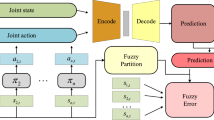
Abstract
In reinforcement learning, a reward function is a priori specified mapping that informs the learning agent how well its current actions and states are performing. From the viewpoint of training, reinforcement learning requires no labeled data and has none of the errors that are induced in supervised learning because responsibility is transferred from the loss function to the reward function. Methods that infer an approximated reward function using observations of demonstrations are termed inverse reinforcement learning or apprenticeship learning. A reward function is generated that reproduces observed behaviors. In previous studies, the reward function is implemented by estimating the maximum likelihood, Bayesian or information theoretic methods. This study proposes an inverse reinforcement learning method that has an approximated reward function as a linear combination of feature expectations, each of which plays a role in a base weak classifier. This approximated reward function is used by the agent to learn a policy, and the resultant behaviors are compared with an expert demonstration. The difference between the behaviors of the agent and those of the expert is measured using defined metrics, and the parameters for the approximated reward function are adjusted using an ensemble fuzzy method that has a boosting classification. After some interleaving iterations, the agent performs similarly to the expert demonstration. A fuzzy method is used to assign credits for the rewards in respect of the most recent decision to the neighboring states. Using the proposed method, the agent approximates the expert behaviors in fewer steps. The results of simulation demonstrate that the proposed method performs well in terms of sampling efficiency.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Zhifei, S., Joo, E.M.” A review of inverse reinforcement learning theory and recent advances. In: 2012 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Brisbane, QLD, pp. 1–8 (2012)
Hwang, K.S., Chiang, H.Y., Jiang, W.C.: Adaboost-like method for inverse reinforcement learning. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Vancouver, BC, pp. 1922–1925 (2016)
Abbeel, P., Ng, A.Y.: Apprenticeship learning via inverse reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 1–8 (2004)
Natarajan, S., Kunapuli, G., Judah, K., Tadepalli, P., Kersting, K., Shavlik, J.: Multi-agent inverse reinforcement learning. In: 2010 Ninth International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Washington, DC, pp. 395–400 (2010)
Sutton, R.S., Barto, A.G.: Reinforcement learning: an introduction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 9(5), 1054 (1998)
Ollis, M., Huang, W.H., Happold, M.: A Bayesian approach to imitation learning for robot navigation. In: 2007 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Diego, CA, pp. 709–714 (2007)
Shi*, H., Lin, Z., Zhang, S., Li, X., Hwang, K.-S.: An adaptive decision-making method with fuzzy Bayesian reinforcement learning for robot soccer. Inf. Sci. 436–437, 268–281 (2018)
Michini, B., Walsh, T.J., Agha-Mohammadi, A.A., How, J.P.: Bayesian nonparametric reward learning from demonstration. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(2), 369–386 (2015)
Awheda, M.D., Schwartz, H.M.: A residual gradient fuzzy reinforcement learning algorithm for differential games. Int. J Fuzzy Syst. 19, 1058 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-016-0284-8
Syed, U., Schapire, R.: A game-theoretic approach to apprenticeship learning. In: Advances in Neural Information, Processing Systems, Vol. 20 (NIPS’08), pp. 1449–1456 (2008)
Ziebart, B., Bagnell, A., Dey, A.: Modeling interaction via the principle of maximum causal entropy. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML’10), pp. 1255–1262 (2010)
Hwang, K.S., Lin, J.L., Shi, H., et al.: Policy learning with human reinforcement. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 18, 618 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-016-0194-9
Hwang, K.S., Hsieh, C.W., Jiang, W.C., Lin, J.L.: A reinforcement learning method with implicit critics from a bystander. In: Advances in Neural Networks—ISNN 2017, pp. 363–270
Ng, A.Y., Russell, S.: Algorithms for inverse reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 663–670 (2000)
Vapnik, V.N.: Statistical Learning Theory. Wiley, London (1998)
Shi, H., Li, X., Hwang, K.-S., Pan, W., Genjiu, X.: Decoupled visual servoing with fuzzy Q-learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 14(1), 241–252 (2018)
Pan, W., Lyu, M., Hwang, K-Sh, Ju, M.-Y., Shi, H.: A neuro-fuzzy visual servoing controller for an articulated manipulator. IEEE Access 6(1), 3346–3357 (2018)
An, T.K., Kim, M.H.: A new diverse AdaBoost classifier. In: 2010 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computational Intelligence, Sanya, pp. 359–363 (2010)
R.E. Schapire (2002) The boosting approach to machine learning an overview. In: MSRI Workshop on Nonlinear Estimation and Classification, Dec. 19, 2001, pp. 1–23 (2002)
Eibl, G., Pfeiffer, K.P.: How to make AdaBoost.m1 work for weak base classifiers by changing only one line of the code. In: Processing of the 13th European Conference on Machine Learning Helsinki, pp. 72–83 (2002)
Auer, P.: Using confidence bounds for exploitation-exploration trade-offs. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 3, 397–422 (2002)
Browne, C.B., et al.: A survey of monte carlo tree search methods. IEEE Trans. Comput. Intell. AI Games 4(1), 1–43 (2012)
Nicolescu, M., Jenkins, O.C., Olenderski, A.: Learning behavior fusion estimation from demonstration. In: ROMAN 2006—the 15th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Hatfield, pp. 340–345 (2006)
Acknowledgements
Research in this work was supported by the Seed Foundation of Innovation and Creation for Graduate Students in North-western Polytechnical University (No. zz2018166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, W., Qu, R., Hwang, KS. et al. An Ensemble Fuzzy Approach for Inverse Reinforcement Learning. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 95–103 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0535-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-018-0535-y