Abstract
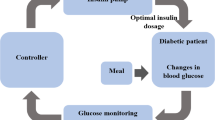
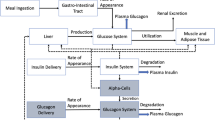
Artificial pancreas systems the courage to remove this risk by taking existing pump technology to a new level. In this paper, we modified the existing model for type 1 diabetes mellitus to discuss different control strategies for the artificial pancreas. A model consists of eight states variables and various parameters, numerous of which are undefined and complicated to find out correctly. The stability of glucose-insulin in humans has been created and validated the non-negative unique solution. Controllability and observability for the glucose-insulin system is treated for feedback design to develop the artificial pancreas. We design glucose insulin algorithm for whole body having eight sub-compartments according to parameters values given in Liu and Tang (J Theor Biol 252:608–620, 2008) which provide the continues monitoring of glucose and insulin in finite time. Numerical simulation are carried out for closed-loop design which is helpful for the development of artificial pancreas. The developed model provides the estimation values for normal day life to measure the glucose-insulin system in humans.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A, Farman M, Yasin F, Ahmad MO (2018a) Dynamical transmission and effect of smoking in society. Int J Adv Appl Sci 5(2):71–75
Ahmad A, Farman M, Ahmad MO, Raza N, Abdullah (2018b) Dynamical behavior of SIR epidemic model with non-integer time fractional derivatives: a mathematical analysis. Int J Adv Appl Sci 5(1):123–129
Alkahtani BS, Algahtani OJ, Dubey RS, Goswami P (2017) The solution of modified fractional Bergman’s minimal blood glucose-insulin model. Entropy 19:114
Anguelov R, Lubuma JMS (2001) Contributions to the mathematics of the nonstandard finite difference method and applications. Numer Methods Partial Differ Equ 17:518–543
Ashraf F, Ahmad MO (2019) Nonstandard finite difference scheme for control of measles epidemiology. Int J Adv Appl Sci 6(3):79–85
Ashraf F, Ahmad A, Saleem MU, Farman M, Ahmad MO (2018) Dynamical behavior of HIV immunology model with non-integer time fractional derivatives. Int J Adv Appl Sci 5(3):39–45
Bergman R, Phillips L, Cobelli C (1981) Physiologic evaluation of factors controlling glucose tolerance in man. J Clin Investig 68(6):1456–1467
Boutayeb DT, Chetouani A (2006) A critical review of mathematical models and data used in diabetology. Biomed Eng 5:43
Chee G, Fernando T (2007) Closed-loop control of blood glucose, number 368 in lecture notes in control and information sciences. Springer, Berlin
Coron JM (2007) Control and nonlinearity. Am Math Soc 136:1–66
Dalla Man C, Rizza RA, Cobelli C (2007) Meal simulation model of the glucose-insulin system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54(10):1740–1749
De Gaetano A, Panunzi S, Matone A, Samson A, Vrbikova J, Bendlova B et al (2013) Routine OGTT: a robust model including incretin effect for precise identification of insulin sensitivity and secretion in a single individual. PLoS ONE 8:e70875
Erlandsen M, Martinussen C, Gravholt CH (2018) Integrated model of insulin and glucose kinetics describing both hepatic glucose and pancreatic insulin regulation. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 56:121–131
Farman M, Saleem MU, Meraj MA (2016) Control of glucose insulin regulatory system for type 1 diabetes. Sci Int (Lahore) 28(1):27–29
Farman M, Saleem MU, Ahmad MO, Ahmad A (2018) Stability analysis and control of glucose insulin glucagon system in human. Chin J Phys 56:1362–1369
Farman M, Saleem MU, Tabassum MF, Ahmad A, Ahmad MO (2019) A linear control of composite model for glucose insulin glucagon. Ain Shamas Eng J 10:867–872
Li L, Zheng W (2010) Global stability of a delay model of glucose–insulin interaction. Math Comput Model 52(4):472–480
Liu W, Tang F (2008) Modelling a simplified regulatory system of blood glucose at molecular levels. J Theor Biol 252:608–620
Lunze K, Brendel MD, Leonhardt S (2011) Preliminary results of a type-1 diabetes swine model. In: 5th European IFMBE conference. Hungary, Budapest, pp 307–310
Makroglou A, Li J, Kuang Y (2006) Mathematical models and software tools for the glucose-insulin regulatory system and diabetes: an overview Appl Numer Math 56:559–573
Mickens RE (1994) Nonstandard finite difference Models of differential equations. World Scientific, Singapore
Naik PA, Yavuz M, Qureshi S, Zu J, Townley S (2020) Modeling and analysis of COVID-19 epidemics with treatment in fractional derivatives using real data from Pakistan. Eur Phys J Plus 135(10):795
Parker RS, Doyle FJI, Peppas NA (2001) The intravenous route to blood glucose control. A review of control algorithms for noninvasive monitoring and regulation in type I diabetic patients. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 20(1):65–73
Saleem MU, Farman M, Ahmad MO, Rizwan M (2017) Control of an artificial human pancreas. Chin J Phys 55:2273–2282
Saleem MU, Farman M, Rizwan M, Ahmad MO, Ahmad A (2018) Controllability and observability of glucose insulin glucagon systems in human. Chin J Phys 56(5):1909–1916
Saleem MU, Farman M, Ahmad A, Naeem M, Ahmad MO (2019) Stability analysis and control of fractional order diabetes mellitus model for artificial pancreas. Punjab Univ J Math 51(4):97-113
Salinari S, Bertuzzi A, Mingrone G (2011) Intestinal transit of a glucose bolus and incretin kinetics: a mathematical model with application to the oral glucose tolerance test. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 300:E955–E965
Schmidt S, Boiroux D, Ranjan A, Jorgensen JB, Madsen H, Norgaard K (2015) An artificial pancreas for automated blood glucose control in patients with Type 1 diabetes. Ther Deliv 6:609–619
Yavuz M, Ozdemir N (2020) Analysis of an epidemic spreading model with exponential decay law. Math Sci Appl E-Notes 8(1):142–154
Yavuz M, Sene N (2020) Stability analysis and numerical computation of the fractional predator-prey model with the harvesting rate. Fractal Fract 4(35):1–22
Yavuza M, Bonyah E (2019) New approaches to the fractional dynamics of schistosomiasis disease model. Physica A Stat Mech Appl 525:373–393
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MFT: analysis, writing-original draft. MF: methodology, writing-original draft. PAN: conceptualization, review and editing, Supervision. AA: software, validation, numerical simulations. ASA: analysis, writing-original draft. SMH: methodology, writing-original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies performed on human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabassum, M.F., Farman, M., Naik, P.A. et al. Modeling and simulation of glucose insulin glucagon algorithm for artificial pancreas to control the diabetes mellitus. Netw Model Anal Health Inform Bioinforma 10, 42 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-021-00316-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13721-021-00316-4