Abstract
Purpose
Human emotion recognition using electroencephalograms (EEG) is a critical area of research in human–machine interfaces. Furthermore, EEG data are convoluted and diverse; thus, acquiring consistent results from these signals remains challenging. As such, the authors felt compelled to investigate EEG signals to identify different emotions.
Methods
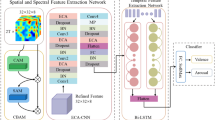
A novel deep learning (DL) model stacked long short-term memory with attention (S-LSTM-ATT) model is proposed for emotion recognition (ER) in EEG signals. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and attention networks effectively handle time-series EEG data and recognise intrinsic connections and patterns. Therefore, the model combined the strengths of the LSTM model and incorporated an attention network to enhance its effectiveness. Optimal features were extracted from the metaheuristic-based firefly optimisation algorithm (FFOA) to identify different emotions efficiently.
Results
The proposed approach recognised emotions in two publicly available standard datasets: SEED and EEG Brainwave. An outstanding accuracy of 97.83% in the SEED and 98.36% in the EEG Brainwave datasets were obtained for three emotion indices: positive, neutral and negative. Aside from accuracy, a comprehensive comparison of the proposed model’s precision, recall, F1 score and kappa score was performed to determine the model’s applicability. When applied to the SEED and EEG Brainwave datasets, the proposed S-LSTM-ATT achieved superior results to baseline models such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) and LSTM.
Conclusion
Combining an FFOA-based feature selection (FS) and an S-LSTM-ATT-based classification model demonstrated promising results with high accuracy. Other metrics like precision, recall, F1 score and kappa score proved the suitability of the proposed model for ER in EEG signals.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are publicly available online.
References
Lu G, Yuan L, Yang W, Yan J, Li H. Speech emotion recognition based on long short-term memory and convolutional neural networks. J Nanjing Univ Posts Telecommun. 2018;38(5):63–9.
Zhang H. Expression-EEG based collaborative multimodal emotion recognition using deep autoencoder. IEEE Access. 2020;8:164130–43.
Kamble K, Sengupta J. A comprehensive survey on emotion recognition based on electroencephalograph (EEG) signals. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-14489-9.
Bota PJ, Wang C, Fred AL, Da Silva HP. A review, current challenges, and future possibilities on emotion recognition using machine learning and physiological signals. IEEE Access. 2019;7:140990–1020.
Chen JX, Jiang DM, Zhang YN. A hierarchical bidirectional GRU model with attention for EEG-based emotion classification. IEEE Access. 2019;7:118530–40.
Rajpoot AS, Panicker MR. Subject independent emotion recognition using EEG signals employing attention driven neural networks. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022;75: 103547.
Li C, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Huang G, Liu Y, Chen X. EEG-based emotion recognition via transformer neural architecture search. IEEE Trans Industr Inf. 2022;19(4):6016–25.
Liu YH, Huang S, Huang YD. Motor imagery EEG classification for patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using fractal dimension and Fisher’s criterion-based channel selection. Sensors. 2017;17(7):1557.
Mathersul D, Williams LM, Hopkinson PJ, Kemp AH. Investigating models of affect: relationships among EEG alpha asymmetry, depression, and anxiety. Emotion. 2008;8(4):560.
Acharya D, Billimoria A, Srivastava N, Goel S, Bhardwaj A. Emotion recognition using Fourier transform and genetic programming. Appl Acoust. 2020;164: 107260.
Jenke R, Peer A, Buss M. Feature extraction and selection for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans Affect Comput. 2014;5(3):327–39.
Dogan S, Baygin M, Tasci B, Loh HW, Barua PD, Tuncer T, Tan RS, Acharya UR. Primate brain pattern-based automated Alzheimer’s disease detection model using EEG signals. Cogn Neurodyn. 2023;17(3):647–59.
Torres EP, Torres EA, Hernández-Álvarez M, Yoo SG. EEG-based BCI emotion recognition: a survey. Sensors. 2020;20(18):5083.
