Abstract
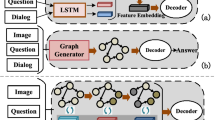
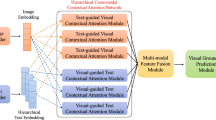
As a challenging cross-media task, visual dialog assesses whether an AI agent can converse in human language based on its understanding of visual content. So the critical issue is to pay attention not only to the problem of coreference in vision, but also to the problem of coreference in and between vision and language. In this paper, we propose the multi-aware coreference relation network (MACR-Net) to solve it from both textual and visual perspectives and to do fusion in complementary awareness. Specifically, its textual coreference relation module identifies textual coreference relations based on multi-aware textual representation from textual view. Furthermore, the visual coreference relation module adaptively adjusts visual coreference relations based on contextual-aware relations representation from visual view. Finally, the multi-modals fusion module fuses multi-aware relations to get an aligned representation. Extensive experiments on the VisDial v1.0 benchmarks show that MACR-Net achieves state-of-the-art performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
Research data policy and data availability statements
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Das A, Kottur S, Gupta K, Singh A, Yadav D, Moura JM, Parikh D, Batra D (2017) Visual dialog. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 326–335
Niu Y, Zhang H, Zhang M, Zhang J, Lu Z, Wen J-R (2019) Recursive visual attention in visual dialog. In: The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)
Jiang T, Ji Y, Liu C (2021) Integrating historical states and co-attention mechanism for visual dialog. In: 2020 25th International conference on pattern recognition (ICPR), pp 2041–2048. IEEE
Yu J, Jiang X, Qin Z, Zhang W, Hu Y, Wu Q (2020) Learning dual encoding model for adaptive visual understanding in visual dialogue. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:220–233
Chen F, Chen X, Meng F, Li P, Zhou J (2021) Gog: relation-aware graph-over-graph network for visual dialog. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.08475
Qiao Y, Yu Z, Liu J (2020) Rankvqa: answer re-ranking for visual question answering. In: 2020 IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo (ICME), pp. 1–6. IEEE
Yang T, Zha Z-J, Zhang H (2019) Making history matter: history-advantage sequence training for visual dialog. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2561–2569
Durrett G, Klein D (2013) Easy victories and uphill battles in coreference resolution. In: EMNLP
Clark K, Manning CD (2016) Deep reinforcement learning for mention-ranking coreference models. In: EMNLP
Lee K, He L, Zettlemoyer L (2018) Higher-order coreference resolution with coarse-to-fine inference. In: NAACL
Peters ME, Neumann M, Iyyer M, Gardner M, Clark C, Lee K, Zettlemoyer L (2018) Deep contextualized word representations. In: NAACL
Lu C, Krishna R, Bernstein MS, Fei-Fei L (2016) Visual relationship detection with language priors. In: ECCV
Lv J, Xiao Q-z, Zhong J (2020) Avr: Attention based salient visual relationship detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.07012
Xi Y, Zhang Y, Ding S, Wan S (2020) Visual question answering model based on visual relationship detection. Signal Process Image Commun, 80
Hoang M, Kim S-H, Yang H-J, Lee G-S (2021) Context-aware emotion recognition based on visual relationship detection. IEEE Access 9:90465–90474
Zellers R, Yatskar M, Thomson S, Choi Y (2018) Neural motifs: scene graph parsing with global context. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 5831–5840
Pennington J, Socher R, Manning C (2014) Glove: global vectors for word representation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), pp 1532–1543
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9(8):1735–1780
Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y (2014) Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473
Quan J, Xiong D, Webber BL, Hu C (2019) Gecor: an end-to-end generative ellipsis and co-reference resolution model for task-oriented dialogue. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.12086
Papineni K, Roukos S, Ward T, Zhu W-J (2002) Bleu: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics, pp 311–318
Ren S, He K, Girshick RB, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39:1137–1149
Guo D, Xu C, Tao D (2019) Image-question-answer synergistic network for visual dialog. 2019 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 10426–10435
Kottur S, Moura JM, Parikh D, Batra D, Rohrbach M (2018) Visual coreference resolution in visual dialog using neural module networks. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 153–169
Jiang X, Du S, Qin Z, Sun Y, Yu J (2020) Kbgn: knowledge-bridge graph network for adaptive vision-text reasoning in visual dialogue. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 1265–1273
Lu J, Kannan A, Yang J, Parikh D, Batra D (2017) Best of both worlds: transferring knowledge from discriminative learning to a generative visual dialog model. In: NIPS
Lu J, Yang J, Batra D, Parikh D (2016) Hierarchical question-image co-attention for visual question answering. In: NIPS
Gan Z, Cheng Y, Kholy AE, Li L, Liu J, Gao J (2019) Multi-step reasoning via recurrent dual attention for visual dialog. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.00579
Nguyen V-Q, Suganuma M, Okatani T (2020) Efficient attention mechanism for visual dialog that can handle all the interactions between multiple inputs. In: ECCV
Jiang X, Yu J, Sun Y, Qin Z, Zhu Z, Hu Y, Wu Q (2020) Dam: deliberation, abandon and memory networks for generating detailed and non-repetitive responses in visual dialogue. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.03310
Chen F, Meng F, Chen X, Li P, Zhou J (2021) Multimodal incremental transformer with visual grounding for visual dialogue generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.08478
Lin J, Yang A, Zhang Y, Liu J, Zhou J, Yang H (2020) Interbert: vision-and-language interaction for multi-modal pretraining. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.13198
Tu T, Ping Q, Thattai G, Tur G, Natarajan P (2021) Learning better visual dialog agents with pretrained visual-linguistic representation. 2021 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 5618–5627
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos 61972059, 61773272, 61602332; Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China No 19KJA230001, Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education, Jilin University No93K172016K08; the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interest to disclose. The authors have no competing interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interest in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Jiang, T., Liu, C. et al. Multi-aware coreference relation network for visual dialog. Int J Multimed Info Retr 11, 567–576 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-022-00257-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-022-00257-2