Abstract
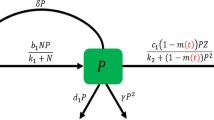
The presence of populations potentially harmful dinoflagellate phytoplankton like Oxyrrhis marina requires vigilance and control, because these species, in high density or under certain conditions, can have serious economic consequences and a negative impact on public health. In this investigation, we formulate bioeconomic model of a prey and predator planktonic species. The positivity and boundedness of the solution are studied. The possible equilibriums and their local stability are analyzed; also the global stability of the system around the interior equilibrium is established. We examine the optimal harvesting policy to discuss the dynamical profit of the interacting planktonic species. To show the impact of the toxicity coefficient, we have made analytical estimates that are validated using simulations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas S, Banerjee M, Hungerbühler N (2010) Existence, uniqueness and stability analysis of allelopathic stimulatory phytoplankton model. J Math Anal Appl 367(1):249–259
Agmour I, Bentounsi M, El foutayeni Y (2017) Optimization of the two fishermen’s profits exploiting three competing species where prices depend on harvest. Int J Differ Equ 3157294:17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3157294
Agmour I, Achtaich N, El foutayeni Y (2018) Carrying capacity influence on the incomes of seiners exploiting marine species in the Atlantic coast of Morocco. Math Biosci 305:10–17
Agmour I, Achtaich N, El foutayeni Y (2018) Stability analysis of a competing fish populations model with the presence of a predator. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci 26(2):108–121
Agmour I, Bentounsi M, Achtaich N, El foutayeni Y (2018) Catchability coefficient influence on the fishermen’s net economic revenues. Commun Math Biol Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.28919/cmbn/3512
Agmour I, Bentounsi M, Baba N, El foutayeni Y, Achtaich N, Aouiti C (2020) Impact of wind speed on fishing effort. Model Earth Syst Environ 6: pp 1-9
Arrow KJ, Kurz M (1970) Public investment, the rate of return, and optimal fiscal policy. Johns Hopkins, Baltimore
Baba N, Agmour I, Achtaich N, El foutayeni Y (2019) The mathematical study for mortality coefficients of small pelagic species. Commun Math Biol Neurosci 2019:1–31
Bandyopadhyay M (2006) Dynamical analysis of a allelopathic phytoplankton model. J Biol Syst 14(02):205–217
Bandyopadhyay M, Saha T, Pal R (2008) Deterministic and stochastic analysis of a delayed allelopathic phytoplankton model within fluctuating environment. Nonlinear Anal Hybrid Syst 2(3):958–970
Bates SS, Garrison DL, Horner RA (1998) Bloom dynamics and physiology of domoic-acid-producing Pseudo-nitzschia species. In: Anderson DM, Cembella AD, Hallegraeff GM (eds) Physiological ecology of harmful algal blooms. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 267–292
Bentounsi M, Agmour I, Achtaich N, El foutayeni Y (2017) Stability analysis of a biological model of a marine resources allowing density dependent migration. Int Front Sci Lett 12:22–34
Bentounsi M, Agmour I, Achtaich N, El foutayeni Y (2018) The Hopf bifurcation and stability of delayed predator-prey system. Comput Appl Math 37(5):5702–5714
Bentounsi M, Agmour I, Achtaich N, El foutayeni Y (2018) The impact of price on the profits of fishermen exploiting tritrophic prey-predator fish populations. Int J Differ Equ 10:2. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2381483
Bentounsi M, Agmour I, Achtaich N, El foutayeni Y (2019) Intrinsic growth rates influence on the net economic rents of fishermen. Int J Dyn Syst Differ Equ 9(4):362–379
Birkhoff G, Rota GC (1982) Ordinary differential equations. Ginn Boston, Boston
Chattopadhyay J (1996) Effect of toxic substances on a two species competitive system. Ecol Model 84:287–289
