Abstract
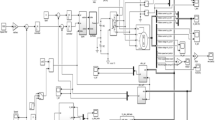
A novel proportional-integral-derivative-based fuzzy neural network (PID-based FNN) controller is proposed in this study to control the speed of a vane-type air motor (VAM) servo system for tracking periodic speed command. First, the structure and operating principles of the VAM servo system are introduced. Then, the dynamics of the VAM servo system is analyzed to derive the second-order state equation of the VAM. Moreover, due to the dynamic characteristics and system parameters of the VAM servo system are highly nonlinear and time-varying, a PID-based FNN controller, which integrates conventional proportional-integral-derivative neural network (PIDNN) control with fuzzy rules, is proposed to achieve precise speed control of VAM servo system under the occurrences of the inherent nonlinearities and external disturbances. The network structure and its on-line learning algorithm using delta adaptation law are described in detail. Meanwhile, the convergence analysis of the speed tracking error is given using the discrete-type Lyapunov function. To enhance the control performance of the proposed intelligent control approach, a 32-bit floating-point digital signal processor (DSP), TMS320F28335, is adopted for the implementation of the proposed control system. Finally, experimental results are illustrated to show the validity and advantages of the proposed PID-based FNN controller for VAM servo system.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saidur, R., Rahim, N.A., Hasanuzzaman, M.: A review on compressed-air energy use and energy savings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14(4), 1135–1153 (2010)
Huang, K.D., Tzeng, S.C.: Development of a hybrid pneumatic-power vehicle. Appl. Energy 80, 47–59 (2005)
Hwang, Y.R., Huang, S.Y.: System identification and integration design of an air/electric motor. Energies 6, 921–933 (2013)
Shen, Y.T., Hwang, Y.R.: Design and implementation of an air-powered motorcycles. Appl. Energy 86, 1105–1110 (2009)
Lu, C.H., Hwang, Y.R., Shen, Y.T.: Backstepping sliding mode tracking control of a vane-type air motor X-Y table motion system. ISA Trans. 50, 278–286 (2011)
Takemura, F., Mizutani, H., Pandian, S. R., Hayakawa, Y., Nagase, Y., Kawamura, S.: Control of a hybrid pneumatic/electric motor. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 209–214. (2000)
Wang, J., Pu, J., Moore, P.: Accurate position control of servo pneumatic actuator systems: an application to food packaging. Control Eng. Pract. 7, 699–706 (1999)
Dov, D.B., Salcudean, S.E.: A force-controlled pneumatic actuator. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 11, 906–911 (1995)
Taleb, M., Levant, A., Plestan, F.: Pneumatic actuator control: solution based on adaptive twisting and experimentation. Control Eng. Pract. 21, 727–736 (2013)
Plestan, F., Shtessel, Y., Bre’geault, V., Poznyak, A.: Sliding mode control with gain adaptation—application to an electropneumatic actuator. Control Eng. Pract. 21, 679–688 (2013)
Rahmat, M.F., Salim, S.N.S., Sunar, N.H., Faudz, A.A.M., Ismail, Z.H., Huda, K.: Identification and non-linear control strategy for industrial pneumatic actuator. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 7(17), 2565–2579 (2012)
Ahn, K., Yokota, S.: Intelligent switching control of pneumatic actuator using on/off solenoid valves. Mechatronics 15, 683–702 (2005)
Messina, A., Giannoccaro, N.I., Gentile, A.: Experimenting and modelling the dynamics of pneumatic actuators controlled by the pulse width modulation (PWM) technique. Mechatronics 15, 859–881 (2005)
Tokhi, M.O., Al-Miskiry, M., Brisland, M.: Real-time control of air motors using a pneumatic H-bridge. Control Eng. Pract. 9, 449–457 (2001)
Lu, C.H., Hwang, Y.R.: Modeling of an air motor servo system and robust sliding mode controller design. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26(4), 1161–1169 (2012)
Hwang, Y.R., Da Shen, Y., Jen, K.K.: Fuzzy MRAC controller design for vane-type air motor systems. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 22, 497–505 (2008)
Marumo, R., Tokhi, M.O.: Neural-model reference control of an air motor. In: 7th AFRICON Conference in Africa, vol. 1, pp. 467–472, 17-17 September (2004)
Votrubec, R., Vavrousek, M.: Control system of a rotary pneumatic motor. In: 2014 16th International Conference on Mechatronics—Mechatronika (ME), pp. 588–593, 3–5 December 2014
