Abstract
With the increasing demand for the real-world applications such as autonomous driving and video surveillance, lightweight semantic segmentation methods achieving good trade-offs in terms of parameter size, speed and accuracy have attracted more and more attention. In this context, we propose a novel real-time semantic segmentation model. First, we design a two-branch depth-wise asymmetric attention bottleneck (DAAB) based on residual network to reduce the number of parameters and improve the inference speed. Particularly, an attention refinement module (ARM) is added in the DAAB module to make the information extracted from the two branches complement each other. Second, we design a strip pooling attention (SPA) module which combines the strip pooling module and the attention mechanism to pay more attention to strip-shaped objects and to establish long-range dependencies between discrete distributed regions, so that to address the problem of poor segmentation of strip shape objects. In addition, we also fuse information from different stages to compensate for the loss of spatial information, thus improving the ability of the network to segment small objects. Experiments on CityScapes and CamVid dataset demonstrate that the proposed method achieves impressive trade-offs in terms of parameter size, speed and accuracy. Code is available at: https://github.com/mhhz/DAABnet1.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availibility Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from https://www.Cityscapes-dataset.com and https://github.com/lih627/CamVid.
Notes
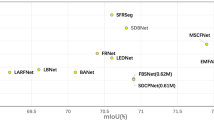
In this case, DAABNet obtains \(68.8\%\) mIoU at 92.68 FPS with 0.94M parameters. The model achieves a good balance between low-resolution datasets CamVid and high-resolution datasets CityScapes.
References
Minaee S, Boykov YY, Porikli F, Plaza AJ, Kehtarnavaz N, Terzopoulos D (2021) Image segmentation using deep learning: a survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(7):3523–3542
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3431–3440
Noh H, Hong S, Han B (2015) Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 1520–1528
Zhao H, Qi X, Shen X, Shi J, Jia J (2018) ICNet for real-time semantic segmentation on high-resolution images. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 418–434
Yang Z, Yu H, Feng M et al (2020) Small object augmentation of urban scenes for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:5175–5190
Romera E, Alvarez JM, Bergasa LM, Arroyo R (2018) ERFNet: efficient residual factorized convnet for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 19:263–272
Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V (2017) Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Thirty-first AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (AAAI), pp 4278–4284
Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen L-C (2018) MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 4510–4520
Howard A, Sandler M, Chu G, Chen L-C, Chen B, Tan M, Wang W, Zhu Y, Pang R, Vasudevan V, Le QV, Adam H (2019) Searching for MobileNetv3. In: IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 1314–1324
Zhang X, Zhou X Y, Lin M X, Sun R (2018) ShuffleNet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 6848–6856
Chollet F (2017) Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In: 30th IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1800–1807
Wu Z, Shen C, Hengel A (2017) Real-time semantic image segmentation via spatial sparsity. arXiv preprint arXiv:1712.00213
Badrinarayanan V, Kendal A, Cipolla R (2017) SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder–decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(12):2481–2495
Paszke A, Chaurasia A, Kim S, Culurciello E (2016) Enet: a deep neural network architecture for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.02147
Hou Q, Zhang L, Cheng M M, et al (2020) Strip pooling: rethinking spatial pooling for scene parsing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 4003–4012
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, et al (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1–9
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, et al (2016) Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2818–2826
Howard A G, Zhu M, Chen B, et al (2017) Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04861
Chen LC, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I et al (2017) Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848
Wu T, Tang S, Zhang R et al (2021) CGNet: a light-weight context guided network for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1169–1179
Mehta S, Rastegari M, Caspi A, et al (2018) ESPNet: efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 552–568
Zhuang M, Zhong X, Gu D et al (2021) LRDNet: a lightweight and efficient network with refined dual attention decoder for real-time semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 459:349–360
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 234–241
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, Wang X, Jia J (2017) Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2881–2890
Li H, Xiong P, Fan H, et al (2019) DFANet: deep feature aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 9522–9531
Li G, Yun I, Kim J, et al (2019) DABNet: depth-wise asymmetric bottleneck for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11357
Wang Y, Zhou Q, Liu J, et al (2019) LEDNet: a lightweight encoder–decoder network for real-time semantic segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp 1860–1864