Hihi S, Bengio Y. Hierarchical recurrent neural networks for long-term dependencies. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 1995;8:493–99.
Walther D, Viehweg J, Haueisen J, Mäder P. A systematic comparison of deep learning methods for EEG time series analysis. Front Neuroinform. 2023;17:1067095.
Fukushima K, Miyake S, Ito T. Neocognitron: a neural network model for a mechanism of visual pattern recognition. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. 1983;5:826–34.
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997;9(8):1735–80.
Cho K, Van Merriënboer B, Gulcehre C, Bahdanau D, Bougares F, Schwenk H, Bengio Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv:1406.1078. 2014.
Zheng WL, Lu BL. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans Auton Ment Dev. 2015;7(3):162–75.
Bird JJ, Manso LJ, Ribeiro EP, Ekart A, Faria DR. A study on mental state classification using EEG-based brain-machine interface. In: 2018 international conference on intelligent systems (IS). IEEE; 2018. p. 795–800.
Abgeena A, Garg S. A novel convolution bi-directional gated recurrent unit neural network for emotion recognition in multichannel electroencephalogram signals. Technol Health Care. 2023;31:1215–34.
Patlar AF. Hybrid deep convolutional model-based emotion recognition using multiple physiological signals. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng. 2022;25(15):1678–90.
Jin L, Kim EY. E-EmotiConNet: EEG-based emotion recognition with context information. In: 2022 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE; 2022. p. 1–8.
Houssein EH, Hammad A, Ali AA. Human emotion recognition from EEG-based brain–computer interface using machine learning: a comprehensive review. Neural Comput Appl. 2022;34(15):12527–57.
Li X, Zhang Y, Tiwari P, Song D, Hu B, Yang M, Zhao Z, Kumar N, Marttinen P. EEG based emotion recognition: a tutorial and review. ACM Comput Surv. 2022;55(4):1–57.
Ari B, Siddique K, Alçin ÖF, Aslan M, Şengür A, Mehmood RM. Wavelet ELM-AE based data augmentation and deep learning for efficient emotion recognition using EEG recordings. IEEE Access. 2022;10:72171–81.
Olamat A, Ozel P, Atasever S. Deep learning methods for multi-channel EEG-based emotion recognition. Int J Neural Syst. 2022;32(05):2250021.
Du Y, Liu J. IENet: a robust convolutional neural network for EEG based brain-computer interfaces. J Neural Eng. 2022;19(3): 036031.
Dillen A, Steckelmacher D, Efthymiadis K, Langlois K, De Beir A, Marusic U, Vanderborght B, Nowé A, Meeusen R, Ghaffari F, Romain O. Deep learning for biosignal control: insights from basic to real-time methods with recommendations. J Neural Eng. 2022;19(1): 011003.
Alhagry S, Fahmy AA, El-Khoribi RA. Emotion recognition based on EEG using LSTM recurrent neural network. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl. 2017;8(10):355–58.
Koelstra S, Muhl C, Soleymani M, Lee JS, Yazdani A, Ebrahimi T, Pun T, Nijholt A, Patras I. Deap: a database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals. IEEE Trans Affect Comput. 2011;3(1):18–31.
Qing C, Qiao R, Xu X, Cheng Y. Interpretable emotion recognition using EEG signals. IEEE Access. 2019;7:94160–70.
Acharya D, Goel S, Bhardwaj H, Sakalle A, Bhardwaj A. A long short term memory deep learning network for the classification of negative emotions using EEG signals. In: 2020 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE; 2020. p. 1–8.
Klibi S, Mestiri M, Farah IR. Emotional behavior analysis based on EEG signal processing using machine learning: a case study. In: 2021 international congress of advanced technology and engineering (ICOTEN). IEEE; 2021. p. 1–7.
Joshi VM, Ghongade RB. Optimal number of electrode selection for EEG based emotion recognition using linear formulation of differential entropy. Biomed Pharmacol J. 2020;13(2):645–53.
