Abstract
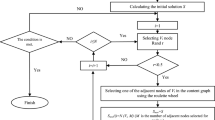
Detection of communities within social networks is a nontrivial problem. Allowing communities to overlap—i.e. nodes can belong to more than one community simultaneously—further complicates the problem. Nevertheless, people do belong to multiple social groups simultaneously and being able to detect overlapping communities is an important step into being able to understand and analyze social networks. A common practice in community detection (clustering) is to view the network (graph) as a whole and have a central control process determine how nodes are clustered. That central control, we believe, is a limitation to performance. In our previous work, we showed that the individual’s view of his or hers social groups could be aggregated to produce communities. In this paper, we propose a unique approach to community detection that combines the individual’s view of a community, not having the view the graph as a whole, with swarm intelligence as a means of removing the central control mechanism. Our approach offers a community detection solution that finds overlapping communities while running in O(n log2 n) time.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barabási A-L (2002) Linked: the new science of networks. Perseus, Cambridge
Baumes J, Goldberg M, Magdon-ismail M (2005) Efficient identification of overlapping communities. In: IEEE international conference on intelligence and security informatics (ISI), pp 27–36
Beni G, Wang J (1989) Swarm intelligence in cellular robotic systems. In: NATO advanced workshop on robots and biological systems, vol 102
Boguna M, Pastor-Satorras R, Diaz-Guilera A, Arenas A (2004) Models of social networks based on social distance attachment. Phys Rev E 70:056122
Brandes U, Delling D, Gaertler M, Gorke R, Hoefer M, Nikoloski Z, Wagner D (2008) On modularity clustering. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 20(2):172–188
Buchanan M (2003) Nexus: small worlds and the groundbreaking theory of networks, W. W. Norton & Company
Chartrand G (1985 [1977]). Introductory graph theory, Dover Publications, Inc., New York
Clauset A (2005) Finding local community structure in networks. Phys Rev E 72:026132+
Clauset A, Newman MEJ, Moore C (2004) Finding community structure in very large networks. Phys Rev E 70:066111+
Davis G, Carley K (2008) Clearing the fog: Fuzzy, overlapping groups for social networks. Social Netw 30:201–212
de Oliveira TBS, Zhao L (2008). Complex network community detection based on swarm aggregation. In: Proceedings of the 2008 fourth international conference on natural computation, vol 7, ICNC’08, IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, pp 604–608
Deŕenyi I, Palla G, Vicsek T (2005) Clique percolation in random networks. Phys Rev Lett 94:160202+
Donetti L, Munoz MA (2004) Detecting network communities: a new systematic and efficient algorithm, 2004. J Stat Mech Theory Exp 10:10012
Du N, Wu B, Pei X, Wang B, Xu L (2007) Community detection in large-scale social networks. In: WebKDD/SNA-KDD’07 proceedings of the 9th WebKDD and 1st SNA-KDD 2007 workshop on web mining and social network analysis, ACM, NY, pp 16–25
Du N, Wang B, Wu B (2008) Overlapping community structure detection in networks. In: CIKM’08 proceeding of the 17th ACM conference on information and knowledge management, NY, pp 1371–1372
Everett MG, Borgatti SP (2005) Ego network betweenness. Social Netw 27(1):31–38
Ferber J (1999). Multi-agent systems: an introduction to distributed artificial intelligence, 1st edn. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc., Boston
Fortunato S (2010) Community detection in graphs. Phys Rep 486(3–5):75–174
Freeman LC (1979) Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Social Netw 1(3)
Freeman LC (1982) Centered graphs and the structure of ego networks. Math Soc Sci 3:291–304
Girvan M, Newman ME (2002) Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(12):7821–7826
Gleiser PM, Danon L (2003) Community structure in jazz. Adv Complex Syst (ACS) 6(4):565–573
Granovetter MS (1973) The strength of weak ties. Am J Sociol 78(6):1360–1380
Gregory S (2007) An algorithm to find overlapping community structure in networks. In: PKDD 2007 proceedings of the 11th European conference on principles and practice of knowledge discovery in databases, Springer, Berlin, pp 91–102
Guimera, Danon L, Diaz-Guilera A, Giralt F, Arenas A (2003) Phys Rev E 68:065103(R)
Hartmann V (2005) Evolving agent swarms for clustering and sorting. In: Proceedings of the 2005 conference on genetic and evolutionary computation, GECCO’05, ACM, New York, pp. 217–224
Hwang W, Kim T, Ramanathan M, Zhang A (2008) Bridging centrality: graph mining from element level to group level. In: KDD’08 proceeding of the 14th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, ACM, pp 336–344
