Abstract
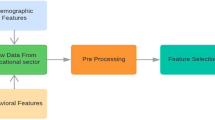
Education systems have significantly changed with the emergence of the internet. It has a significant impact on how students learn things. Nevertheless, its impact can also be contradicting. Internet addiction can slowly poison the minds of our youths and stand in the way of pursuing their goals. Although Bangladesh has internet connectivity across the country, its potential could be more utilized, particularly in the educational sector. Therefore, proper analysis of the effects of the internet on students, as well as determining the prominent factors relevant to the internet, is a necessary task. In addition, predicting students' academic performance can help determine the changes that must be incorporated to improve the educational system. Hence, this research analyzes the effects of internet usage on students' academic progress and then predicts the students' performance using distinct machine learning (ML) algorithms. The data were collected through an offline survey from Noakhali, Bangladesh. The collected data is preprocessed to select the most relevant features. The preprocessed data were fed into ML algorithms to investigate their behaviors. We have employed logistic regression, decision tree, random forest, and Naïve Bayes algorithms to see their classification performance on our dataset. To minimize the overfitting issue, k-fold cross-validation and hyperparameter optimization have been applied. The results were presented in two parts—exploratory data analysis and classification. Exploratory data analysis shows that the main purpose of internet usage is education and entertainment for school students, social media and entertainment for college students, and education and social media for university students. School and university students browse the internet mainly for academic purposes, whereas college students browse mainly for non-academic purposes. Students prefer to browse the internet at night. For all schools, colleges, and universities, students with better results generally visited websites like Google and YouTube. Students with moderate or bad results generally spent time on social media platforms (mainly Facebook and WhatsApp). Then, the results of the numerical analysis performed with classification algorithms are presented. Results indicate that random forest gives the maximum score in our dataset in all sectors, like accuracy, precision, recall, and f1 score. It gives a maximum of 85% accuracy on the test set. Logistic regression gives the second-best score of 69%. The practical applications and policy recommendations for Bangladesh's education sector are also discussed. The output of this work can contribute to building a policy on internet usage. In this way, it is possible to make the students more concentrative on their education and learning.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afrin S et al (2013) The impact of internet addiction on academic performance among medical students in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional study and the potential role of yoga. medRxiv, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Ahmed S, Fateha IJ (2018) Student’s performance prediction using data mining. Daffodil International University, Dhaka
Al Shuaeb SMA, Alam S, Rahman MdM, Matin MdA (2021) Polytechnic students’ academic performance prediction based on using deep neural network. Asian J Res Comput Sci. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajrcos/2021/v12i430289
Al-Alawi and AI, Alsubaiee NMA (2023) Predicting student’s academic performance using data mining methods: review paper. In: 2023 international conference on cyber management and engineering (CyMaEn), Bangkok, Thailand: IEEE, 2023, pp 18–23. https://doi.org/10.1109/CyMaEn57228.2023.10050962
Albreiki B, Zaki N, Alashwal H (2021) A systematic literature review of student’ performance prediction using machine learning techniques. Educ Sci (basel) 11(9):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11090552
Al-Neyazy SJM (2021) The use of a multinomial logistic regression model in analyzing the characteristics of married women using family planning methods in Iraq 2018. Turk J Comput Math Edu 12(12):4723–4742
Al-Shehri H et al. (2017) Student performance prediction using support vector machine and K-nearest neighbor. In: 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering (CCECE), IEEE, pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCECE.2017.7946847
Altabrawee H, Ali OAJ, Ajmi SQ (2019) Predicting students’ performance using machine learning techniques. J Univ Babylon Pure Appl Sci 27(1):194–205. https://doi.org/10.29196/jubpas.v27i1.2108