Mehmood RM, Lee HJ. Emotion classification of EEG brain signal using SVM and KNN. In: 2015 IEEE international conference on multimedia & expo workshops (ICMEW). IEEE; 2015. p. 1–5.
Bhardwaj A, Gupta A, Jain P, Rani A, Yadav J. Classification of human emotions from EEG signals using SVM and LDA Classifiers. In: 2015 2nd international conference on signal processing and integrated networks (SPIN). IEEE; 2015. p. 180–5.
Xu X, Jia T, Li Q, Wei F, Ye L, Wu X. EEG feature selection via global redundancy minimization for emotion recognition. IEEE Trans Affect Comput. 2021
Ma X, Liu P, Wang X, Bai X. EEG emotion recognition based on optimal feature selection. J Phys. 2021;1966(1):012043.
Tian Z, Li D, Song Y, Gao Q, Kang Q, Yang Y. EEG-based emotion recognition of deaf subjects by integrated genetic firefly algorithm. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. 2021;70:1–11.
He H, Tan Y, Ying J, Zhang W. Strengthen EEG-based emotion recognition using firefly integrated optimization algorithm. Appl Soft Comput. 2020;94: 106426.
Liu ZT, Xie Q, Wu M, Cao WH, Li DY, Li SH. Electroencephalogram emotion recognition based on empirical mode decomposition and optimal feature selection. IEEE Trans Cognit Dev Syst. 2018;11(4):517–26.
Nakisa B, Rastgoo MN, Tjondronegoro D, Chandran V. Evolutionary computation algorithms for feature selection of EEG-based emotion recognition using mobile sensors. Expert Syst Appl. 2018;93:143–55.
Soleymani M, Lichtenauer J, Pun T, Pantic M. A multimodal database for affect recognition and implicit tagging. IEEE Trans Affect Comput. 2011;3(1):42–55.
Li Z, Qiu L, Li R, He Z, Xiao J, Liang Y, Wang F, Pan J. Enhancing BCI-based emotion recognition using an improved particle swarm optimization for feature selection. Sensors. 2020;20(11):3028.
Yang XS. Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. In: International symposium on stochastic algorithms, vol. 26. Berlin: Springer; 2009. p. 169–78.
Fister Jr I, Yang XS, Fister I, Brest J. Memetic firefly algorithm for combinatorial optimization. arXiv:1204.5165. 2012.
Yang S, Yu X, Zhou Y. LSTM and GRU neural network performance comparison study: taking yelp review dataset as an example. In: 2020 international workshop on electronic communication and artificial intelligence (IWECAI). IEEE; 2020. p. 98–101.
Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv:1409.0473. 2014.
Zhang Y, Liu H, Zhang D, Chen X, Qin T, Zheng Q. EEG-based emotion recognition with emotion localization via hierarchical self-attention. IEEE Trans Affect Comput. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAFFC.2022.3145623.
Sagnika S, Mishra BS, Meher SK. An attention-based CNN-LSTM model for subjectivity detection in opinion-mining. Neural Comput Appl. 2021;33:17425–38.
Zheng WL, Zhu JY, Lu BL. Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans Affect Comput. 2017;10(3):417–29.
Bird JJ, Faria DR, Manso LJ, Ekárt A, Buckingham CD. A deep evolutionary approach to bioinspired classifier optimisation for brain-machine interaction. Complexity. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4316548.
Sakalle A, Tomar P, Bhardwaj H, Acharya D, Bhardwaj A. A LSTM based deep learning network for recognizing emotions using wireless brainwave driven system. Expert Syst Appl. 2021;173: 114516.
Varsamopoulos S, Bertels K, Almudever CG. Comparing neural network based decoders for the surface code. IEEE Trans Comput. 2019;69(2):300–11.
Kumari N, Anwar S, Bhattacharjee V. A comparative analysis of machine and deep learning techniques for EEG evoked emotion classification. Wireless Pers Commun. 2023;128(4):2869–90.
Sharma R, Pachori RB, Sircar P. Automated emotion recognition based on higher order statistics and deep learning algorithm. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2020;58: 101867.
