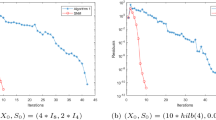
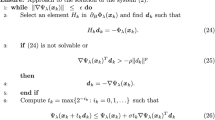Abstract
We present a sufficient condition for monotonicity of the nonlinear nonsmooth system generated by Fischer–Burmeister function associated with nonlinear complementarity problem. Based on the presented condition, the nonlinear complementarity problem considered in this paper is equivalently formulated to a nonsmooth monotone system. We then propose a modified multivariate spectral gradient projection method for the resulting system, and establish the global convergence without smoothness and Lipschitz condition. Preliminary numerical experiments show that, compared to some existing methods, the proposed method is effective.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data (source codes and testing problems) underlying this article are available in the article.
Notes
A function \(\phi :\mathbb {R}^2 \rightarrow \mathbb {R}\) is called NCP-function, if \(\forall ~(a,b) \in \mathbb {R}^2\), we have: \(\phi (a,b)=0 \Longleftrightarrow (a,b) \ge 0\) and \(ab=0\).
References
Abubakar AB, Kumam P (2019) A descent Dai-Liao conjugate gradient method for nonlinear equations. Numer Alg 81(1):197–210
Amini K, Kamandi A (2015) A new line search strategy for finding separating hyperplane in projection-based methods. Numer Alg 70(3):559–570
Chen BL, Ma CF (2011) A new smoothing broyden-like method for solving nonlinear complementarity problem with a \(P_0\)-function. J Glob Optim 51(3):473–495
Chen JS, Pan SH (2008) A family of NCP functions and a descent method for the nonlinear complementarity problem. Comput Optim Appl 40(3):389–404
Chen BT, Chen XJ, Kanzow C (2000) A penalized Fischer-Burmeister NCP-function. Math Program 88(1):211–216
Facchinei F, Kanzow C (1997) A nonsmooth inexact Newton method for the solution of large-scale nonlinear complementarity problems. Math Program 76(3):493–512
Fan B (2015) A smoothing Broyden-like method with a nonmonotone derivative-free line search for nonlinear complementarity problems. J Comput Appl Math 290:641–655
Ferris MC, Pang JS (1997) Engineering and economic applications of complementarity problems. SIAM Rev 39(4):669–713
Harker PT, Pang JS (1990) Finite-dimensional variational inequality and nonlinear complementarity problems: a survey of theory, algorithms and applications. Math Program 48(1–3):161–220
Jiang HY (1996) Unconstrained minimization approaches to nonlinear complementarity problems. J Glob Optim 9(2):169–181
Kanzow C, Pieper H (1999) Jacabian smoothing Newton methods for nonlinear complementarity problems. SIAM J Optimiz 9(2):342–373
La Cruz W (2017) A spectral algorithm for large-scale systems of nonlinear monotone equations. Numer Alg 76(4):1109–1130
Luca TD, Facchinei F, Kanzow C (1996) A semismooth equation approach to the solution of nonlinear complementarity problems. Math Program 75(3):407–439
Ma CF (2010) A new smoothing and regularization newton method for \(P_0\)-NCP. J Glob Optim 48(2):241–261
Ma CF, Chen XH (2008) The convergence of a one-step smoothing newton method for \(P_0\)-\(NCP\) based on a new smoothing \(NCP\)-function. J Comput Appl Math 216(1):1–13
Mangasarian OL, Solodov MV (1999) A linearly convergent derivative-free descent method for strongly monotone complementarity problems. Comput Optim Appl 14(1):5–16
Moré JJ (1996) Global methods for nonlinear complementarity problems. Math Oper Res 21(3):589–614
Nie PY, Fan JY (2005) A derivative-free filter method for solving nonlinear complementarity problems. Appl Math Comput 161(3):787–797
Ou YG, Li JY (2018) A new derivative-free SCG-type projection method for nonlinear monotone equations with convex constraints. J Appl Math Comput 56(1):195–216
Solodov MV, Svaiter BF (1998) A globally convergent inexact Newton method for systems of monotone equations, reformulation: nonsmooth, piecewise smooth, semismooth and smoothing methods. Kluwer Academic Publishers, New York
Yang B, Gao L (1991) An efficient implementation of merrill’s method for sparse or partially separable systems of nonlinear equations. SIAM J Optim 1(2):206–221
Yang J, Liu HW (2018) A modified projected gradient method for monotone variational inequalities. J Optim Theory Appl 179(1):197–211
Yang YF, Qi LQ (2005) Smoothing trust region methods for nonlinear complementarity problems with \(P_0\)-functions. Ann Oper Res 133(1–4):99–117
Yu GH, Niu SZ, Ma JH (2013) Multivariate spectral gradient projection methodfor nonlinear monotone equations with convex constraints. J Ind Manag Optim 9(1):117–129
Zhang X, Peng Z (2020) A modulus-based nonmonotone line search method for nonlinear complementarity problems. Appl Math Comput 387:125175
Zhao YB, Li D (2001) Monotonicity of fixed point and normal mappings associated with variational inequality and its application. SIAM J Optim 11(4):962–973
Zhu JG, Liu HW, Liu CH, Cong WJ (2011) A nonmonotone derivative-free algorithm for nonlinear complementarity problems based on the new generalized penalized Fischer-Burmeister merit function. Numer Alg 58(4):573–591
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported partly by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 12071398, the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province under Grant No. 2020JJ4567, and the Science Foundation of Provincial Education Department of Hunan under Grant No. 18A351.
Appendix
Appendix
Example 1
(La Cruz 2017) The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 2
The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 3
This problem is a modification of Example 1, and the function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 4
(Abubakar and Kumam 2019) The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 5
(Fan 2015) This is the Kojima–Shindo problem, and the function f(x) is given by
Example 6
(La Cruz 2017) The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 7
(Ou and Li 2018) The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 8
(Ou and Li 2018) The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 9
(Yang and Gao 1991) A tridiagonal exponential function \(f_h(x)\), which is endowed with the component as follows:
where \(x_0 = x_{n+1} = 0\) and \(h = \frac{1}{n+1}\).
Example 10
A nonsmooth modified of Example 9, which is endowed with the component as follows:
where \(x_0 = x_{n+1} = 0\) and \(h = \frac{1}{n+1}\).
Example 11
(Zhang and Peng 2020) The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 12
The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 13
A nonsmooth modification of Example 1, where f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 14
The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
Example 15
The function f(x) is endowed with the component as follows:
where \(sinh(\cdot )\) is the hyperbolic sine function, i.e., \(\sinh (t) = \frac{e^t - e^{-t}}{2}\).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Z., Zhang, X. & Yao, Z. A modified multivariate spectral gradient projection method for nonlinear complementarity problems. Comp. Appl. Math. 42, 323 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-023-02465-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-023-02465-w
Keywords
- Nonlinear complementarity problem
- Monotone system
- Fischer–Burmeister function
- Non-Lipschitz mapping
- Multivariate spectral gradient projection.