Alwarthan SA, Aslam N, Khan IU (2022) Predicting student academic performance at higher education using data mining: a systematic review. Appl Comput Intell Soft Comput 2022:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8924028
Alyahyan E, Düştegör D (2020) Predicting academic success in higher education: literature review and best practices. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 17(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-0177-7
Asogwa OC, Oladugba A (2015) Of Students academic performance rates using artificial neural networks (ANNs). Am J Appl Math Stat 3(4):151–155
Balaji P, Alelyani S, Qahmash A, Mohana M (2021) Contributions of machine learning models towards student academic performance prediction: a systematic review. Appl Sci 11(21):10007. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110007
(2023) BBS: functional literacy rate (7+above years) in Bangladesh 62.92%, Dhaka Tribune, Dhaka
Ben Brahim G (2022) Predicting student performance from online engagement activities using novel statistical features. Arab J Sci Eng 47(8):10225–10243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06548-w
Bhat MA, Joshi J, Wani IA (2016) Effect of socio economic status on academic performance of secondary school students. Int J Indian Psychol. https://doi.org/10.25215/0304.004
Bhuiyan M, Khan TT (2021) Knowledge Index: R&D tugs down Bangladesh below global average. The Business Standard, Dhaka
Bhusal A (2021) Predicting student’s performance through data mining
Bilal M, Omar M, Anwar W, Bokhari RH, Choi GS (2022) The role of demographic and academic features in a student performance prediction. Sci Rep 12(1):12508. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-15880-6
Bou-Hamad I (2020) The impact of social media usage and lifestyle habits on academic achievement: insights from a developing country context. Child Youth Serv Rev 118:105425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105425
Chakrapani P, Chitradevi D (2022) Academic performance prediction using machine learning: a comprehensive and systematic review. In: 2022 international conference on electronic systems and intelligent computing (ICESIC), IEEE, pp 335–340. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICESIC53714.2022.9783512
Cheung SY, Ng KY (2021) Application of the educational game to enhance student learning. Front Educ (Lausanne), vol 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2021.623793
Daud A, Aljohani NR, Abbasi RA, Lytras MD, Abbas F, Alowibdi JS (2017) Predicting student performance using advanced learning analytics. In Proceedings of the 26th international conference on World Wide Web Companion - WWW ’17 Companion, New York, New York, USA: ACM Press, pp 415–421. https://doi.org/10.1145/3041021.3054164
Fatema K, Nasreen S, Parvez MdS, Rahaman MdA (2020) Impact of using the internet on students: a sociological analysis at Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman science and technology University, Gopalganj, Bangladesh. Open J Soc Sci 08(12):71–83. https://doi.org/10.4236/jss.2020.812007
Haleem A, Javaid M, Qadri MA, Suman R (2022) Understanding the role of digital technologies in education: a review. Sustain Oper Comput 3:275–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susoc.2022.05.004
Hamadneh NN, Atawneh S, Khan WA, Almejalli KA, Alhomoud A (2022) Using artificial intelligence to predict students’ academic performance in blended learning. Sustainability 14(18):11642. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811642
Hira AA (2021) Student performance prediction using artificial neural network. Daffodil International University, Dhaka
Hossain MdJ, Ahmmed F, Rahman SMA, Sanam S, Bin Emran T, Mitra S (2021) Impact of online education on fear of academic delay and psychological distress among university students following one year of COVID-19 outbreak in Bangladesh. Heliyon 7(6):e07388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07388
Hossain MdA, Ahammad I, Ahmed MdK, Ahmed MI (2023) Prediction of the computer science department’s educational performance through machine learning model by analyzing students’ academic statements. Artific Intell Evolut. https://doi.org/10.37256/aie.4120232569
Hussain S, Khan MQ (2021) Student-performulator: predicting students’ academic performance at secondary and intermediate level using machine learning. Ann Data Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-021-00341-0
Hussain S, Khan MQ (2023) Student-performulator: predicting students’ academic performance at secondary and intermediate level using machine learning. Ann Data Sci 10(3):637–655. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40745-021-00341-0/FIGURES/4
Ibrahim Z, Rusli D (2007) Predicting students’ academic performance: comparing artificial neural network, decision tree and linear regression. In: 21st Annual SAS Malaysia Forum, Kuala Lumpur, pp 1–6