Clark CW (1976) Mathematical bioeconomics: the optimal management resources. Wiley, Hoboken
De Luna JT, Hallam TG (1987) Effects of toxicants on populations: a qualitative approach IV. Resource-consumer-toxicant models. Ecol Model 35(3–4):249–273
El foutayeni Y (2012) A bio-economic model of fishery where prices depend harvest. J Adv Model Optim 14:543–555
El foutayeni Y, Khaladi M (2012) A generalized bio-economic model for competing multiple-fish populations where prices depend on harvest. J Adv Model Optim 14:531–542
El foutayeni Y, Khaladi M, Zegzouti A (2012) A generalized Nash equilibrium for a bioeconomic problem of fishing. Stud Inf Univ 10(1):186–204
El foutayeni Y, Khaladi M, Zegzouti A (2013) Profit maximization of fishermen. J Adv Model Optim 15(2013):457–469
Flynn KJ, Davidson K (1993) Predator-prey interactions between Isochrysis galbana and Oxyrrhis marina. II. Release of non-protein amines and faeces during predation of Isochrysis. J Plank Res 15(8):893–905
Freedman HI, Shukla JB (1991) Models for the effect of toxicant in single-species and predator-prey systems. J Math Biol 30(1):15–30
Hale JK (1971) Functional differential equations. In: Hsieh PF, Stoddart AWJ (eds) Analytic Theory of Differential Equations. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol 183. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0060406
Hallam TG, Clark CE (1981) Non-autonomous logistic equations as models of populations in a deteriorating environment. J Theoret Biol 93(2):303–311
Hallam TG, De Luna JT (1984) Effects of toxicants on populations: a qualitative: approach III. Environmental and food chain pathways. J Theoret Biol 109(3):411–429
Hallegraeff GM (2003) Harmful algal blooms: a global overview. Man Harmful Mar Microalgae 33:1–22
Kar K, Chaudhuri KS (2003) On non-selective harvesting of two competing fish species in the presence of toxicity. Ecol Model 161(1–2):125–137
Kot M (2001) Elements of mathematical. Ecology 50:205–207
Maynard-Smith J (1978) Models in ecology. CUP Archive, Cambridge
Montagnes DJ, Lowe CD, Martin L, Watts PC, Downes-Tettmar N, Yang Z, Davidson K (2011) Oxyrrhis marina growth, sex and reproduction. J Plankton Res 33(4):615–627
Mukhopadhyay A, Chattopadhyay J, Tapaswi PK (1998) A delay differential equations model of plankton allelopathy. Math Biosci 149(2):167–189
Mukhopadhyay A, Tapaswi PK, Chattopadhyay J (2003) A space-time state-space model of phytoplankton allelopathy. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl 4(3):437–456
Pontryagin LS (2018) Mathematical theory of optimal processes. Routledge, London
Sommer H, Meyer KF (1937) Paralytic shell-fish poisoning. Arch Pathol 24:560–98
Sommer H, Whedon WF, Kofoid CA, Stohler R (1937) Relation of paralytic shell-fish poison to certain plankton organisms of the genus Gonyaulax. Arch Pathol 24:537–59
Taylor FJR (1998) The neurotoxic dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium halim: general introduction. In: Anderson DM, Cembella AD, Hallegraeff GM (eds) Physiological ecology of harmful algal blooms. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–11
Yasumoto T, Oshima Y, Sugawara W, Fukuyo Y, Oguri H, Igarashi T, Fujita N (1980) Identification of Dinophysis fortii as the causative organism of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 46(11):1405–1411
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Jose Alberto Cuminato.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agmour, I., Baba, N., Bentounsi, M. et al. Mathematical study and optimal control of bioeconomic model concerning harmful dinoflagellate phytoplankton. Comp. Appl. Math. 40, 129 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-021-01509-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-021-01509-3
Keywords
- Fishery bioeconomic model
- Toxicity
- Heterotrophic dinoflagellate Oxyrrhis marina
- Optimal harvesting policy