Abstract
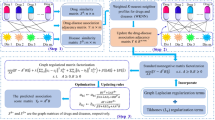
Drug–drug interaction (DDI) prediction prepares substantial information for drug discovery. As the exact prediction of DDIs can reduce human health risk, the development of an accurate method to solve this problem is quite significant. Despite numerous studies in the field, a considerable number of DDIs are not yet identified. In the current study, we used Integrated Similarity-constrained matrix factorization (ISCMF) to predict DDIs. Eight similarities were calculated based on the drug substructure, targets, side effects, off-label side effects, pathways, transporters, enzymes, and indication data as well as Gaussian interaction profile for the drug pairs. Subsequently, a non-linear similarity fusion method was used to integrate multiple similarities and make them more informative. Finally, we employed ISCMF, which projects drugs in the interaction space into a low-rank space to obtain new insights into DDIs. However, all parts of ISCMF have been proposed in previous studies, but our novelty is applying them in DDI prediction context and combining them. We compared ISCMF with several state-of-the-art methods. The results show that It achieved more appropriate results in five-fold cross-validation. It improves AUPR, and F-measure to 10% and 18%, respectively. For further validation, we performed case studies on numerous interactions predicted by ISCMF with high probability, most of which were validated by reliable databases. Our results provide support for the notion that ISCMF might be used unequivocally as a powerful method for predicting the unknown DDIs. The data and implementation of ISCMF are available at https://github.com/nrohani/ISCMF.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjornsson TD, Callaghan JT, Einolf HJ, Fischer V, Gan L, Grimm S, Kao J, King SP, Miwa G, Ni L et al (2003) The conduct of in vitro and in vivo drug-drug interaction studies: a pharmaceutical research and manufacturers of america (phrma) perspective. Drug metabolism and disposition 31(7):815–832
CYP2C9 C, CYP2D6 C (2007) The effect of cytochrome p450 metabolism on drug response, interactions, and adverse effects. Am Fam Phys 76:391–396
Gottlieb A, Stein GY, Oron Y, Ruppin E, Sharan R (2012) Indi: a computational framework for inferring drug interactions and their associated recommendations. Mol Syst Biol 8(1):592
Hanton G (2007) Preclinical cardiac safety assessment of drugs. Drugs R & D 8(4):213–228
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Hirakawa M (2009) Kegg for representation and analysis of molecular networks involving diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 38(suppl–1):D355–D360
Knox C, Law V, Jewison T, Liu P, Ly S, Frolkis A, Pon A, Banco K, Mak C, Neveu V et al (2010) Drugbank 3.0: a comprehensive resource for ‘omics’ research on drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 39(suppl–1):D1035–D1041
Koren Y, Bell R, Volinsky C (2009) Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer 8:30–37
Kuhn M, Campillos M, Letunic I, Jensen LJ, Bork P (2010) A side effect resource to capture phenotypic effects of drugs. Mol Syst Biol 6(1):343
Kusuhara H (2014) How far should we go? perspective of drug-drug interaction studies in drug development. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 29(3):227–228
van Laarhoven T, Nabuurs SB, Marchiori E (2011) Gaussian interaction profile kernels for predicting drug-target interaction. Bioinformatics 27(21):3036–3043
Law V, Knox C, Djoumbou Y, Jewison T, Guo AC, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Arndt D, Wilson M, Neveu V et al (2013) Drugbank 4.0: shedding new light on drug metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res 42(D1):D1091–D1097
Lazarou J, Pomeranz BH, Corey PN (1998) Incidence of adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. JAMA 279(15):1200–1205
Li Q, Cheng T, Wang Y, Bryant SH (2010) Pubchem as a public resource for drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 15(23–24):1052–1057
Magnus D, Rodgers S, Avery A (2002) Gps’ views on computerized drug interaction alerts: questionnaire survey. J Clin Pharm Ther 27(5):377–382
Menon AK, Elkan C (2011) Link prediction via matrix factorization. Joint European conference on machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases. Springer, New York, pp 437–452
Olayan RS, Ashoor H, Bajic VB (2017) Ddr: efficient computational method to predict drug-target interactions using graph mining and machine learning approaches. Bioinformatics 34(7):1164–1173
Percha B, Altman RB (2013) Informatics confronts drug–drug interactions. Trends Pharmacol Sci 34(3):178–184
Prueksaritanont T, Chu X, Gibson C, Cui D, Yee KL, Ballard J, Cabalu T, Hochman J (2013) Drug–drug interaction studies: regulatory guidance and an industry perspective. AAPS J 15(3):629–645
Rohani N, Eslahchi C (2019) Drug–drug interaction predicting by neural network using integrated similarity. Sci Rep 9(1):1–11
Stražar M, Žitnik M, Zupan B, Ule J, Curk T (2016) Orthogonal matrix factorization enables integrative analysis of multiple RNA binding proteins. Bioinformatics 32(10):1527–1535
Tatonetti NP, Patrick PY, Daneshjou R, Altman RB (2012) Data-driven prediction of drug effects and interactions. Sci Transl Med 4(125):125ra31
Vilar S, Harpaz R, Uriarte E, Santana L, Rabadan R, Friedman C (2012) Drug-drug interaction through molecular structure similarity analysis. J Am Med Inform Assoc 19(6):1066–1074
Wang B, Mezlini AM, Demir F, Fiume M, Tu Z, Brudno M, Haibe-Kains B, Goldenberg A (2014) Similarity network fusion for aggregating data types on a genomic scale. Nat Methods 11(3):333
Wang Y, Xiao J, Suzek TO, Zhang J, Wang J, Bryant SH (2009) Pubchem: a public information system for analyzing bioactivities of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res 37(suppl–2):W623–W633
Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M (2007) Drugbank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res 36(suppl–1):D901–D906
Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Shrivastava S, Hassanali M, Stothard P, Chang Z, Woolsey J (2006) Drugbank: a comprehensive resource for in silico drug discovery and exploration. Nucleic Acids Res 34(suppl–1):D668–D672
Zhang P, Wang F, Hu J, Sorrentino R (2015) Label propagation prediction of drug-drug interactions based on clinical side effects. Sci Rep 5:12339
Zhang W, Chen Y, Liu F, Luo F, Tian G, Li X (2017) Predicting potential drug-drug interactions by integrating chemical, biological, phenotypic and network data. BMC Bioinform 18(1):18
Zhang W, Yue X, Lin W, Wu W, Liu R, Huang F, Liu F (2018) Predicting drug-disease associations by using similarity constrained matrix factorization. BMC Bioinform 19(1):233
Zhang Y, Chen M, Huang D, Wu D, Li Y (2017) idoctor: personalized and professionalized medical recommendations based on hybrid matrix factorization. Future Gener Comput Syst 66:30–35
Acknowledgements
All authors thank Fatemeh Ahmadi Moughari for her helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rohani, N., Eslahchi, C. & Katanforoush, A. ISCMF: Integrated similarity-constrained matrix factorization for drug–drug interaction prediction. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinforma 9, 11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-019-0215-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-019-0215-3