Kabakchieva D (2013) Predicting student performance by using data mining methods for classification. Cybern Inf Technol 13(1):61–72. https://doi.org/10.2478/cait-2013-0006
Kabirikopaei A, Lau J, Nord J, Bovaird J (2021) Identifying the K-12 classrooms’ indoor air quality factors that affect student academic performance. Sci Total Environ 786:147498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147498
Karamouzis ST, Vrettos A (2008) An artificial neural network for predicting student graduation outcomes. In: Proceedings of the world congress on engineering and computer science, San Francisco, 2008
Khan IM, Ahmad AR, Jabeur N, Mahdi MN (2021) A Conceptual framework to aid attribute selection in machine learning student performance prediction models. Int J Interact Mob Technol 15(15):4. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijim.v15i15.20019
Khan MAR, Akter J, Ahammad I, Ejaz S, Jaman Khan T (2022) Dengue outbreaks prediction in Bangladesh perspective using distinct multilayer perceptron NN and decision tree. Health Inf Sci Syst 10(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-022-00202-x
Khan AR et al (2022) Stock market prediction in bangladesh perspective using artificial neural network. Int J Adv Technol Eng Explor 9(95):1397–1427. https://doi.org/10.19101/IJATEE.2021.875852
Khan MdAR et al (2023) An effective approach for early liver disease prediction and sensitivity analysis. Iran J Comput Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/S42044-023-00138-9
Kumar M, Mondal A (2018) A study on Internet addiction and its relation to psychopathology and self-esteem among college students. Ind Psychiatry J 27(1):61–66. https://doi.org/10.4103/ipj.ipj_61_17
Lau ET, Sun L, Yang Q (2019) Modelling, prediction and classification of student academic performance using artificial neural networks. SN Appl Sci 1(9):982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0884-7
Lin M, van Stan JT (2020) Impacts of urban landscapes on students’ academic performance. Landsc Urban Plan 201:103840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2020.103840
Literacy rate by country 2023. World Population Review.
Livieris IE, Drakopoulou K, Tampakas VT, Mikropoulos TA, Pintelas P (2019) Predicting secondary school students’ performance utilizing a semi-supervised learning approach. J Edu Comput Res 57(2):448–470. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633117752614
Marchant A et al (2017) A systematic review of the relationship between internet use, self-harm and suicidal behaviour in young people: the good, the bad and the unknown. PLoS ONE 12(8):e0181722. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181722
Nawang H, Makhtar M, Fazamin WMA, Hamza W (2021) A systematic literature review on student performance predictions. Int J Adv Technol Eng Explor. https://doi.org/10.19101/IJATEE.2021.874521
Oancea B, Dragoescu R, Ciucu S (2019) Predicting students’ results in higher education using a neural network. In: International conference on applied information and communication technologies (AICT2013 ), MRPA, 2019, pp 190–193
Oladokun V, Adebanjo AT, Charles-Owaba OE (2008) Predicting students academic performance using artificial neural network: a case study of an engineering course. Pac J Sci Technol 9(1):72–79
Oliveira Silva G, Aredes NDA, Galdino-Júnior H (2021) Academic performance, adaptation and mental health of nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ Pract 55:103145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2021.103145
Pham L (2017) Effects of the internet on young people: a view from neuroscience. VNU J Sci Edu Res. https://doi.org/10.25073/2588-1159/vnuer.4068
Prosad R, Khan MdAR, Ahammad I (2022) Design of class routine and exam hall invigilation system based on genetic algorithm and greedy approach. Asian J Res Comput Sci. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajrcos/2022/v13i330316
Rahman K, Khan MdAR, Ahammad I (2022) Online support for education, medication, agriculture and relief work at COVID-19 pandemic time. Asian J Res Comput Sci. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajrcos/2022/v13i430322
Rahman S, Munam AM, Hossain A, Hossain ASMD, Bhuiya RA (2023) Socio-economic factors affecting the academic performance of private university students in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional bivariate and multivariate analysis. SN Soc Sci 3(2):26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43545-023-00614-w
Ramesh V, Parkavi P, Ramar K (2013) Predicting student performance: a statistical and data mining approach. Int J Comput Appl 63(8):35–39. https://doi.org/10.5120/10489-5242
Roy M (2018) The push for education in bangladesh. The Borgen Project. Blog - Latest News. https://borgenproject.org/the-push-for-education-in-bangladesh/.