Wang F, Jiang M, Qian C, Yang S, Li C, Zhang H, Wang X, Tang X (2017) Residual attention network for image classification. In: 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 6450–6458
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS (2018) CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 3–19
Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P, Li P, Hu Q (2020) ECANet: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional. In: IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (ECCV), pp 11531–11539
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: 31st IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 7132–7141
Wang X, Girshick R B, Gupta A, He K (2018) Non-local neural networks. In: IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 7794–7803
Cao Y, Xu J, Lin S, Wei F, Hu H (2019) GCNet: non-local networks meet squeeze excitation networks and beyond. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision workshop (ICCVW), pp 1971–1980
Huang Z, Wang X, Huang L, Huang C, Wei Y, Shi H, Liu W (2019) CCNet: criss cross attention for semantic segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 603–612
Kundu S, Sundaresan S (2021) AttentionLite: towards efficient self-attention models for vision. In: ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp 2225–2229
Zhao H, Zhang Y, Liu S, Shi, J, Loy C C, Lin D, Jia J (2018) PSANet: point-wise spatial attention network for scene parsing. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 267–283
Hou Q, Zhou D, Feng J (2021) Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 13713–13722
Yu C, Wang J, Peng C, Gao C, Yu G, Sang G (2018) Bisenet: bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 325–341
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 770–778
Yu C, Gao C, Wang J et al (2021) BiSeNetv2: bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 129(11):3051–3068
Elhassan M, Huang C, Yang C et al (2021) DSANet: dilated spatial attention for real-time semantic segmentation in urban street scenes. Expert Syst Appl 183:115090
Fan M, Lai S, Huang J, et al (2021) Rethinking bisenet for real-time semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 9716–9725
Brostow GJ, Fauqueur J, Cipolla R (2009) Semantic object classes in video: a high-definition ground truth database. Pattern Recogn Lett 30:88–97
Cordts M, Omran M, Ramos S, Rehfeld T, Enzweiler M, Benenson R, Franke U, Roth S, Schiele B (2016) The CityScapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3213–3223
Orsic M, Kreso I, Bevandic P, Segvic S (2019) In defense of pre-trained imagenet architectures for real-time semantic segmentation of road-driving images. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 12607–12616
Zhou Q, Wang Y, Fan Y, Wu X, Kang B (2020) AGLNet: towards real-time semantic segmentation of self-driving images via attention-guided lightweight network. Appl Soft Comput 96:106682
Gao G, Xu G, Yu Y et al (2021) MSCFNet: a lightweight network with multi-scale context fusion for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 23(12):25489–25499
Lu M, Chen Z, Wu Q et al (2022) FRNet: factorized and regular blocks network for semantic segmentation in road scene. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 23(4):3522–3530
Li Y, Li M, Li Z et al (2022) EFRNet: efficient feature reuse network for real-time semantic segmentation. Neural Process Lett 55(1):873–873
Hu X, Jing L, Sehar U (2022) Joint pyramid attention network for real-time semantic segmentation of urban scenes. Appl Intell Int J Artif Intell 52(1):580–594
Hu X, Gong J (2022) LARFNet: lightweight asymmetric refining fusion network for real-time semantic segmentation. Comput Graph 109:55–64
Mazhar S, Atif N, Bhuyan MK, Ahamed SR (2023) Block attention network: a lightweight deep network for real-time semantic segmentation of road scenes in resource-constrained devices. Eng Appl Artif Intell (PC) 126:107086
Hu X, Liu Y (2023) Lightweight multi-scale attention-guided network for real-time semantic segmentation. Image Vis Comput 139:1041823
Li G, Jiang S, Yun I, Kim J, Kim J (2020) Depth-wise asymmetric bottleneck with point-wise aggregation decoder for real-time semantic segmentation in urban scenes. IEEE Access 8:27495–27506
Zhang X, Chen Z, Wu Q et al (2019) Fast semantic segmentation for scene perception. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 15(2):1183–1192
Poudel R, Liwicki S, Cipolla R (2019) Fast-SCNN: fast semantic segmentation network. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.04502
Yang Z, Yu H, Fu Q et al (2020) NDNet: narrow while deep network for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 22(9):5508–5519
Poudel R, Bonde U, Liwicki S, et al (2018) ContextNet: exploring context and detail for semantic segmentation in real time. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.04554
Lo S, Hang H, Chan S, et al (2019) Efficient dense modules of asymmetric convolution for real-time semantic segmentation. ACM Multimedia Asia, pp 1–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QT: Methodology, Investigation, Writing-original draft. YC: Investigation, Code, Writing-review and editing. MZ: Investigation, Data curation, Visualization. SM: Investigation, Concept. WJ: Investigation, Concept Writing - review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Q., Chen, Y., Zhao, M. et al. DAABNet: depth-wise asymmetric attention bottleneck for real-time semantic segmentation. Int J Multimed Info Retr 13, 12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-024-00321-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13735-024-00321-z