Abstract
In this paper, a new finite-time dynamic surface control (DSC) method is proposed to enhance the convergence rate and robustness of a DSC system on the basis of the traditional infinite-time stability viewpoint for application to nonlinear large-scale systems. By defining a novel recursive finite-time virtual error variable, a virtual controlled stabilizing functions are derived, and the finite-time control performance is ensured by means of the finite-time-based Lyapunov stability theorem. An adaptive fuzzy logic system is adopted to approximate the unknown functions. The applicability of the proposed control strategy is verified by simulation and an experiment for a mobile manipulator and an articulated manipulator.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Kokotovic, P., Kalil, H.K., O’Reilly, J.: Singular Perturbation Methods in Control: Analysis and Design. SIAM, London (1986)
Krishnamurthy, P., Khorrami, F.: A singular perturbation based global dynamic high gain scaling control design for systems with nonlinear input uncertainties. IEEE Trans. A. C. 58(10), 2686–2692 (2013)
Isidori, A., Rubeti, A.: On the synthesis of linear input-output responses for nonlinear systems. Syst. Control Lett. 4(1), 16–22 (1984)
Slotine, J.J., Hedrick, J.K.: Robust input-output linearization. Int. J. Control 57(5), 1133–1139 (1993)
Kristic, K., Kanellakopoulos, I., Kokotovic, P.V.: Nonlinear and Adaptive Control Design. Wiley, New York (1995)
Swaroop, S., Hedrick, J.K., Yip, P.P., Gerdes, J.C.: Dynamic surface control for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. A. C. 45(10), 1893–1899 (2000)
Chwa, D.: Global tracking control of underactuated ships with input and velocity constraints using dynamic surface control method. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 19(6), 1357–1370 (2011)
Wang, L.X.: A Course in Fuzzy Systems and Control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1997)
Leu, Y.G.: Backstpping nonlinear control using nonlinear parametric fuzzy systems. Inter. J. Fuzzy Syst. 11(4), 225–231 (2009)
Tong, S.C., Liu, C., Li, Y.: Fuzzy-adaptive decentralized output-feedback control for large-scale nonlinear systems with dynamical uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 18(5), 845–861 (2010)
Tong, S.C., Li, Y., Feng, G., Li, T.: Observer-based adaptive fuzzy backstepping dynamic surface control for a class of MIMO nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber Part B. 41(4), 1124–1135 (2011)
Tong, S.C., Li, Y., Li, Y., Liu, Y.: Observer-based adaptive fuzzy backstepping control for a class of stochastic nonlinear strict-feedback systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber 41(6), 1693–1704 (2011)
Yu, J.: Adaptive fuzzy stabilization for a class of pure-feedback systems with unknown dead-zones. Inter. J. Fuzzy Syst. 15(3), 18–26 (2013)
Tong, S.C., Wang, T., Li, Y.M., Chen, B.: Combined backstepping and stochastic small-gain approach to robust adaptive fuzzy output feedback control. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 21(2), 265–275 (2013)
Tong, S.C., Sui, S., Li, Y.M.: Fuzzy adaptive output feedback control of MIMO nonlinear systems with partial tracking errors constrained. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(4), 729–742 (2015)
Li, T.S., Tong, S.C., Feng, G.: A novel robust adaptive-fuzzy- tracking control for a class of nonlinear multi-input/multi-output systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 18(1), 150–160 (2010)
Li, Y.M., Tong, S.C., Li, T.S.: Adaptive fuzzy output feedback dynamic surface control of interconnected nonlinear pure-feedback systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 45(1), 138–149 (2015)