Crowe, J., Control, P.I.D.: New Identification and Design Methods. Springer, London (2005)
Yamamoto, T., Takao, K., Yamada, T.: Design of a data-driven PID controller. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 17(1), 29–39 (2009)
Ren, T.J., Chen, T.C.: Motion control for a two-wheeled vehicle using a self-tuning PID controller. Control Eng. Pract. 16(3), 365–375 (2008)
Cong, S., Liang, Y.: PID-like neural network nonlinear adaptive control for uncertain multivariable motion control systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56(10), 3872–3879 (2009)
Chen, S.Y., Lin, F.J.: Decentralized PID neural network control for five degree-of-freedom active magnetic bearing. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 26(3), 962–973 (2013)
Su, X., Wu, L., Shi, P., Song, Y.D.: A novel approach to output feedback control of fuzzy stochastic systems. Automatica 50(12), 3268–3275 (2014)
Tong, S., Sui, S., Li, Y.: Fuzzy adaptive output feedback control of MIMO nonlinear systems with partial tracking errors constrained. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(4), 729–742 (2015)
Li, Y., Tong, S., Li, T.: Observer-based adaptive fuzzy tracking control of MIMO stochastic nonlinear systems with unknown control directions and unknown dead zones. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(4), 1228–1241 (2015)
Su, X., Shi, P., Wu, L., Song, Y.D.: Fault detection filtering for nonlinear switched stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control (2015). doi:10.1109/TAC.2015.2465091
Li, H., Yin, S., Pan, Y., Lam, H.K.: Model reduction for interval type-2 Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems. Automatica 61, 308–314 (2015)
Li, H., Pan, Y., Zhou, Q.: Filter design for interval type-2 fuzzy systems with D stability constraints under a unified frame. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(3), 719–725 (2015)
Wu, L., Yang, X., Lam, H.K.: Dissipativity analysis and synthesis for discrete-time T-S fuzzy stochastic systems with time-varying delay. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22(2), 380–394 (2014)
Lin, F.J., Shieh, H.J., Huang, P.K., Teng, L.T.: Adaptive control with hysteresis estimation and compensation using RFNN for piezo-actuator. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 53(9), 1649–1661 (2006)
Wang, W.Y., Li, I.H., Li, S.C., Tsai, M.S., Su, S.F.: A dynamic hierarchical fuzzy neural network for a general continuous function. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 11(2), 130–136 (2009)
Er, M.J., Liu, F., Li, M.B.: Self-constructing fuzzy neural networks with extended Kalman filter. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 12(1), 66–72 (2010)
Ko, C.N.: Identification of Chaotic system using fuzzy neural networks with time-varying learning algorithm. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 14(4), 540–548 (2012)
Lu, C.H., Tai, C.C., Chen, T.C., Wang, W.C.: Fuzzy neural network speed estimation method for induction motor speed sensorless control. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 11(2), 433–446 (2015)
Li, H.W.: A real-time model of an automotive air propulsion system. MS thesis, National Taiwan Normal University, (2014)
Hung, Y.H., Tung, Y.M., Li, H.W.: A real-time model of an automotive air propulsion system. Appl. Energy 129, 287–298 (2014)
Padian, S.R., Takemura, F., Hayakawa, Kawamura, Y.S.: Control performance of an air motor-can air motors replace electric motors? Conf. Robot Autom. 1, 518–524 (1999)
Lin, F.J., Wai, R.J., Hong, C.M.: Recurrent neural network control for LCC-resonant ultrasonic motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 47(3), 737–749 (2000)
Lin, F.J., Chen, S.Y., Huang, M.S.: Tracking control of thrust active magnetic bearing system via Hermite polynomial-based recurrent neural network. IET Electr. Power Appl. 4(9), 701–714 (2010)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan, R.O.C. through its Grant MOST 103-2218-E-003 -001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, SY., Hung, YH. & Gong, SS. Speed Control of Vane-Type Air Motor Servo System Using Proportional-Integral-Derivative-Based Fuzzy Neural Network. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 18, 1065–1079 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0134-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0134-0