Abstract
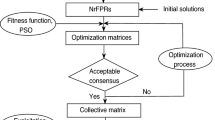
The most desired alternative in group decision making (GDM) is the one that best reflects the consensus of the group. However, few studies have been conducted on consensus measure in GDM with probabilistic linguistic term sets (PLTSs). In this study, we propose an approach to consensus measure on the basis of the possibility degree of PLTSs in GDM. Firstly, we define the concept of degree of similarity between two PLTSs on the basis of possibility degrees. Then, we extend this concept to the consensus measure between the probabilistic linguistic information provided by group decision makers, and the relevant weight of each group decision maker is derived. Thereafter, we aggregate the PLTSs provided by each group decision maker and the alternatives are then ranked. Finally, two illustrative examples are proposed for the application of our method to evaluate the degree of consensus of collective preference values between experts and large group decision making problems with PLTSs. By comparison analysis, the advantages of the proposed method are verified.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Chen, S.M., Lee, L.W., Yang, S.W., Sheu, T.W.: Adaptive consensus support model for group decision making systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 39(16), 12580–12588 (2012)
Wang, J., Wang, J.Q., Zhang, H.Y., Chen, X.H.: Multi-criteria group decision making approach based on 2-tuple linguistic aggregation operators with multi-hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 18(1), 81–97 (2016)
Martinez, L., Herrera, F.: An overview on the 2-tuple linguistic model for computing with words in decision making: extensions, applications and challenges. Inf. Sci. 207(1), 1–18 (2012)
Liu, W.S., Liao, H.C.: A bibliometric analysis of fuzzy decision research during 1970-2015. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(1), 1–14 (2017)
Cheng, S.H., Chen, S.M., Huang, Z.C.: Autocratic decision making using group recommendations based on ranking interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Information Sciences. s 361–362, 135–161 (2016)
Morente-Molinera, J.A., Pérez, I.J., Ureña, M.R., Herrera-Viedma, E.: On multi-granular fuzzy linguistic modeling in group decision making problems: a systematic review and future trends. Knowl. Based Syst. 74(1), 49–60 (2015)
Meng, F.Y.: A hesitant fuzzy linguistic multi-granularity decision making model based on distance measures. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 28(4), 1519–1531 (2015)
Yager, R.R.: A new methodology for ordinal multi-objective decisions based on fuzzy sets-readings in fuzzy sets for intelligent systems. Read. Fuzzy Sets Intell. Syst. 12(4), 589–600 (1981)
Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E., Verdegay, J.L.: Direct approach processes in group decision making using linguistic OWA operators. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 79(2), 175–190 (1996)
Rodriguez, R.M., Martinez, L., Herrera, F.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 20(1), 109–119 (2012)
Gou, X.J., Xu, Z.S., Liao, H.C.: Multiple criteria decision making based on Bonferroni means with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Soft. Comput. 21(21), 6515–6529 (2017)
Wei, C.P., Zhao, N., Tang, X.J.: Operators and comparisons of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22(3), 575–585 (2014)
Xu, Y.J., Xu, A.W., Merigó, J.M., Wang, H.M.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic ordered weighted distance operators for group decision making. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 49(1), 285–308 (2015)
Zhang, Y.J., Wang, Y.Z., Wang, J.P.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic multiple attribute decision making. In: International Conference on Information Fusion, pp. 1421–1426 (2013)
Farhadinia, B.: Multiple criteria decision making methods with completely unknown weights in hesitant fuzzy linguistic term setting. Knowl. Based Syst. 93, 135–144 (2016)
Hesamian, G., Shams, M.: Measuring similarity and ordering based on hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. IOS Press 28(2), 983–990 (2015)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J.: Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their application in multi-criteria decision making. Inf. Sci. 271(3), 125–142 (2014)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J., Merigó, J.M.: Qualitative decision making with correlation coefficients of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. Knowl. Based Syst. 76, 127–138 (2015)
Wang, J.Q., Wu, J.T., Wang, J., Zhang, H.Y., Chen, X.H.: Multi-criteria decision making methods based on the hausdorff distance of hesitant fuzzy linguistic numbers. Soft. Comput. 20(4), 1621–1633 (2016)
Liu, H.B., Cai, J.F., Jiang, L.: On improving the additive consistency of the fuzzy preference relations based on comparative linguistic expressions. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 29(6), 544–559 (2014)
Zhang, Z.M., Wu, C.: On the use of multiplicative consistency in hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Knowl. Based Syst. 72, 13–27 (2014)
Zhu, B., Xu, Z.S.: Consistency measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22(1), 35–45 (2014)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Herrera-Viedma, E., Herrera, F.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and its application in decision making: a state-of-the art survey. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0432-9