Chang, Y.H., Chan, W.S., Chang, C.W.: T-S fuzzy model-based adaptive dynamic surface control for ball and beam system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 60(6), 2251–2263 (2013)
Han, S.I., Lee, J.M.: Fuzzy echo state neural networks and funnel dynamic surface control for prescribed performance of a nonlinear dynamic system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(2), 1099–1112 (2014)
Bhat, S.P., Bernstein, D.A.: Continuous finite-time stabilization of the translational and rotational double integrators. IEEE Trans. A. C. 43(5), 678–682 (1998)
Bhat, S.P., Bernstein, D.A.: Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems. SIAM J. Control Optim. 38(3), 751–766 (2000)
Hong, Y., Huang, J., Xu, Y.: On an output feedback finite-time stabilization problem”. IEEE Trans. A. C. 46(2), 305–309 (2001)
Yu, S., Yu, X., Shirinzadeh, B., Man, Z.: Continuous finite-time control for robotic manipulators with terminal sliding mode. Automatica 41, 1957–1964 (2005)
Ge, S.S., Wang, C.: Adaptive neural control of uncertain MIMO nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Net. 15(3), 674–692 (2004)
Zhang, T., Ge, S.S.: Adaptive neural network tacking control of MIMO nonlinear systems with unknown dead zones and control directions. IEEE Trans. Neural Net. 20(3), 674–692 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korean Government(MSIP) (NRF-2013R1A1A2021174)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Consider the following Lyapunov function:
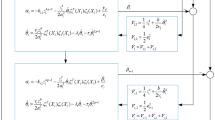
By differentiating (52) with respect to time, and substituting the previous results, we obtain the following:
where \( S_{i} = [s_{i,1}, s_{i,2}, \ldots, s_{i,n_{i}}]^{\text{T}}, \quad K_{i} = {\text{diag}}(k_{i,1} - 2, k_{i,2} - 2, \ldots, k_{i,n_{i}} - 2), \quad k_{i,j} >2 \), for \( i = 1, \ldots, m, \quad j = 1, \ldots, n_{i}, \zeta_{i} = {\text{diag}} \left(c_{i,1} \left|{G_{i,1}} \right|c_{i,2} \left|{G_{i,2} } \right|, \ldots ,c_{i,n_{i}} \left|{G_{i,n_{i}}} \right| \right) \), \( {\tilde{W}}_{Mi} = \left[{\tilde{W}}_{Mi,1}, {\tilde{W}}_{Mi,2}, \ldots, {\tilde{W}}_{Mi,n_{i}} \right]^{\text{T}}, \) \( \mu_{s_{i}} = \sum\limits_{j = 1}^{n_{i}} \left\|{\tilde{W}}_{Mi,n_{i}}^{\text{T}} \chi_{i,n_{i}}\right\|_{\max}^{2}/4 + \sum\limits_{j = 1}^{n_{i}}\left\|{\tilde{W}}_{Mi,n_{i}}^{\text{T}} \chi_{i,n_{i}}\right\|_{\max}^{2}/4,\,\chi_{i} = [\chi_{i,1},\chi_{i,2},\ldots\chi_{i,n_{i}}]^{\text{T}},\) and \( {\tilde{\rho}}_{i} = \left[{\tilde{\rho}}_{1} ,{\tilde{\rho}}_{2} , \ldots ,{\tilde{\rho}}_{n_{i}} \right]^{\text{T}} \). Using the notation [24]
the following inequality is obtained as
where \( {\beta_{1i}} = {\lambda_{\rm min}} (K_{i}) \) and \( {\beta_{1i}} = {\lambda_{\rm min}} (K_{i}) \). Therefore, (52) can be written as
Equation (66) can then be rewritten in the following two forms:
From (67) and (68), if \( \beta_{1i} \) and \( \beta_{2i} \) are selected such that \( \beta_{1i} > \mu_{s_{i} } /V_{s_{i} } \) and \( \beta_{2i} > \mu_{s_{i}} /Vs_{i}^{(\gamma_{i} + 1)/2} \), respectively, the finite-time stability is then guaranteed by Lemma 2, and the tracking errors will reach the regions \( \left\| {S_{i} } \right\| < \Delta = \min (\Delta_{1} ,\Delta_{2} ) \) of the neighborhood in S i = 0 and
in finite time.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, S.I., Ha, H. & Lee, J.M. Fuzzy Finite-Time Dynamic Surface Control for Nonlinear Large-Scale Systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 18, 570–584 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0088-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0088-2