Iyer A, Das SS, Teotia R, Maheshwari S, Sharma RR. CNN and LSTM based ensemble learning for human emotion recognition using EEG recordings. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023;82(4):4883–96.
Asghar MA, Khan MJ, Rizwan M, Shorfuzzaman M, Mehmood RM. AI inspired EEG-based spatial feature selection method using multivariate empirical mode decomposition for emotion classification. Multimed Syst. 2022;28(4):1275–88.
Anuragi A, Sisodia DS, Pachori RB. EEG-based cross-subject emotion recognition using Fourier-Bessel series expansion based empirical wavelet transform and NCA feature selection method. Inf Sci. 2022;610:508–24.
Liu J, Wu G, Luo Y, Qiu S, Yang S, Li W, Bi Y. EEG-based emotion classification using a deep neural network and sparse autoencoder. Front Syst Neurosci. 2020;14:43.
Chowdary MK, Anitha J, Hemanth DJ. Emotion recognition from EEG signals using recurrent neural networks. Electronics. 2022;11(15):2387.
Sarkar A, Singh A, Chakraborty R. A deep learning-based comparative study to track mental depression from EEG data. Neurosci Inform. 2022;2(4): 100039.
Alsubai S. Emotion detection using deep normalized attention-based neural network and modified-random forest. Sensors. 2022;23(1):225.
Deniz E, Sobahi N, Omar N, Sengur A, Acharya UR. Automated robust human emotion classification system using hybrid EEG features with ICBrainDB dataset. Health Inf Sci Syst. 2022;10(1):31.
Bajaj V, Taran S, Sengur A. Emotion classification using flexible analytic wavelet transform for electroencephalogram signals. Health Inf Sci Syst. 2018;6:1–7.
Kansal S, Garg D, Upadhyay A, Mittal S, Talwar GS. A novel deep learning approach to predict subject arm movements from EEG-based signals. Neural Comput Appl. 2023;2:1–11.
Le XH, Ho HV, Lee G, Jung S. Application of long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network for flood forecasting. Water. 2019;11(7):1387.
Karevan Z, Suykens JA. Transductive LSTM for time-series prediction: an application to weather forecasting. Neural Netw. 2020;125:1–9.
Zhang N, Shen SL, Zhou A, Jin YF. Application of LSTM approach for modelling stress–strain behaviour of soil. Appl Soft Comput. 2021;100: 106959.
De Santo A, Galli A, Gravina M, Moscato V, Sperlì G. Deep learning for HDD health assessment: an application based on LSTM. IEEE Trans Comput. 2020;71(1):69–80.
Xu D, Zhang Q, Ding Y, Zhang D. Application of a hybrid ARIMA-LSTM model based on the SPEI for drought forecasting. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022;29(3):4128–44.
Tigga NP, Garg S. Efficacy of novel attention-based gated recurrent units transformer for depression detection using electroencephalogram signals. Health Inf Sci Syst. 2022;11(1):1.
Ding Y, Jia M, Miao Q, Cao Y. A novel time–frequency transformer based on self–attention mechanism and its application in fault diagnosis of rolling bearings. Mech Syst Signal Process. 2022;168: 108616.
Majid S, Alenezi F, Masood S, Ahmad M, Gündüz ES, Polat K. Attention based CNN model for fire detection and localization in real-world images. Expert Syst Appl. 2022;189: 116114.
Fang W, Zhuo W, Yan J, Song Y, Jiang D, Zhou T. Attention meets long short-term memory: a deep learning network for traffic flow forecasting. Physica A. 2022;587: 126485.
Kumar V. Evaluation of computationally intelligent techniques for breast cancer diagnosis. Neural Comput Appl. 2021;33(8):3195–208.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author confirms that there is no conflict of interest and there are no financial funds.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abgeena, A., Garg, S. S-LSTM-ATT: a hybrid deep learning approach with optimized features for emotion recognition in electroencephalogram. Health Inf Sci Syst 11, 40 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-023-00242-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-023-00242-x