Abstract
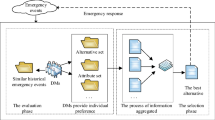
According to the characteristics of emergency decision-making in crisis management, this paper proposes a dynamic decision-making method using the hesitant probabilistic fuzzy set to deal with the inadequate information, uncertainty and dynamic trends. This method is suitable for emergency decision-making as it provides supports for the dynamic and evolutionary characteristics of emergency responses and the uncertain probability about external environment is also considered. In order to make a continuous adjustment with the development of situations, we give a definition of the expectation level, based on which the dynamic reference point method is proposed to obtain the optimal emergency response plan under the hesitant probabilistic fuzzy environment. We also analyze the probability of different situations that may occur in the process of emergency decision-making and provide an algorithm for solving this problem. Finally, a practical case of hazardous goods leakage pollution accident is given to illustrate our method, and then, the optimal decision alternative chain is obtained.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, L., Fan, Z.P., Zhang, Y.: Risk decision analysis in emergency response: a method based on cumulative prospect theory. Comput. Oper. Res. 42, 75–82 (2014)
Yang, L., Fan, Z.P., Yuan, Y., Li, H.Y.: A FTA-based method for risk decision-making in emergency response. Comput. Oper. Res. 42, 49–57 (2014)
Hämäläinen, R.P., Lindstedt, M.R., Sinkko, K.: Multiattribute risk analysis in nuclear emergency management. Risk Anal. 20(4), 455–468 (2000)
Shim, K.C., Fontane, D.G., Labadie, J.W.: Spatial decision support system for integrated river basin flood control. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 128(3), 190–201 (2002)
Levy, J.K., Taji, K.: Group decision support for hazards planning and emergency management: a Group Analytic Network Process (GANP) approach. Math. Comput. Model. 46(7), 906–917 (2007)
Fu, G.: A fuzzy optimization method for multicriteria decision making: an application to reservoir flood control operation. Expert Syst. Appl. 34(1), 145–149 (2008)
Zhang, G.Q., Ma, J., Lu, J.: Emergency management evaluation by a fuzzy multi-criteria group decision support system. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 23(4), 517–527 (2009)
Zhou, Q., Huang, W.L., Zhang, Y.: Identifying critical success factors in emergency management using a fuzzy DEMATEL method. Saf. Sci. 49(2), 243–252 (2011)
Yan, F., Chen, L.S., Zhang, F., Zhao, Y.F.: Application of improved FAHP for nuclear reactor accident emergency decision. Appl. Mech. Mater. 389, 136–142 (2013)
Zhang, Q.S., Xie, B.L., Zhang, X.M.: Uncertain internet public opinion emergency decision system based on case reasoning and grey relational analysis. Open Cybern. Syst. J. 8, 274–282 (2014)
Sun, B.Z., Ma, W.M., Chen, X.T.: Fuzzy rough set on probabilistic approximation space over two universes and its application to emergency decision making. Expert Syst. 32(4), 507–521 (2015)
Qu, J.H., Meng, X.L., You, H.: Multi-stage ranking of emergency technology alternatives for water source pollution accidents using a fuzzy group decision making tool. J. Hazard. Mater. 310, 68–81 (2016)
Zhao, J.D., Jin, T., Shen, H.Z.: A case-based evolutionary group decision support method for emergency response. In: Intelligence and Security Informatics, pp. 94–104. (2007)
Pauwels, N., Van De Walle, B., Hardeman, F., Soudan, K.: The implications of irreversibility in emergency response decisions. Theory Decis. 49(1), 25–51 (2000)
Yang, J.J., Xu, C.H.: Emergency decision engineering model based on sequential games. Syst. Eng. Proced. 5, 276–282 (2012)
Ge, L., Mourits, M.C., Kristensen, A.R., Huirne, R.B.: A modelling approach to support dynamic decision-making in the control of FMD epidemics. Prev. Vet. Med. 95(3), 167–174 (2010)
Georgiadou, P.S., Papazoglou, I.A., Kiranoudis, C.T., Markatos, N.C.: Modeling emergency evacuation for major hazard industrial sites. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 92(10), 1388–1402 (2007)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(3), 338–353 (1965)
Dubois, D., Prade, H.: Bridging gaps between several forms of granular computing. Granul. Comput. 1(2), 115–126 (2016)
Pérez, I.J., Cabrerizo, F.J., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A mobile decision support system for dynamic group decision making problems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 40(6), 1244–1256 (2010)
Yao, Y.: A triarchic theory of granular computing. Granul. Comput. 1(2), 145–157 (2016)
Pedrycz, W., Rocha, A.F.: Fuzzy-set based models of neurons and knowledge-based networks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 1(4), 254–266 (1993)
Cai, M., Li, Q., Lang, G.: Shadowed sets of dynamic fuzzy sets. Granul. Comput. 1–10 (2016)
Wilke, G., Portmann, E.: Granular computing as a basis of human–data interaction: a cognitive cities use case. Granul. Comput. 1(3), 181–197 (2016)
