Abstract
In this paper, we consider the problem of social networks whose edges may be characterized with uncertainty, space, and time. We propose a model called spatio-temporal uncertain networks (STUN) to formally define such networks, and then we propose the concept of STUN subgraph matching (or SM) queries. We develop a hierarchical index structure to answer SM queries to STUN databases and show that the index supports answering very complex queries over 1M+ edge networks in under a second. We also introduce the class of STUNRank queries in which we characterize the importance of vertices in STUN databases, taking space, time, and uncertainty into account. We show query-aware and query-unaware versions of STUNRank as well as alternative ways of defining it. We report on an experimental evaluation of STUNRank showing that it performs well on real world networks.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We were unable to use the open source dataset for experiments as it is too small.
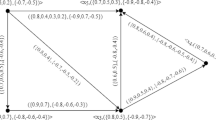
There may also be situations in which a vertex may have spatial and temporal components, e.g., Hassan may have a date of birth or a home address. These can either be stored as a property of the vertex, or as an edge labeled “date of birth” or “home address” to another vertex containing the values of those properties – this is what RDF would do.
Given a set of MBRs M, MBR(M) = (min(X), max(X), min(Y), max(Y)) where X = {x | (x, MX, mY, MY) ∈ M}∪{x | (mX, x, mY, MY) ∈ M} and Y = {y | (mX, MX, y, MY) ∈ M}∪{y | (mX, MX, mY, y) ∈ M}.
References
Albanese M, Broecheler M, Grant J, Martinez MV, Subrahmanian V (2011) Plini: a probabilistic logic program framework for inconsistent news information. In: Logic programming, knowledge representation, and nonmonotonic reasoning, Springer, LNAI 6565, pp 347–376
Baeza-Yates RA, Davis E (2004) Web page ranking using link attributes. In: Feldman SI, Uretsky M, Najork M, Wills CE (eds), WWW (Alternate Track Papers & Posters), ACM, New York, pp 328–329
Bahmani B, Chakrabarti K, Xin D (2011) Fast personalized pagerank on mapreduce. In: Sellis TK, Miller RJ, Kementsietsidis A, Velegrakis Y (eds) SIGMOD Conference. ACM, New York, pp 973–984
Berkhin P (2005) Survey: a survey on pagerank computing. Internet Math 2(1):73–120
Bhattacharya I, Getoor L (2007) Collective entity resolution in relational data. ACM Trans Knowl Discov Data (TKDD) 1(1):5
Boldi P (2005) Totalrank: ranking without damping. In: Ellis A, Hagino T (eds) WWW (Special interest tracks and posters), ACM, New York, pp 898–899
Brocheler M, Pugliese A, Subrahmanian V (2011) Probabilistic subgraph matching on huge social networks. In: Advances in social networks analysis and mining (ASONAM), IEEE International Conference 2011 pp 271–278
Broecheler M, Pugliese A, Subrahmanian VS (2009) DOGMA: a disk-oriented graph matching algorithm for RDF databases. In: ISWC, pp 97–113
Broecheler M, Pugliese A, Subrahmanian VS (2010) Cosi: Cloud oriented subgraph identification in massive social networks. In: ASONAM, pp 248–255
Catanese S, Ferrara E, Fiumara G (2013) Forensic analysis of phone call networks. Soc Netw Anal Min 3(1):15–33
Chakrabarti S (2007) Dynamic personalized pagerank in entity-relation graphs. In: Williamson CL, Zurko ME, Patel-Schneider PF, Shenoy PJ (eds) WWW ACM, New York, pp 571–580
Cheng J, Yu JX, Ding B, Yu PS, Wang H (2008) Fast graph pattern matching. In: ICDE conference, pp 913–922
Chitrapura KP, Kashyap SR (2004) Node ranking in labeled directed graphs. In: Grossman DA, Gravano L, Zhai C, Herzog O, Evans DA (eds) CIKM, ACM, New York, pp 597–606
Di Natale R, Ferro A, Giugno R, Mongiovì M, Pulvirenti A, Shasha D (2010) SING: subgraph search in non-homogeneous graphs. BMC Bioinformatics 11:96
Fogaras D, Rácz B, Csalogány K, Sarlós T (2005) Towards scaling fully personalized pagerank: Algorithms, lower bounds, and experiments. Internet Math 2(3):333–358
Gullapalli A, Carley K (2013) Extracting ordinal temporal trail clusters in networks using symbolic time-series analysis. Soc Netw Anal Mining 3(4):1179–1194
