Abstract
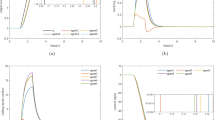
This paper is to present our new results on practical finite-time fuzzy control scheme for a class of Hamiltonian systems by an adaptive event-triggered approach. An unknown function of the system is approximated by an adaptive fuzzy system. According to a semi-global practical finite-time stability criterion, a novel adaptive fuzzy finite-time controller is presented. In the interest of saving resources, an event-triggered approach is developed where the controller is updated under the respective triggering conditions. Based on the special structure of Hamiltonian systems and Lyapunov theory, a sufficient condition is obtained so that the states of original systems converge to a small neighborhood containing the origin in a finite time. Meanwhile, with the proposed controller, there exists a positive lower bound for the interexecution time, and the Zeno phenomenon is avoided. The design processes of the proposed controller, adaptive law and event-triggered conditions are also proved by a circuit system simulation example.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, M., Borja, P., Ortega, R., et al.: PID passivity-based control of port-Hamiltonian systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 63(4), 1032–1044 (2018)
Nageshrao, S.P., Lopes, G.A.D., Jeltsema, D., et al.: Port-Hamiltonian systems in adaptive and learning control: a survey. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 61(5), 1223–1238 (2016)
Schiffer, J., Fridman, E., Ortega, R., et al.: Stability of a class of delayed port-Hamiltonian systems with application to microgrids with distributed rotational and electronic generation. Automatica 74(12), 71–79 (2016)
Yaghmaei, A., Yazdanpanah, M.J.: Output control design and separation principle for a class of port-Hamiltonian systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 29(4), 867–881 (2019)
Liu, X., Liao, X.: Fixed-time stabilization control for port-Hamiltonian systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 96(2), 1497–1509 (2019)
Sun, W., Fu, B.: Adaptive control of time-varying uncertain nonlinear systems with input delay: a Hamiltonian approach. IET Control Theory Appl. 15(10), 1844–1858 (2016)
Sun, W., Wu, Y., Wang, L.: Trajectory tracking of constrained robotic systems via a hybrid control strategy. Neurocomputing 330, 188–195 (2019)
Sun, W., Peng, L.: Robust adaptive control of uncertain stochastic Hamiltonian systems with time varying delay. Asian J. Control 18(2), 642–651 (2016)
Haddad, W.M., Rajpurohit, T., Jin, X.: Energy-based feedback control for stochastic port-controlled Hamiltonian systems. Automatica 97, 134–142 (2018)
Jagtap, P., Zamani, M.: Backstepping design for incremental stability of stochastic Hamiltonian systems with jumps. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 63(1), 255–261 (2018)
Bhat, S.P., Bernstein, D.S.: Continuous finite-time stabilization of the translational and rotational double integrators. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 43(5), 678–682 (1998)
Zhu, Z., Xia, Y., Fu, M.: Attitude stabilization of rigid spacecraft with finite-time convergence. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 21(6), 686–702 (2011)
Zhao, H., Niu, Y.: Finite-time sliding mode control of switched systems with one-sided Lipschitz nonlinearity. J. Frankl. Inst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.05.019
Yang, R., Wang, Y.: Finite-time stability analysis and \(H_\infty \) control for a class of nonlinear time-delay Hamiltonian systems. Automatica 49(2), 390–401 (2013)
Sun, L., Feng, G., Wang, Y.: Finite-time stabilization and \(H_\infty \) control for a class of nonlinear Hamiltonian descriptor systems with application to affine nonlinear descriptor systems. Automatica 50(8), 2090–2097 (2014)
Fu, B., Li, S., Guo, L., et al.: Finite-time stabilization of port-controlled Hamiltonian systems with nonvanishing disturbances. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 40(10), 2973–2981 (2018)
Yang, R., Sun, L., Zhang, G., et al.: Finite-time stability and stabilization of nonlinear singular time-delay systems via Hamiltonian method. J. Frankl. Inst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.04.033
Chen, B., Liu, X.P., Ge, S.S., et al.: Adaptive fuzzy control of a class of nonlinear systems by fuzzy approximation approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 20(6), 1012–1021 (2012)
Li, Y., Shao, X., Tong, S.: Adaptive fuzzy prescribed performance control of non-triangular structure nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2937046
Zhang, T., Ge, S.S.: Adaptive neural network tracking control of MIMO nonlinear systems with unknown dead zones and control directions. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 20(3), 483–497 (2009)
Van Kien, C., Son, N.N., Anh, H.P.H.: Observer-based adaptive fuzzy decentralized control of uncertain large-scale nonlinear systems with full state constraints. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(3), 755–768 (2019)
Zhang, Q., Zhai, D., Dong, J.: Adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control for nonlinear uncertain SISO system optimized by differential evolution algorithm. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(4), 1085–1103 (2019)
