cat. No. 98EX170), Vol. 1. IEEE, pp. 545–549. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDAR.1995.598994
Islam MS, Saif-Ur-Rahman KM, Bulbul M, Islam M, Singh D (2020) Prevalence and factors associated with tobacco use among men in India: findings from a nationally representative data. Environ Health Prev Med 25(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12199-020-00898-x
Jain S, Shukla S, Wadhvani R (2018) Dynamic selection of normalization techniques using data complexity measures. Expert Syst Appl 106:252–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.04.008
Ladusingh L, Dhillon P, Narzary PK (2017) Why do the youths in northeast India use tobacco? J Environ Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1391253
Lahoti S, Dixit P (2021) Declining trend of smoking and smokeless tobacco in India: a decomposition analysis. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0247226
Lewis RJ (2000) An introduction to classification and regression tree (CART) analysis. In Annual meeting of the society for academic emergency medicine in San Francisco, California (Vol. 14)
Loh WY (2011) Classification and regression trees. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Data Min Knowl Discov 1(1):14–23. https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.8
Menard S (2002) Applied logistic regression analysis (Vol. 106). Sage
Meyer D, Leisch F, Hornik K (2003) The support vector machine under test. Neurocomputing 55(1–2):169–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-2312(03)00431-4
Naive Bayes Classifier in Machine Learning. Java Point. naive-bayes-classifier.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2021 Aug 11]. https://www.ic.unicamp.br/~rocha/teaching/2011s2/mc906/aulas/naive-bayes-classifier.pdf
Pednekar MS, Vasa J, Narake SS, Sinha DN, Gupta PC (2016) Tobacco and alcohol associated mortality among men by socioeconomic status in In-dia. Epidemiol Open J 1(1):2–15
Rao O (2017) Number of tobacco users down, but India still world’s second largest consumer, producer. Hindustan times. https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/number-of-tobacco-users-down-but-india-still-world-s-second-largest-consumer-producer/story-DIP9MwqlES1k8vJd1cmlPJ.html
Saikia B, Marbaniang SP, Kumar P, Dhillon P (2021) Changing pattern of tobacco consumption and quitting behavior in Northeast India. J Subst Use. https://doi.org/10.1080/14659891.2021.1875068
Sarica A, Cerasa A, Quattrone A (2017) Random forest algorithm for the classification of neuroimaging data in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Front Aging Neurosci 9:329. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00329
Sarkar (2021) What is linear discriminant analysis (LDA)?. Knowledge Hut
Sutton O (2012) Introduction to k nearest neighbour classification and condensed nearest neighbour data reduction. University lectures, University of Leicester, p 1
Svetnik V, Liaw A, Tong C, Culberson JC, Sheridan RP, Feuston BP (2003) Random forest: a classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 43(6):1947–1958
Uddin S, Khan A, Hossain ME, Moni MA (2019) Comparing different supervised machine learning algorithms for disease prediction. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 19(1):1–16
US Department of Health and Human Services (2014) The health consequences of smoking—50 years of progress: a report of the Surgeon General. https://doi.org/10.1037/e510072014-001
Vogt WP, Johnson B (2011) Dictionary of statistics & methodology: A nontechnical guide for the social sciences. Sage
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Yu X (2020) A comparative assessment of credit risk model based on machine learning—a case study of bank loan data. Procedia Comput Sci 174:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.06.069
WHO (2007) Smokeless tobacco and some tobacco-specific N-nitrosamines, Vol. 89. World Health Organization
World Health Organization (2019) WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2019: Offer help to quit tobacco use. World Health Organization
Wright RE (1995) Logistic regression. In: Grimm LG, Yarnold PR (eds) Reading and understanding multivariate statistics. American Psychological Association, pp 217–244
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge Ms. Sunita Sharma, Techinical Officer, ICMR-NIMS for her contribution in data management. They also acknowledge all respondent for their active participation in nationally representative survey, NHFS-4 (2015-16).
Funding
The authors did not receive any kind of fund or financial support to conduct the study. This study did not receive any grants from any funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was concieved by JKS and AJM and devised the plan for analysis. The Analysis was led by JKS and AJM. JKS, AJM, NTA and MK drafted the first manuscript. JKS, AJM, NTA, MK and HNS did the manuscript writing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflicting interest among the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jitenkumar Singh, K., Jiran Meitei, A., Alee, N.T. et al. Machine learning algorithms for predicting smokeless tobacco status among women in Northeastern States, India. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 13, 2629–2639 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-022-01720-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-022-01720-3