Gupta R, Sarawagi S (2006) Creating probabilistic databases from information extraction models. In: VLDB 32:965
Harth A, Decker S (2005) Optimized index structures for querying RDF from the Web. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Latin American Web Congress, pp 71–80
Haveliwala TH (2002) Topic-sensitive pagerank. In: WWW, pp 517–526
Kang C, Pugliese A, Grant J, Subrahmanian VS (2012) STUN: spatio-temporal uncertain (social) networks. In: ASONAM
Karypis G, Kumar V (1998) A fast and high quality multilevel scheme for partitioning irregular graphs. SIAM J Sci Comput 20(1):359–392
Kas M, Carley KM, Carley LR (2012) Trends in science networks: understanding structures and statistics of scientific networks. Soc Netw Anal Mining 2(2):169–187
Kashima H, Kato T, Yamanishi Y, Sugiyama M, Tsuda K (2009) Link propagation: a fast semi-supervised learning algorithm for link prediction. In: SDM 9:1099–1110
Kim M, Leskovec J (2011) The network completion problem: inferring missing nodes and edges in networks. In: SDM pp 47–58
Langville AN, Meyer CD (2003) Survey: deeper inside pagerank. Internet Math 1(3):335–380
Li H, Homer N (2010) A survey of sequence alignment algorithms for next-generation sequencing. Brief Bioinf 11(5):473–483
Liben-Nowell D, Kleinberg J (2007) The link-prediction problem for social networks. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 58(7):1019–1031
Mani I (2004) Recent developments in temporal information extraction. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing (RANLP03) pp 45–60
Mislove A, Marcon M, Gummadi PK, Druschel P, Bhattacharjee B (2007) Measurement and analysis of online social networks. In: Internet Measurement Conference pp 29–42
Nemirovsky D, Avrachenkov K (2008) Weighted pagerank: Cluster-related weights. In: Voorhees EM, Buckland LP (eds) TREC, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), special publication vol 500-277
Page L, Brin S, Motwani R, Winograd T (1999) The pagerank citation ranking: Bringing order to the web. Technical Report 1999–66, Stanford InfoLab
Sintek M, Kiesel M (2006) RDFBroker: a signature-based high-performance RDF store. In: ESWC, pp 363–377
Theoharis Y, Christophides V, Karvounarakis G (2005) Benchmarking database representations of rdf/s stores. In: Gil Y, Motta E, Benjamins VR, Musen MA (eds) International Semantic Web Conference, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, 3729:685–701
Udrea O, Recupero DR, Subrahmanian VS (2010) Annotated rdf. ACM Trans Comput Logic 11(2):10:1–10:41
UzZaman N., Allen JF (2010) Trips and trios system for tempeval-2: extracting temporal information from text. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, Association for Computational Linguistics, pp 276–283
Vacic V, Jin H, Zhu JK, Lonardi S (2008) A probabilistic method for small rna flowgram matching. In: Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing, NIH Public Access, p 75
Wang DZ, Franklin MJ, Garofalakis M, Hellerstein JM (2010) Querying probabilistic information extraction. Proc VLDB Endow 3(1-2):1057–1067
Wilkinson K, Sayers C, Kuno H, Reynolds D (2003) Efficient RDF storage and retrieval in Jena2. SWDB Conf 3:7–8
Zhang S, Li S, Yang J (2009) GADDI: distance index based subgraph matching in biological networks. In: EDBT Conference pp 192–203
Zhang S, Li S, Yang J (2010) SUMMA: subgraph matching in massive graphs. In: CIKM Conference pp 1285–1288
Zhu K, Zhang Y, Lin X, Zhu G (2010) NOVA: a novel and efficient framework for finding subgraph isomorphism mappings in large graphs. In: DASFAA Conference, pp 140–154
Zou L, Chen L, Özsu MT (2009) Distancejoin: pattern match query in a large graph database. VLDB Conf 2(1):886–897
Acknowledgements
This work was principally funded by ONR grant N000140910685.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, C., Pugliese, A., Grant, J. et al. STUN: querying spatio-temporal uncertain (social) networks. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 4, 156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-014-0156-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-014-0156-x