Wang, Z., Xu, Y., Lu, R., et al.: Finite-time state estimation for coupled Markovian neural networks with sensor nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(3), 630–638 (2017)
Wang, F., Chen, B., Liu, X., et al.: Finite-time adaptive fuzzy tracking control design for nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(3), 1207–1216 (2018)
Sun, Y., Chen, B., Lin, C., et al.: Finite-time adaptive control for a class of nonlinear systems with nonstrict feedback structure. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 48(10), 2774–2781 (2018)
Li, K., Tong, S.: Fuzzy adaptive practical finite-time control for time delays nonlinear systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(4), 1013–1025 (2019)
Li, Y., Li, K., Tong, S.: Finite-time adaptive fuzzy output feedback dynamic surface control for MIMO nonstrict feedback systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 27(1), 96–110 (2019)
Xu, P., Li, Y., Tong, S.: Fuzzy adaptive finite time fault-tolerant control for multi-input and multi-output nonlinear systems with actuator faults. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 17(7), 1655–1665 (2019)
Li, Y.-X.: Finite time command filtered adaptive fault tolerant control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica 106, 117–123 (2019)
Li, Y., Li, H., Sun, W.: Event-triggered control for robust set stabilization of logical control networks. Automatica 95, 556–560 (2018)
Song, J., Niu, Y., Xu, J.: An event-triggered approach to sliding mode control of Markovian jump Lur’e systems under hidden mode detections. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2018.2847315
Wang, X., Lemmon, M.D.: Event-triggered in distributed networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(3), 586–601 (2011)
Girard, A.: Dynamic triggering mechanisms for event-triggered control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 60(7), 1992–1997 (2015)
Wang, S., Li, H., Li, Y., et al.: Event-triggered control for disturbance decoupling problem of mix-valued logical networks. J. Frankl. Inst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.10.005
Wang, Y., Zheng, W.X., Zhang, H.: Dynamic event-based control of nonlinear stochastic systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 62(12), 6544–6551 (2017)
Yuan, Y., Wang, Z., Guo, L.: Event-triggered strategy design for discrete-time nonlinear quadratic games with disturbance compensations: the noncooperative case. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 48(11), 1885–1896 (2018)
Wang, M., Wang, Z., Chen, Y., Sheng, W.: Adaptive neural event-triggered control for discrete-time strict-feedback nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2921733
Yi, X., Yang, T., Wu, J., et al.: Distributed event-triggered control for global consensus of multi-agent systems with input saturation. Automatica 100, 1–9 (2019)
Li, Y.-X., Yang, G.-H.: Observer-based fuzzy adaptive event-triggered control codesign for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(3), 1589–1599 (2018)
Li, Y.X., Tong, S., Yang, G.H.: Observer-based adaptive fuzzy decentralized event-triggered control of interconnected nonlinear system. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2894024
Zhang, H., Yue, D., Yin, X., et al.: Finite-time distributed event-triggered consensus control for multi-agent systems. Inf. Sci. 339, 132–142 (2016)
Liu, J., Yu, Y., Wang, Q., et al.: Fixed-time event-triggered consensus control for multi-agent systems with nonlinear uncertainties. Neurocomputing 260, 497–504 (2017)
Wang, L., Wang, Z., Wei, G., et al.: Finite-time state estimation for recurrent delayed neural networks with component-based event-triggering protocol. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(4), 1046–1057 (2018)
Wang, Y., Li, C., Cheng, D.: Generalized Hamiltonian realization of time invariant nonlinear systems. Automatica 39, 1437–1443 (2003)
Beckenbach, E., Bellman, R.: Inequalities, p. 15. Springer, New York (1965)
Peng, Z., Wang, D., Wang, J.: Predictor-based neural dynamic surface control for uncertain nonlinear systems in strict-feedback form. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 28(9), 2156–2167 (2017)
Anderson, R.P., Milutinovi, D., Dimarogonas, D.V.: Self-triggered sampling for second-moment stability of state-feedback controlled SDE systems. Automatica 54, 8–15 (2015)
Heemels, W.P.M.H., Johansson, K.H., Tabuada, P.: An introduction to event-triggered and self-triggered control. In: Proceedings of 51th IEEE conference on decision and control, Maui, Hawail, USA (2012)
Tabuada, P.: Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 52(9), 1680–1685 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61703232, and in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province under Grant ZR2017MF068 and ZR2017QF013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, W., Lv, X. Practical Finite-Time Fuzzy Control for Hamiltonian Systems via Adaptive Event-Triggered Approach. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 35–45 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00773-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00773-0