Said JA (2020) Impact of internet usage on academic performance in tertiary education level: Bangladesh perspectives. J Creat Writ 4(1):54–102
Sekeroglu B, Abiyev R, Ilhan A, Arslan M, Idoko JB (2021) Systematic literature review on machine learning and student performance prediction: critical gaps and possible remedies. Appl Sci 11(22):10907. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112210907
Shahjahan M, Ahmed KR, Al Hadrami A, Islam MdR, Hossain S, Khan MdS (2021) Factors influencing poor academic performance among urban university students in Bangladesh. Int J Evaluation Res Edu 10(4):1140. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v10i4.21158
Sikder Md F, Uddin Md J, Halder S (2016) Predicting students yearly performance using neural network: a case study of BSMRSTU. In: 2016 5th international conference on informatics, electronics and vision (ICIEV), IEEE, May 2016, pp 524–529. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIEV.2016.7760058
Star Digital Report (2022) Bangladesh’s literacy rate now 74.66%, The Daily Star, Dhaka. 27 Jul 2022
Stošić L, Stošić I (2015) Perceptions of teachers regarding the implementation of the internet in education. Comput Human Behav 53:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.027
Thai-Nghe N, Drumond L, Krohn-Grimberghe A, Schmidt-Thieme L (2010) Recommender system for predicting student performance. Procedia Comput Sci 1(2):2811–2819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2010.08.006
Timotheou S et al (2022) Impacts of digital technologies on education and factors influencing schools’ digital capacity and transformation: a literature review. Educ Inf Technol (dordr) 28(6):6695–6726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11431-8
Van TD, Thi KCN, Thi HPT (2020) Data survey on the factors affecting students’ satisfaction and academic performance among private universities in Vietnam. Data Brief 33:106357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2020.106357
Xu X, Wang J, Peng H, Wu R (2019) Prediction of academic performance associated with internet usage behaviors using machine learning algorithms. Comput Human Behav 98:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.04.015
Yağcı M (2022) Educational data mining: prediction of students’ academic performance using machine learning algorithms. Smart Learn Environ 9(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-022-00192-z
Zárate-Grajales RA, Ostiguín-Meléndez RM, Aristizabal P, Serván-Mori E, Nigenda G (2021) Predictors of nursing students’ academic performance in the National Autonomous University of Mexico, 2010–2019: a retrospective study. Nurse Educ Today 100:104790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104790
Zulfiker MdS, Kabir N, Amin A, Chakraborty P, Mahfujur Md (2020) Predicting students’ performance of the private Universities of Bangladesh using machine learning approaches. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl. https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2020.0110383
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SHH Conceptualization, investigation, data collection, data curation, writing—original draft, model training, analysis and interpretation of results. MdARK conceptualization, investigation, writing—review and editing, model training, analysis and interpretation of results, supervision and investigation on challenges. IA draft manuscript preparation, writing—review and editing, analysis and interpretation of results. MR, MdASK, and SE study conception, design, data collection.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hemal, S.H., Khan, M.A.R., Ahammad, I. et al. Predicting the impact of internet usage on students’ academic performance using machine learning techniques in Bangladesh perspective. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 14, 66 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-024-01234-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-024-01234-9