Zhou, X.: Membership grade mining of mutually inverse fuzzy implication propositions. Granul. Comput. 2(1), 55–62 (2017)
Syau, Y.R., Skowron, A., Lin, E.B.: Inclusion degree with variable-precision model in analyzing inconsistent decision tables. Granul. Comput. 1–8 (2016)
Wang, C., Fu, X., Meng, S., He, Y.: SPIFGIA operators and their applications to decision making. Granul. Comput. 1–10 (2016)
Sanchez, M.A., Castro, J.R., Castillo, O., Mendoza1, O., Rodriguez-Diaz, A., Melin, P.: Fuzzy higher type information granules from an uncertainty measurement. Granul. Comput. 1–9 (2016)
Turksen, I.B.: Interval valued fuzzy sets based on normal forms. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20(2), 191–210 (1986)
Xu, Z.S., Gou, X.J.: An overview of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy information aggregations and applications. Granul. Comput. 2, 1–27 (2017)
Dubois, D., Prade, H.: Fuzzy Sets and Systems: Theory and Applications, pp. 1–12. Academic Press, New York (1980)
Mendel, J.M.: A comparison of three approaches for estimating (synthesizing) an interval type-2 fuzzy set model of a linguistic term for computing with words. Granul. Comput. 1(1), 59–69 (2016)
Atanassov, K.T.: Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20, 87–96 (1986)
Das, S., Kar, S., Pal, T.: Robust decision making using intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Granul. Comput. 2(1), 41–54 (2017)
Torra, V.: Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 25(6), 529–539 (2010)
Zhang, Z.M., Wang, C., Tian, D.Z., Li, K.: Induced generalized hesitant fuzzy operators and their application to multiple attribute group decision making. Comput. Ind. Eng. 67, 116–138 (2014)
Zhang, Z.M.: Hesitant fuzzy power aggregation operators and their application to multiple attribute group decision making. Inf. Sci. 234, 150–181 (2013)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J.: Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their application in multi-criteria decision making. Inf. Sci. 271, 125–142 (2014)
Xu, Z.S., Wang, H.: Managing multi-granularity linguistic information in qualitative group decision making: an overview. Granul. Comput. 1(1), 21–35 (2016)
Busemeyer, J.R., Pleskac, T.J.: Theoretical tools for understanding and aiding dynamic decision making. J. Math. Psychol. 53(3), 126–138 (2009)
Saaty, T.L.: Time dependent decision-making; dynamic priorities in the AHP/ANP: generalizing from points to functions and from real to complex variables. Math. Comput. Model. 46(7), 860–891 (2007)
Li, L., Lai, K.K.: Fuzzy dynamic programming approach to hybrid multiobjective multistage decision-making problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 117(1), 13–25 (2001)
Chen, S.Y., Fu, G.T.: Combining fuzzy iteration model with dynamic programming to solve multiobjective multistage decision making problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 152(3), 499–512 (2005)
Nielsen, T.D., Jaffray, J.Y.: Dynamic decision making without expected utility: an operational approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 169(1), 226–246 (2006)
Bulinskaya, E.V.: Some aspects of decision making under uncertainty. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 137(8), 2613–2632 (2007)
Xu, Z.S., Yager, R.R.: Dynamic intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 48(1), 246–262 (2008)
Xu, Z.S., Zhou, W.: Consensus building with a group of decision makers under the hesitant probabilistic fuzzy environment. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 1–23 (2016)
Xu, Z.S., Xia, M.M.: Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf. Sci. 181(11), 2128–2138 (2011)
Diamond, P., Kloeden, P.E.: Metric Spaces of Fuzzy Sets: Theory and Applications. World Scientific, Singapore (1994)
Kacprzyk, J.: Multistage Fuzzy Control: A Prescriptive Approach. Wiley, New York (1997)
Zhu, B., Xu, Z.S.: Consistency measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22(1), 35–45 (2014)
Chen, S.J., Hwang, C.L.: Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision Making. Springer, Berlin (1992)
Cheng, T.J., Wu, F.P., Li, J.B.: Risk decision model for emergency response based on cumulative prospective theory with incomplete information. Syst. Eng. 04, 70–75 (2014). (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions, which have led to an improved version of this paper. The work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71571123, 71501135, 71532007), the Scientific Research Found of Sichuan Provincial Education Department (Nos. 16ZB0343, DSWL16-12) and the Young scholars high level academic team construction project at Sichuan University (skgt201501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Xu, Z. & Liao, H. A Dynamic Reference Point Method for Emergency Response Under Hesitant Probabilistic Fuzzy Environment. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19, 1261–1278 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0311-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0311-4