Kleinberg J (2000) The small-world phenomenon: an algorithmic perspective. In: Proceedings of the 32nd ACM symposium on theory of computing, pp 163–170
Kossinets G, Watts DJ (2006) Empirical analysis of an evolving social network. Science 311(5757):88–90
Lancichinetti A, Fortunato S (2009a) Community detection algorithms: a comparative analysis. Phys Rev E 80:056117
Lancichinetti A, Fortunato S (2009b) Benchmarks for testing community detection algorithms on directed and weighted graphs with overlapping communities. Phys Rev E 80:016118
Lancichinetti A, Fortunato S, Radicchi F (2008) Benchmark graphs for testing community detection algorithms. Phys Rev E 78:046110
Lancichinetti A, Fortunato S, Kertesz J (2009). Detecting the overlapping and hierarchical community structure of complex networks, New J Phys 11
Leung H, Kothari R, Minai AA (2003) Phase transition in a swarm algorithm for self-organized construction. Phys Rev E 68:046111
Liu Y, Wang Q, Wang Q, Yao Q, Liu Y (2007) Email community detection using artificial ant colony clustering. In: Chang KC-C, Wang W, 0002 LC, Ellis CA, Hsu C-H, Tsoi AC, Wang H (eds) APWeb/WAIM Workshops, Lecture notes in computer science, vol 4537, Springer, pp 287–298
Liu Y, Luo J, Yang H, Liu L (2010) Finding closely communicating community based on ant colony clustering model. In: International conference on artificial intelligence and computational intelligence, vol 3, pp 127–131
Lusseau D, Schneider K, Boisseau OJ, Haase P, Slooten E, Dawson SM (2003) The bottlenose dolphin community of doubtful sound features a large proportion of long-lasting associations. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 54:396–405
Moody J, White DR (2003) Structural cohesion and embeddedness: a hierarchical concept of social groups. Am Sociol Rev 68(1):103–127
Newman MEJ (2001) The structure of scientific collaboration networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:404–409
Newman MEJ (2004) Fast algorithm for detecting community structure in networks. Phys Rev E 69(6):066133+
Newman MEJ, Girvan M (2003) Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys Rev E 69(12):026113
Newman ME, Park J (2003) Why social networks are different from other types of networks. Phys Rev E 68(3):036122+
Noack A, Rotta R (2009) Multi-level algorithms for modularity clustering. In: SEA’09 proceedings of the 8th international symposium on experimental algorithms, Springer, Berlin, pp 257–268
Palla G, Derenyi I, Farkas I, Vicsek T (2005) Uncovering the overlapping community structure of complex networks in nature and society. Nature 435:814
Radicchi F, Castellano C, Cecconi F, Loreto V, Parisi D (2004) Defining and identifying communities in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(9):2658–2663
Rees BS, Gallagher KB (2010) Overlapping community detection by collective friendship group inference. In: International conference on advances in social network analysis and mining, vol 0, pp 375–379
Rees BS, Gallagher KB (2011) EgoClustering: overlapping community detection via merged friendship-groups. In: Özyer T et al. (eds) The influence of technology on social network analysis and mining, Springer Press, (in press)
Xie J, Kelley S, Szymanski, BK (2011) Overlapping community detection in networks: the state of the art and comparative study. CoRR abs/1110.5813
Travers J, Milgram S (1969) An experimental study of the small world problem. Sociometry 32(4):425–443
Wakita K, Tsurumi T (2007) Finding community structure in mega-scale social networks. In: WWW’07 proceedings of the 16th international conference on World Wide Web, ACM, pp 1275–1276
Wasserman S, Faust K (1994) Social network analysis. Methods and applications. University Press, Cambridge
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393(6684):440–442
Weiss G (1999) Multiagent systems: a modern approach to distributed artificial intelligence. MIT Press, Cambridge
Whitney DE, Alderson D (2010) Are technological and social net-works really different? In: Minai A, Braha D, Bar-Yam Y (eds) Unifying themes in complex systems, Springer, Berlin, pp 74–81
Zachary W (1977) An information flow model for conflict and fission in small groups. J Anthropol Res 33:452–473
Zhang S, Wang R, Zhang X (2007) Identification of overlapping community structure in complex networks using fuzzy cc-means clustering. Phys A: Stat Mech Appl 374:483–490
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rees, B.S., Gallagher, K.B. Overlapping community detection using a community optimized graph swarm. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2, 405–417 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-012-0050-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-012-0050-3