Abstract
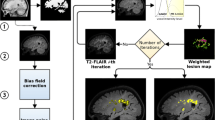
It would be helpful to have an automatic segmentation method to provide an acceptable performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) on Multiple Sclerosis (MS) subtypes that have important roles in cure procedure. This article presents a technique to classify MS lesion subtypes in MR images and then evaluates the correlation between lesion subtypes and Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS). The technique used textural features based on the Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) and histogram information (mean and variance) to describe each lesion and normal tissue of FLAIR Images. Then it discriminated them with Support Vector Machine (SVM). A comprehensive post-processing module improved the quality of segmentation. We found corresponding areas in T2-weighted (T2-w), T1-weighted (T1-w) called black holes, and T1-weighted enhancing (T1-enhancing) by mapping the extracted lesions of FLAIR slices on them. Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) classified the mapped lesions in three classes of T2, black holes and T1-enhancing. Finally, the correlation between lesions volume of each class and EDSS was calculated. The performance evaluation resulted that the presented method allowed a higher value of sensitivity (86.1%) in black holes MS lesion subtypes classification. This sensitivity was higher than that obtained by others. This improvement beside the high accuracy (85.02%) and specificity (85.4%) make this pipeline an interest for clinical applications as an extra helpful way near neurologist for diagnosis. There were meaningful correlations between T2-w lesions volume and EDSS (R = 0.71, p = 0.03) and between black holes lesions and EDSS (R = 0.82, p = 0.004).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah BA, Younis AA, John NM (2012) Multi-sectional views textural based SVM for MS lesion segmentation in multi-channels MRIs. 56–72
Bento M, Sym Y, Frayne R, Lotufo R (2017) Probabilistic segmentation of brain white matter lesions using texture-based classification. Int Conf Image Anal Recognit 3:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59876-5
Buf JMHDU, Kardan M, Spann M (1990) Texture feature performance for image segmentation 23(3):291–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-3203(90)90017-F
Chang C, Lin C (2019 LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines, pp 1–39
Danelakis A, Theoharis T, Verganelakis DA (2018) Survey of automated multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation techniques on magnetic resonance imaging. Comput Med Imaging Graph 70:83–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2018.10.002
Dimitrov I, Georgiev R, Kaprelyan A, Usheva N, Grudkova M, Drenska K, Ivanov B (2015) Brain and lesion volumes correlate with edss in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J IMAB Annu Proc (Sci Papers) 21(4):1015–1018. https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2015214.1015
Eleyan A, Demirel H (2011) Co-occurrence matrix and its statistical features as a new approach for face recognition. https://doi.org/10.3906/elk-0906-27
Gabr RE, Coronado I, Robinson M, Sujit SJ, Datta S, Sun X, Narayana PA (2019) Brain and lesion segmentation in multiple sclerosis using fully convolutional neural networks: a large-scale study. 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458519856843
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K (1973) Textural features for image classification
Karami V, Khayati RM, Nabavi SM (2016) Association assessment between diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging indices and clinical disabilities in MS patients. Biomed Eng Appl Basis Commun 28(5):1. https://doi.org/10.4015/S1016237216500344
Karami V, Nittari G, Amenta F (2019) Neuroimaging computer-aided diagnosis systems for Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 29(1):83–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22300
Kearney H, Rocca MA, Valsasina P, Balk L, Reinhardt J, Ruggieri S, Chard DT (2014) Magnetic resonance imaging correlates of physical disability in relapse onset multiple sclerosis of long disease duration. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458513492245
Keller J, Chen S (1989) Texture classification using discriminant wavelet packet subbands. 150–166
Khayati R, Vafadust M, Towhidkhah F, Nabavi SM (2008a) A novel method for automatic determination of different stages of multiple sclerosis lesions in brain MR FLAIR images 32:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2007.10.003
Khayati R, Vafadust M, Towhidkhah F, Nabavi SM (2008b) Fully automatic segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions in brain MR FLAIR images using adaptive mixtures method and markov random field model 38:379–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2007.12.005
Mary M (1975) Texture Analysis Using Gray Level Run Lengths 179:172–179
Miller DH, Grossman RI, Reingold SC, Mcfarland HF (1998) The role of magnetic resonance techniques in understanding and managing multiple sclerosis 3–24
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan G, Filippi M, Hartung H, Kappos L, Wolinsky JS (2005) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the “McDonald Criteria”. Ann Neurol 11:840–846. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.206703
Popescu V, Agosta F, Hulst HE, Sluimer IC. Knol DL, Sormani MP, Vrenken H (2013) Brain atrophy and lesion load predict long term disability in multiple sclerosis. 1082–1091. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2012-304094
Rajpoor NM (2002) Texture classification using discriminant wavelet packet subbands. 300–303. The 2002 45th Midwest Symposium
Randen T (1999) Filtering for texture classification: a comparative study. Pattern Anal Mach Intell IEEE Trans 21(4):291–310. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.761261
Sakai K, Yamada K (2018) Machine learning studies on major brain diseases: 5-year trends of 2014–2018. Jpn J Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-018-0794-4
Schmidt P, Pongratz V, Küster P, Meier D, Wuerfel J, Lukas C, Mühlau M (2019) Automated segmentation of changes in FLAIR-hyperintense white matter lesions in multiple sclerosis on serial magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage Clin 23:101849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101849
Singh M, Singh S (2002) Spatial texture analysis: a comparative study. Pattern Recogn. https://doi.org/10.1109/icpr.2002.1044843
Sukissian L, Kollias S, Boutalist Y (1994) Adaptive classification of textured images using linear prediction and neural networks 36:209–232
Tadayon E, Khayati R, Karami V, Nabavi SM (2016) A novel method for automatic classification of multiple sclerosis lesion subtypes using diffusion tensor MR images. In: A novel method for automatic classification of multiple sclerosis lesion subtypes using diffusion tensor. (October). https://doi.org/10.4015/S1016237216500381
Vicente FY, Hoai M, Samaras D (2017). Leave-one-out Kernel optimization for shadow detection and removal. 8828(c):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2691703
Vince DG, Dixon KJ, Cothren RM, Cornhill JF (2000) Comparison of texture analysis methods for the characterization of coronary plaques in intravascular ultrasound images. Comput Med Imaging Graph 24:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0895-6111(00)00011-2
Wu Y, Warfield SK, Tan IL, Wells WM, Meier DS, van Schijndel RA, Guttmann CRG (2006) Automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesion subtypes with multichannel MRI. NeuroImage 32(3):1205–1215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.04.211
Zhang H, Alberts E, Pongratz V, Mühlau M, Zimmer C, Wiestler B, Eichinger P (2019) Predicting conversion from clinically isolated syndrome to multiple sclerosis: an imaging-based machine learning approach. NeuroImage Clin 21:101593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2018.11.003
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their special thanks to the university of Camerino for this collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest and funding for this work.
Research involving human participants
All procedure performed in this study involving human participants were by the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards, and informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karami, V., Mahdavifar (Khayati), R., Habibzadeh, A. et al. Identification of Multiple Sclerosis lesion subtypes and their quantitative assessments with EDSS using neuroimaging. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinforma 9, 38 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-020-00245-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-020-00245-8