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic VIKOR method and its application in qualitative multiple criteria decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(5), 1343–1355 (2015)
Zhang, W.K., Ju, Y.B., Liu, X.Y.: Multiple criteria decision analysis based on Shapley fuzzy measures and interval-valued hesitant fuzzy linguistic numbers. Comput. Ind. Eng. 105, 28–38 (2017)
Pang, Q., Wang, H., Xu, Z.S.: Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Inf. Sci. 369, 128–143 (2016)
Bai, C.Z., Zhang, R., Qian, L.X., Wu, Y.N.: Comparisons of probabilistic linguistic term sets for multi-criteria decision making. Knowl. Based Syst. 119, 284–291 (2016)
Gou, X.J., Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Herrera, F.: Double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set and MULTIMOORA method: A case of study to evaluate the implementation status of haze controlling measures. Inf. Fusion 38, 22–34 (2017)
Zhai, Y.L., Xu, Z.S., Liao, H.C.: Probabilistic linguistic vector-term set and its application in group decision making with multi-granular linguistic information. Appl. Soft Comput. 49, 801–816 (2016)
Zhang, Y.X., Xu, Z.S., Wang, H., Liao, H.C.: Consistency-based risk assessment with probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Appl. Soft Comput. 49, 817–833 (2016)
Zhang, Y.X., Xu, Z.S., Liao, H.C.: A consensus process for group decision making with probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Inf. Sci. 414, 260–275 (2017)
Liao, H.C., Jiang, L.S., Xu, Z.S., Xu, J.P., Herrera, F.: A linear programming method for multiple criteria decision making with probabilistic linguistic information. Inf. Sci. 415–416, 341–355 (2017)
Liu, Y., Fan, Z.P., Zhang, X.: A method for large group decision making based on evaluation information provided by participators from multiple groups. Inf. Fusion 29(C), 132–141 (2016)
Peng, H.G., Zhang, H.Y., Wang, J.Q.: Cloud decision support model for selecting hotels on TripAdvisor.com with probabilistic linguistic information. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 3(68), 124–138 (2017)
Yu, S.M., Wang, J., Wang, J.Q., Li, L.: A multi-criteria decision making model for hotel selection with linguistic distribution assessments. Appl. Soft Comput. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.08.009
Perez, I.J., Cabrerizo, F.J., Alonso, S., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A new consensus model for group decision making problems with non-homogeneous experts. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 44(4), 494–498 (2014)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Cabrerizo, F.J., Kacprzyk, J., Pedrycz, W.: A review of soft consensus models in a fuzzy environment. Inf. Fusion 17(1), 4–13 (2014)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J., Merigó, J.M.: Framework of group decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy preference information. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 23(4), 1211–1227 (2015)
Gong, Z.W., Zhang, H.H., Forrest, J., Li, L.S., Xu, X.X.: Two consensus models based on the minimum cost and maximum return regarding either all individuals or one individual. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 240(1), 183–192 (2015)
Zhang, Z.M.: Hesitant fuzzy multi-criteria group decision making with unknown weight information. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19(3), 615–636 (2016)
Plastria, F., Blockmans, T.: Multidimensional theoretic consensus reachability: the impact of distance selection and issue saliences. Group Decis. Negot. 24(1), 1–44 (2015)
Xia, M.M., Chen, J.: Consistency and consensus improving methods for pairwise comparison matrices based on abelian linearly ordered group. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 266, 1–32 (2015)
Sun, B.Z., Ma, W.M.: An approach to consensus measurement of linguistic preference relations in multi-attribute group decision making and application. Omega 51(1), 83–92 (2015)
Gou, X.J., Xu, Z.S., Liao, H.C.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic entropy and cross-entropy measures and alternative queuing method for multiple criteria decision making. Inf. Sci. 388(5), 225–246 (2017)
Nakahara, Y., Sasaki, M., Gen, M.: On the linear programming problems with interval coefficients. Comput. Ind. Eng. 23(1–4), 301–304 (1992)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S.: Approaches to manage hesitant fuzzy linguistic information based on the cosine distance and similarity measures for HFLTSs and their application in qualitative decision making. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(12), 5328–5336 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and constructive suggestions that greatly help the improvement of this paper. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 71701037, 71701038 and 71601041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, M., Gao, Q., Fang, J. et al. An Approach to Consensus Measure Based on Possibility Degrees of PLTSs in Group Decision Making. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20, 2257–2272 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0464-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0464-9